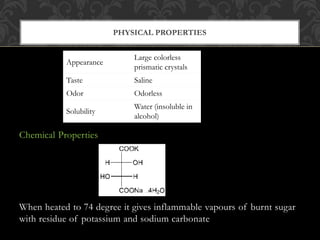
Emetics are drugs that induce vomiting by causing the contents of the stomach to be expelled through the mouth. They are important for treating poisoning cases. Copper sulfate is a common emetic that is blue crystalline powder. It can be assayed through an oxidation-reduction titration with iodine and sodium thiosulfate. Sodium potassium tartrate, also known as Rochelle salt, is a crystalline powder that is soluble in water. It has uses as a laxative, diuretic, and food additive.