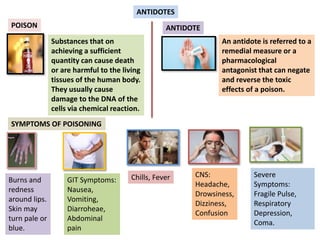
The document discusses various antidotes, including sodium thiosulfate, activated charcoal, and sodium nitrite, detailing their chemical properties, uses, and modes of action against poisoning. Sodium thiosulfate is effective for cyanide poisoning, while activated charcoal serves as a universal antidote due to its absorbent nature, and sodium nitrite also aids in cyanide treatment. Additionally, it outlines their medicinal applications beyond antidotal effects, including antifungal uses and food preservation.

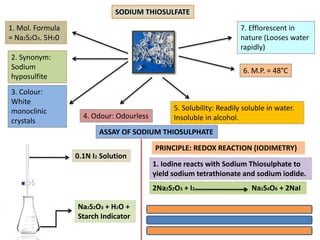
![2. When whole of the sodium thiosulfate has
been consumed, the next drop of Iodine
solution reacts with starch indicator to form
the starch-iodine complex which is blue in
color.
3. Note the titre value
I2 + Starch [Starch-I2 complex]
(Blue colour)
4. Equivalent Weight Factor
Each ml of 0.1N I2 solution = 0.01581g of Na2S2O3
Colourless Blue Colour
Colour Change
5. % Purity =
MEDICINAL USES OF SODIUM THIOSULPHATE
1. As antidote:
As antidote to cyanide poisoning. Sodium thiosulphate donates a sulphur
atom, facilitating rhodenase catalyzed conversion of cyanide to thiocyanate.
The thiocyante formed is less toxic and is easily excreted renally.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidote-210626170559/85/Antidote-PCI-Syllabus-B-Pharm-4-320.jpg)