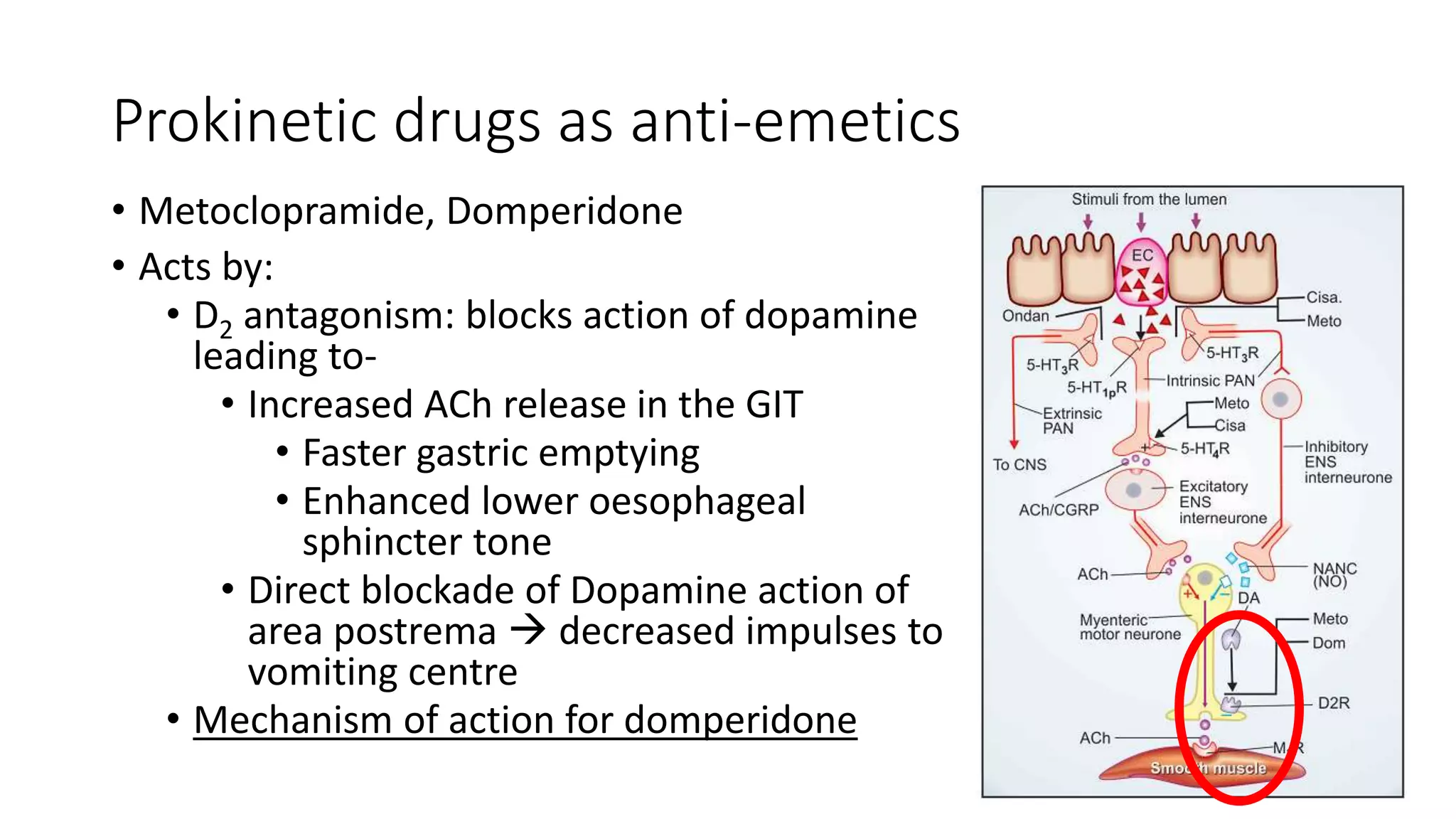
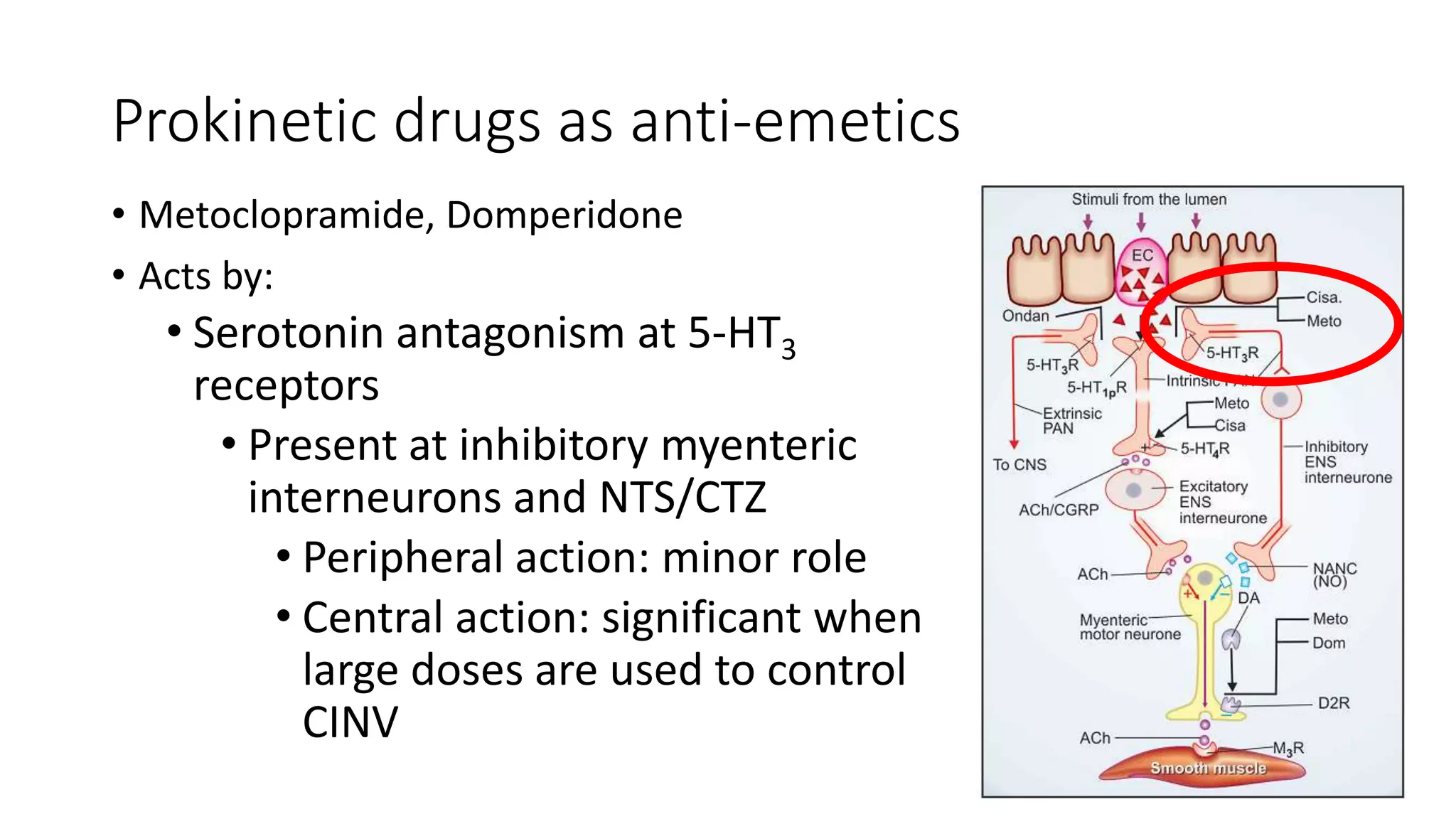
The document discusses 5 case scenarios involving the use of anti-emetic drugs and presents information on the classification and mechanisms of action of common anti-emetic medications. It describes how metoclopramide, dicyclomine, promethazine and other drugs work by blocking receptors involved in vomiting pathways in the brain and gastrointestinal tract. The last case scenario discusses a child who developed dystonia after being given an anti-emetic, likely metoclopramide, indicating its potential side effect.