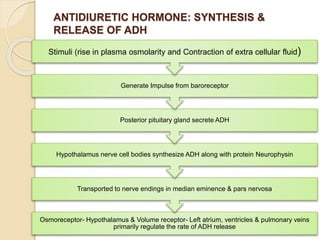
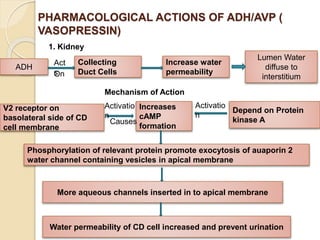
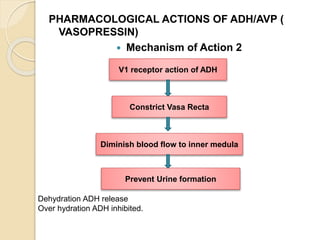
This document discusses various anti-diuretic agents including antidiuretic hormone (ADH or vasopressin), its synthesis and release mechanisms. It classifies anti-diuretic agents into antidiuretic hormone, thiazide diuretics, and miscellaneous agents. It describes the pharmacological actions of ADH including its effects on kidneys to increase water permeability and reduce urine volume, and its effects on blood vessels and other tissues. It also discusses analogues of ADH including lypressin, terlipressin, and desmopressin, and their uses, pharmacokinetics, and adverse effects. Thiazide diuretics and some other miscellaneous drugs that provide alternative anti