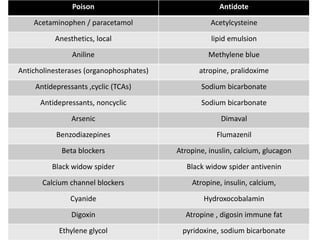
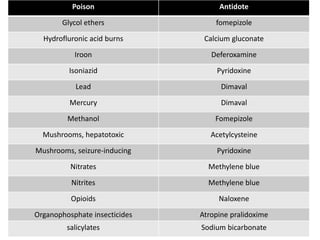
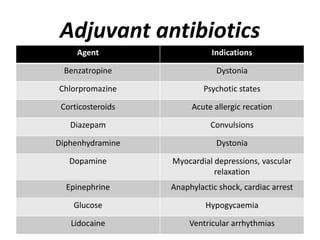
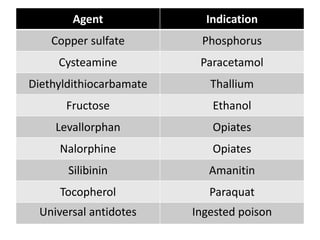
1) Antidotes work by forming inert complexes with poisons, accelerating detoxification, reducing toxic conversion, competing at receptor sites, blocking receptor sites, or bypassing toxic effects.
2) Common antidotes are activated charcoal, acetylcysteine, atropine, calcium gluconate, dimercaprol, digoxin immune fab, fomepizole, hydroxocobalamin, methylene blue, naloxone, pralidoxime, and sodium bicarbonate.
3) While supportive care is often sufficient, antidotes can be life-saving in acute poisoning by quickly counteracting toxic effects and reducing burden on the healthcare