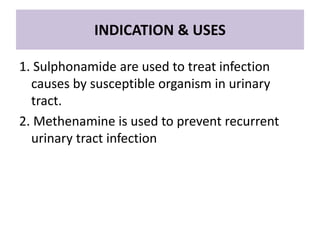
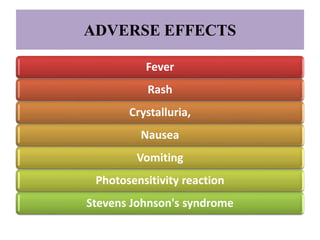
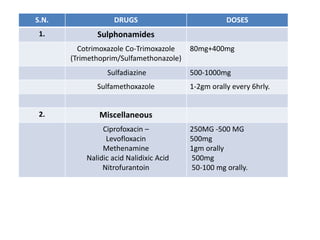
Urinary antiseptics are drugs used to treat and prevent urinary tract infections by killing or inhibiting the growth of microorganisms in the urine. Common urinary antiseptics discussed include sulphonamides, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, methenamine, and nitrofurantoin. These drugs work by being bacteriostatic and inhibiting bacterial growth in the urine. Some potential adverse effects include fever, rash, nausea, vomiting, and crystalluria. Nurses should monitor patients taking these drugs and educate them on proper hygiene, fluid intake, and contraceptive use during treatment.