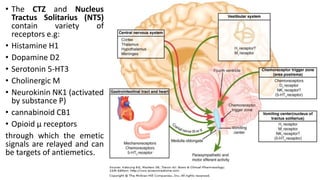
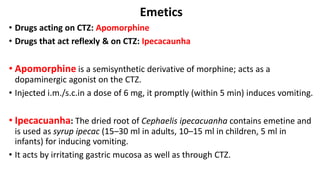
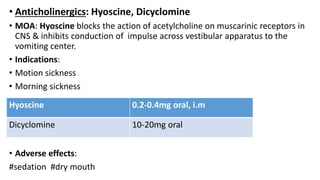
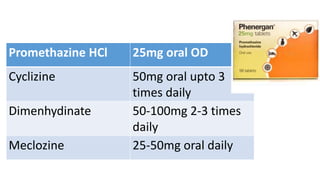
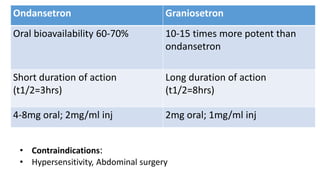
Vomiting is caused by stimulation of the vomiting center in the medulla oblongata by various triggers like toxins, motion, or brain tumors. The vomiting center can be activated through the chemoreceptor trigger zone, vestibular system, or peripheral receptors. Antiemetics work by blocking receptor sites like histamine H1, dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT3, and neurokinin NK1 receptors that transmit emetic signals to the vomiting center. The choice of antiemetic depends on the cause of vomiting and may include antihistamines, anticholinergics, dopamine antagonists, 5-HT3 antagonists, NK1 antagonists, corticosteroids, or cannab