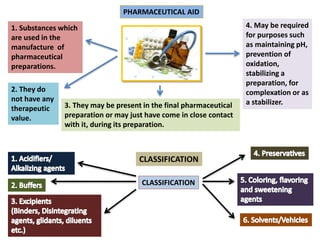
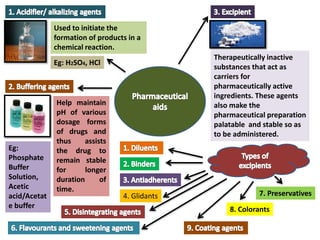
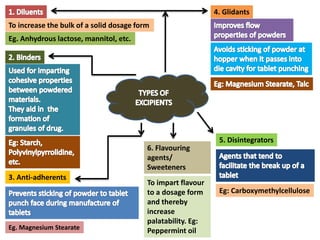
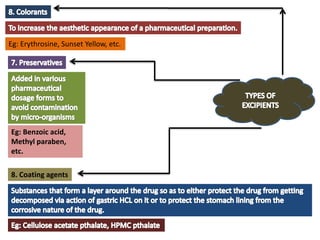
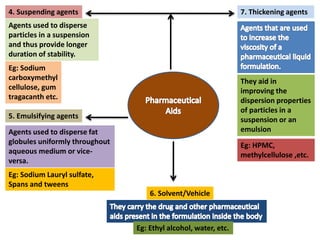
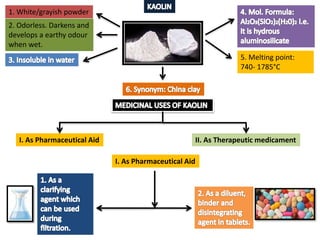
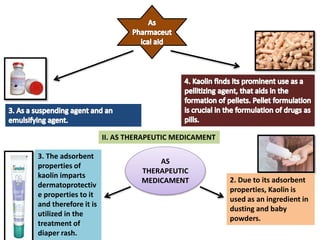
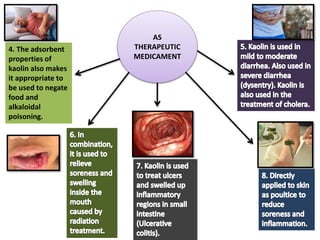
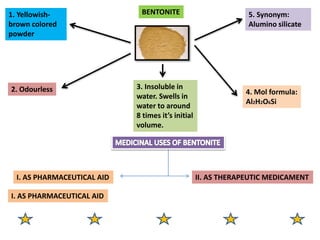
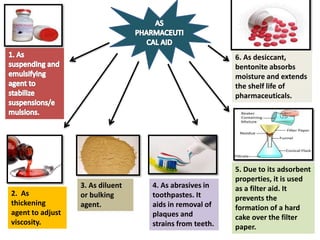
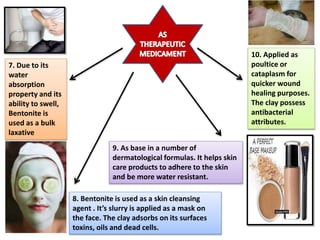
The document outlines various pharmaceutical aids used in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical preparations, highlighting their essential roles while noting that they have no therapeutic value. It details the classification of these substances, including glidants, emulsifying agents, and thickening agents, their functions such as stabilizing formulations and enhancing palatability, and specific examples of each type. Additionally, it discusses the therapeutic applications of specific substances like kaolin and bentonite, emphasizing their properties and uses in both pharmaceutical and medicinal contexts.