Embed presentation


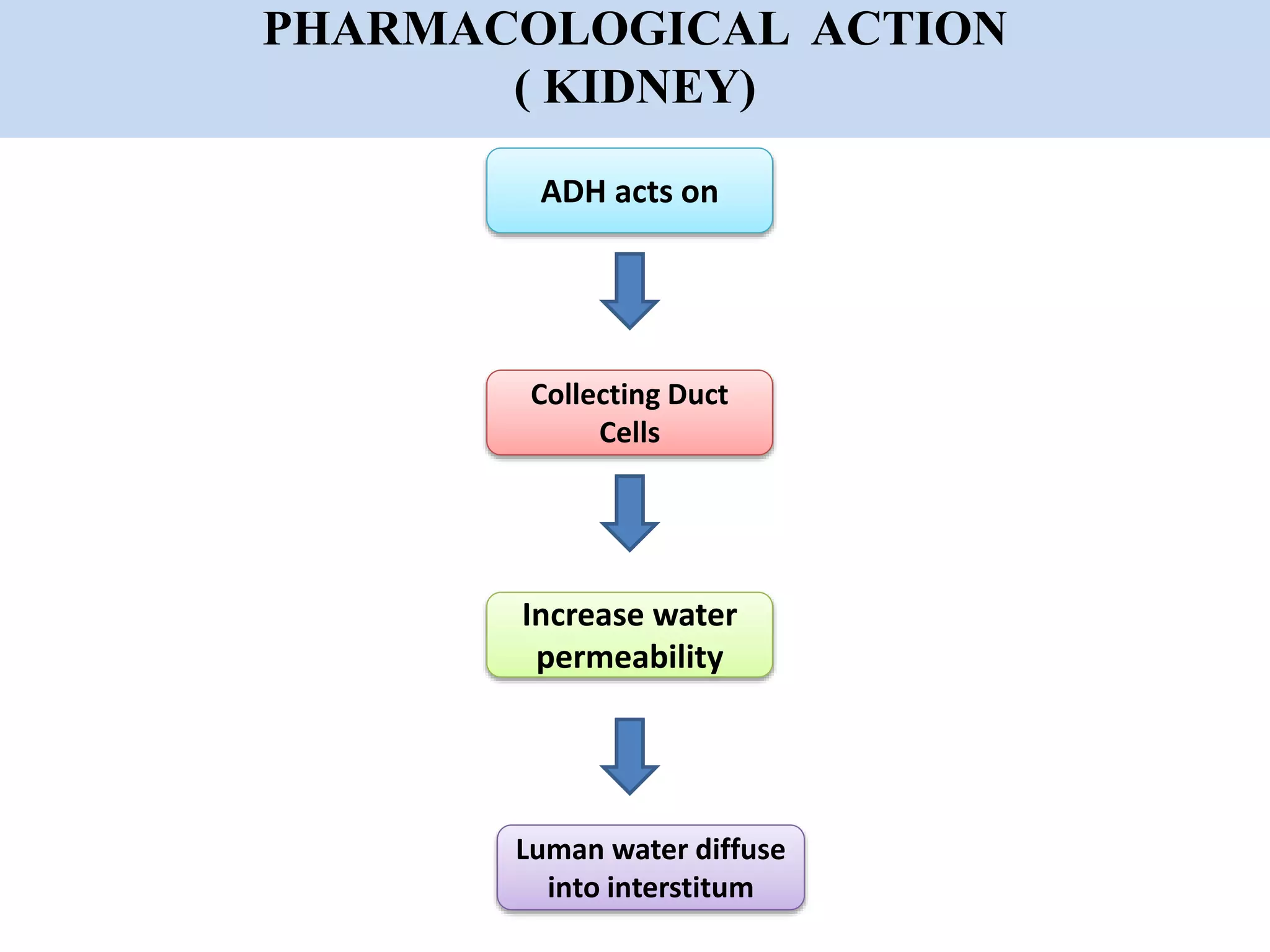







This document discusses anti-diuretic drugs, which reduce urine volume by affecting the reabsorption of water in the kidney tubules. It describes how anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) acts on collecting duct cells in the kidney to increase water permeability and diffusion of water into the interstitum. Example drugs that are anti-diuretic include ADH and desmopressin, which are used to treat conditions like diabetes insipidus and nocturia. Nurses should monitor patients taking these drugs for electrolyte imbalances, vital signs, and signs of adverse effects like nasal irritation or fluid retention.








