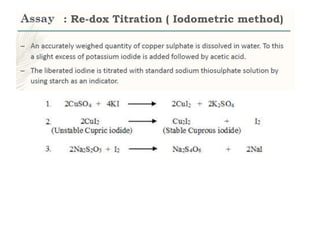
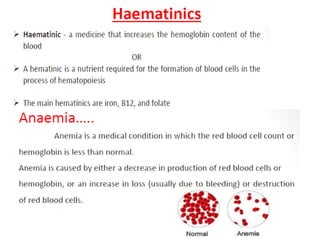
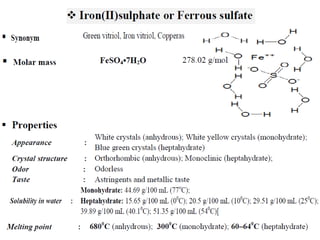
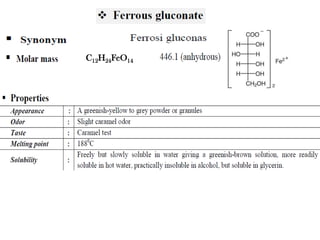
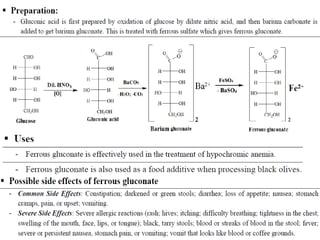
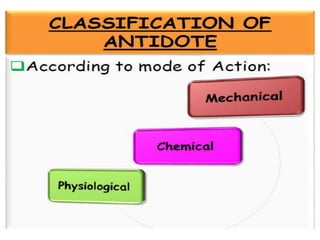
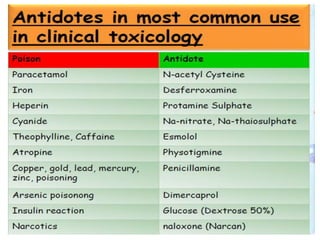
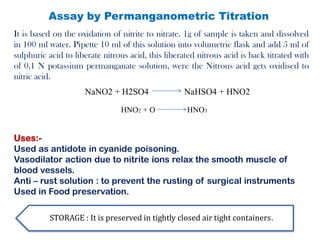
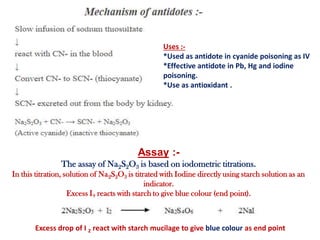
This document provides information on various pharmaceutical compounds including expectorants, potassium iodide, copper sulfate, iron sulfate, zinc sulfate, and methods for their analysis. It discusses the definition, chemical and physical properties, preparation, uses and assays of these compounds by redox titration, gravimetric analysis, and complexometric titration. The document also covers emetics, astringents, antidotes and poisons including sodium nitrite, sodium thiosulfate and activated charcoal.