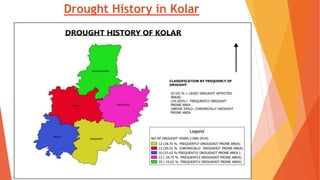
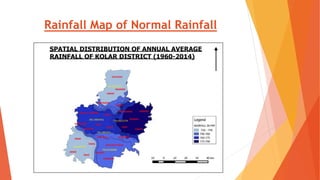
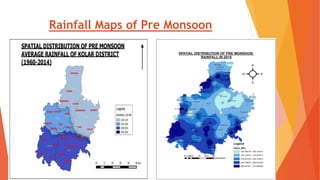
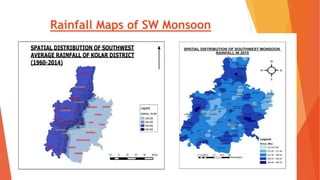
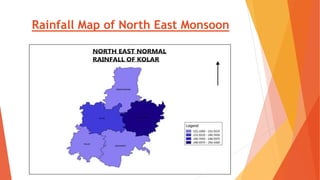
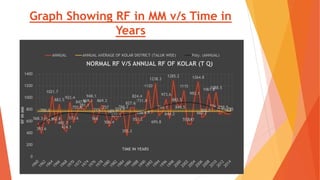
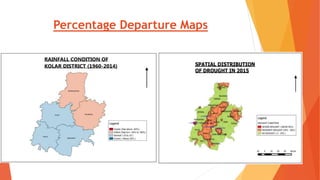
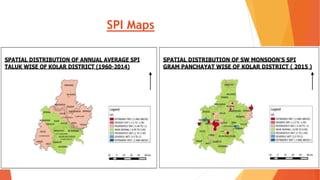
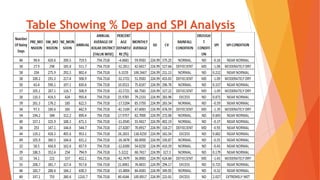
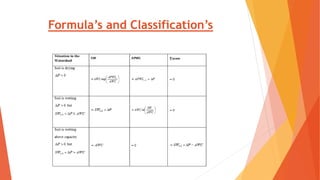
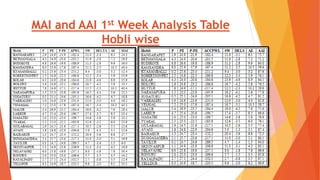
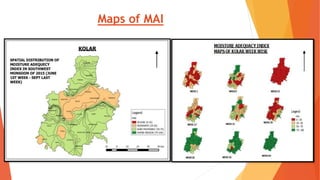
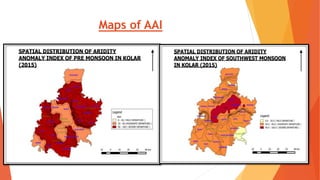
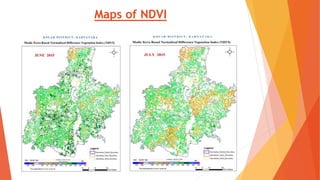
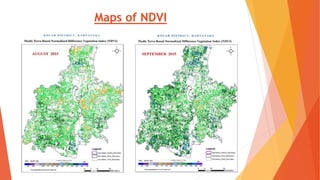
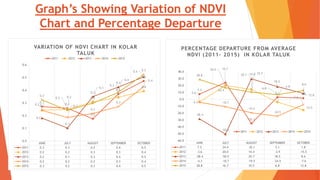
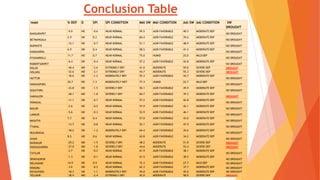
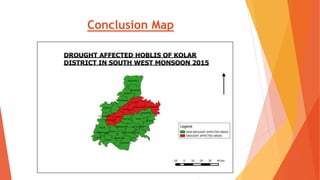
This document analyzes drought conditions in Kolar District using remote sensing and GIS techniques. It begins with an introduction to the study area and analysis of rainfall data. Various drought parameters like percentage rainfall departure, standardized precipitation index, moisture adequacy index, and normalized difference vegetation index are calculated. Maps and tables of these parameters from 2011-2015 are presented. Based on the analysis, 6 of the 27 hoblis in Kolar District met the criteria for drought during the 2015 southwest monsoon season. The document concludes with recommendations for drought management and mitigation.