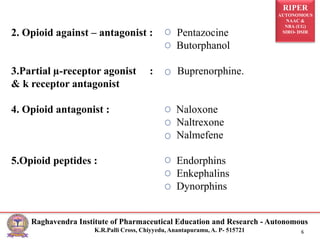
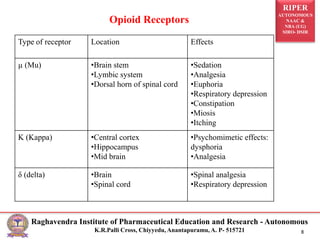
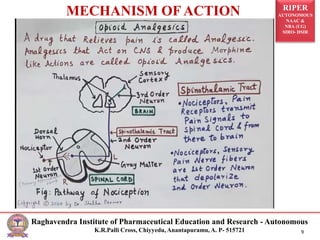
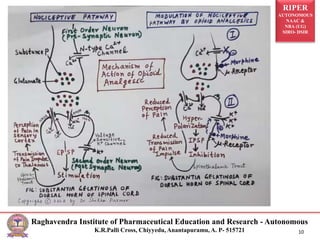
The document is a seminar presentation on opioid analgesics, detailing their history, classification, mechanisms of action, pharmacological effects, and therapeutic uses. It elaborates on morphine as a potent opiate analgesic with various classifications of opioids, including agonists and antagonists, alongside their respective actions and side effects. Additionally, it discusses specific opioids like codeine, tramadol, fentanyl, and the role of endogenous opioid peptides.