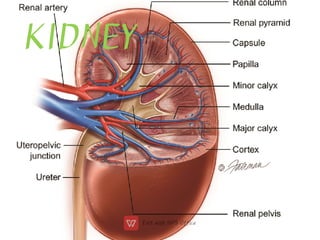
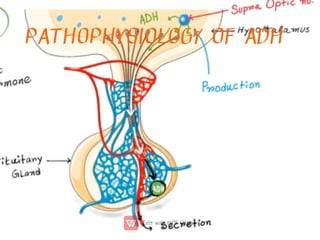
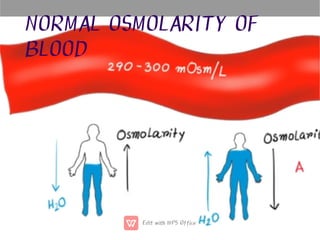
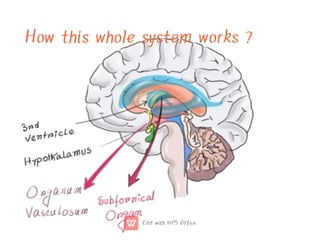
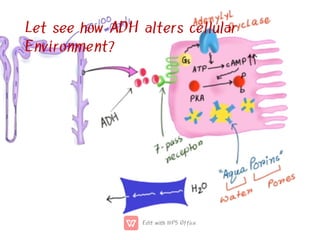
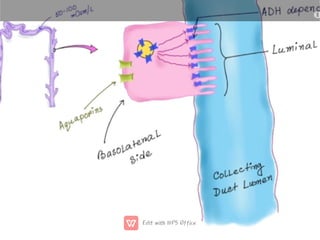
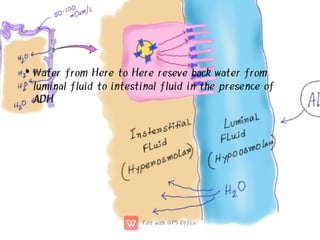
This document discusses anti-diuretic drugs, which inhibit diuresis to maintain water balance in the body. It describes the key roles of the kidneys and hypothalamus in regulating water balance and the pathophysiology of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH). ADH acts on the kidneys to reabsorb water and increase urine concentration by increasing water permeability in the collecting ducts. The document classifies and describes various anti-diuretic drugs and their mechanisms of action, including vasopressin, desmopressin, lypressin, terlipressin, thiazide diuretics, benzothiadiazines, and others used to treat conditions like diabetes ins