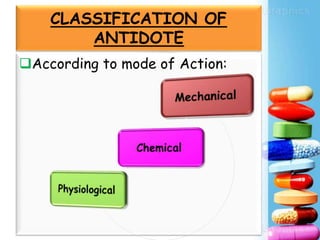
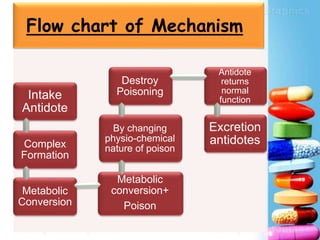
Activated charcoal is commonly used as an antidote to counteract drug and chemical poisonings. It works by binding to poisons in the gastrointestinal tract and preventing absorption. Common side effects include black stools and diarrhea. Antidotes work through various mechanisms like complex formation, metabolic conversion, or changing the physicochemical properties of toxins. In the future, more research on new antidotes and applications of existing treatments is needed, as well as evaluating long term side effects from chronic use. International collaboration helps advance the field of antidotal therapy.