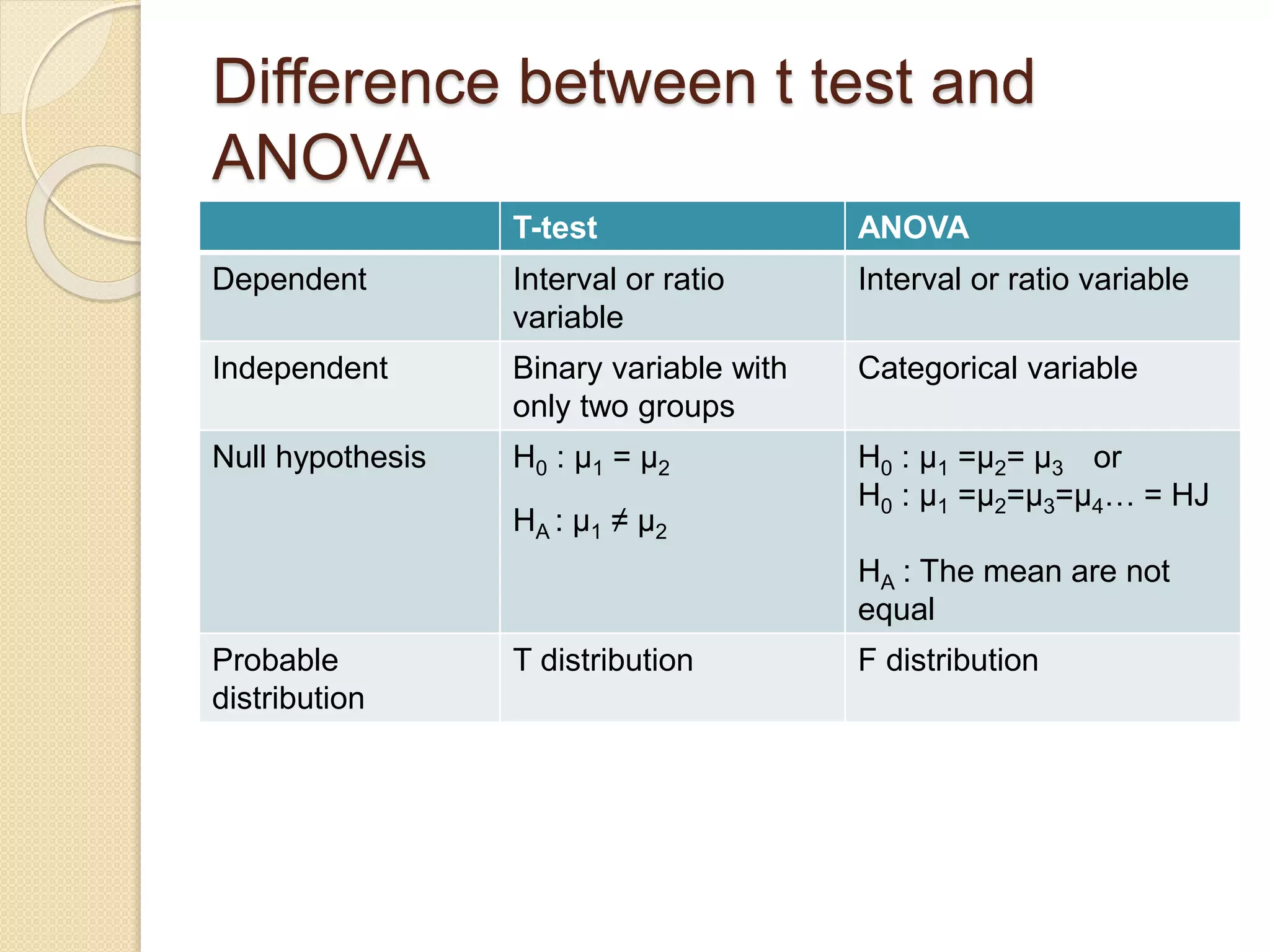
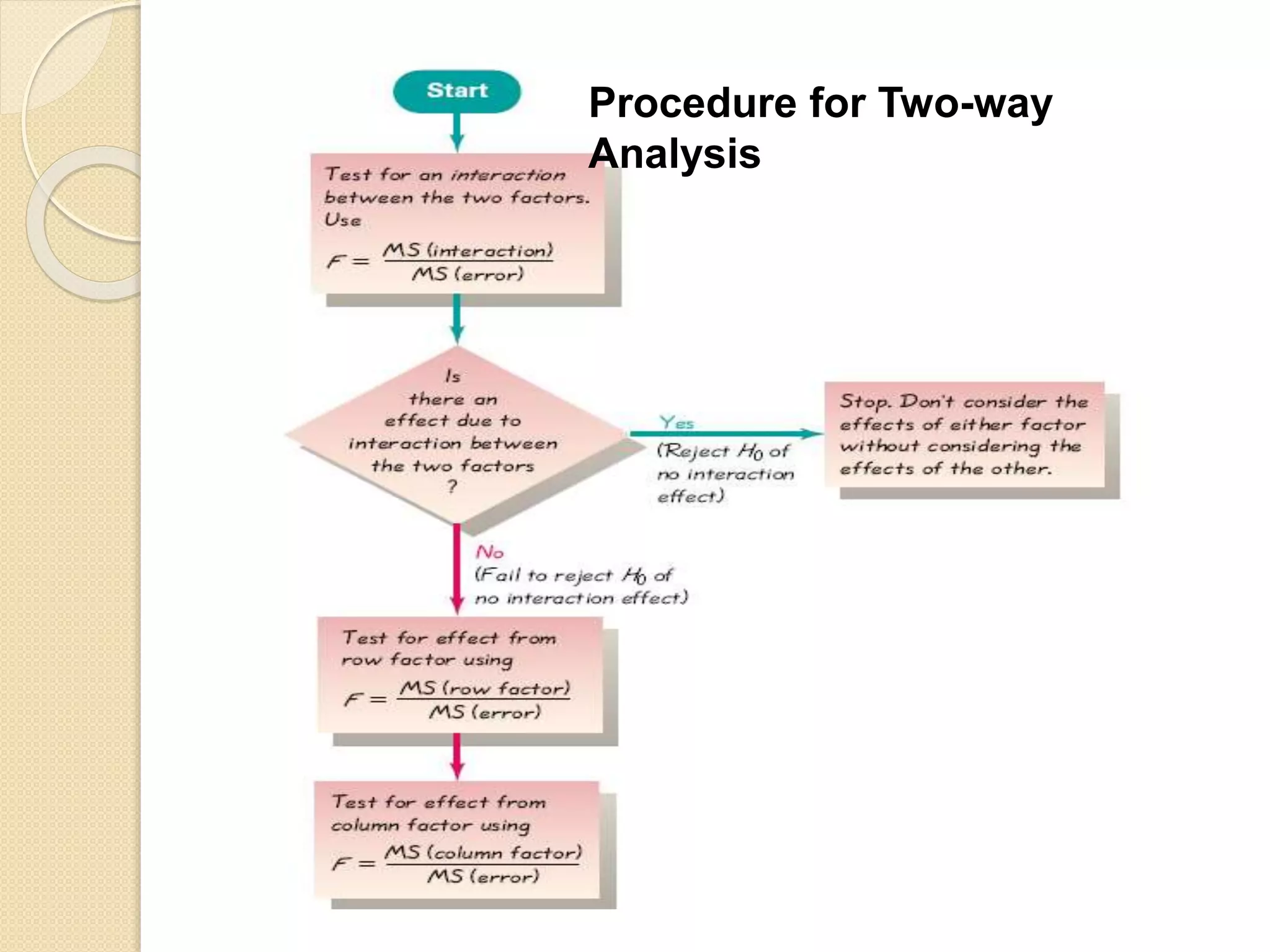
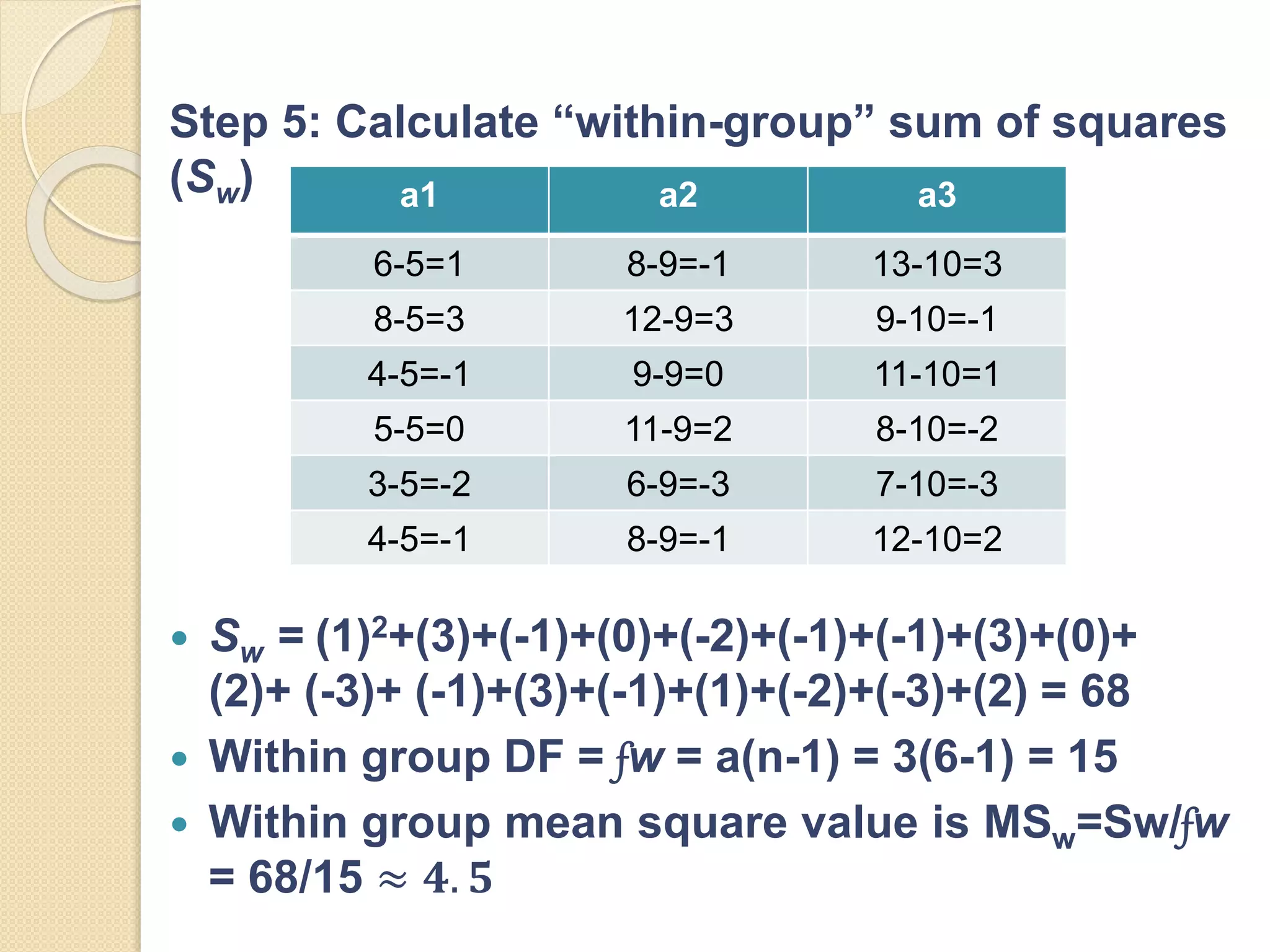
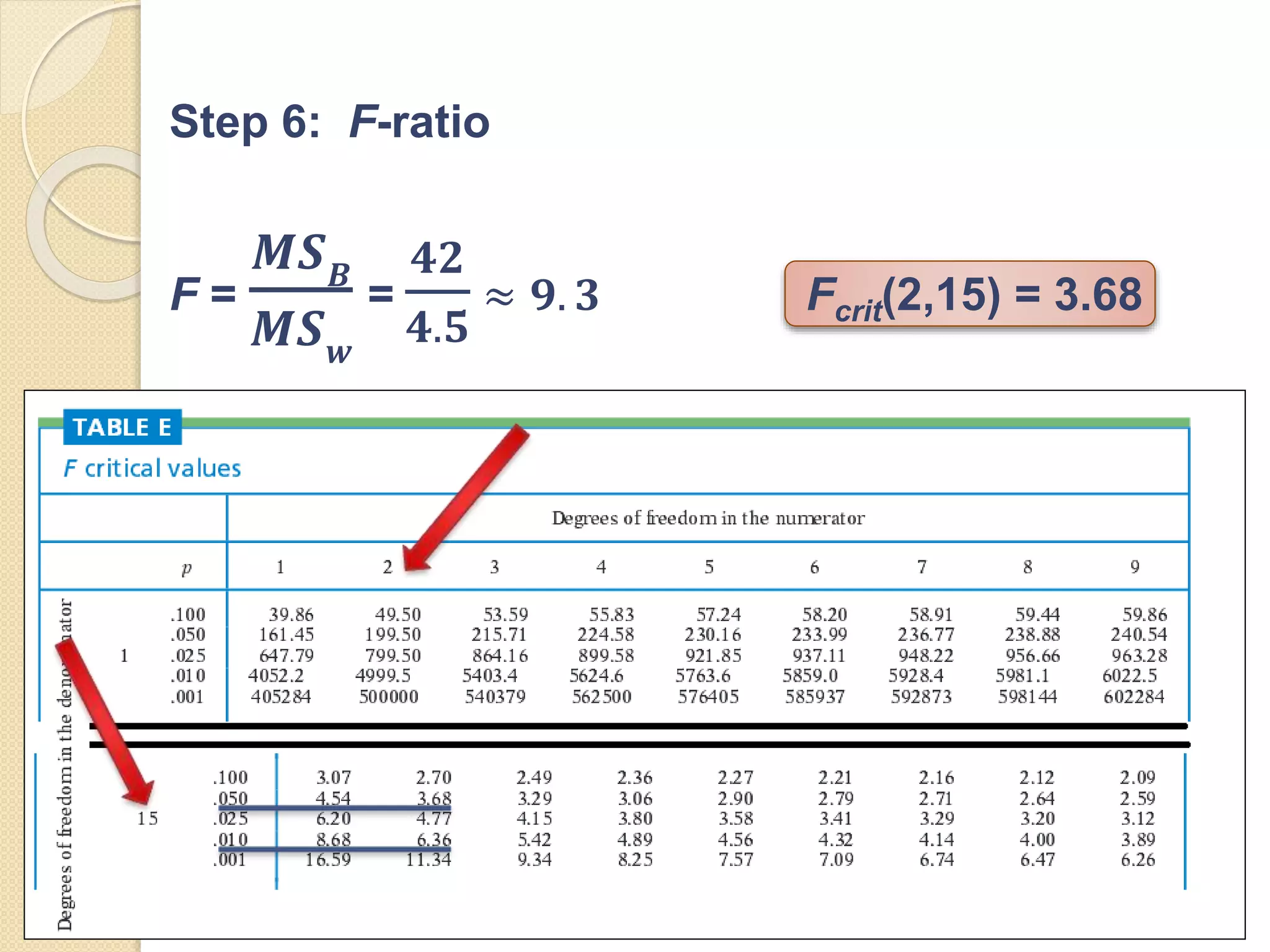
ANOVA (analysis of variance) and mean differentiation tests are statistical methods used to compare means or medians of multiple groups. ANOVA compares three or more means to test for statistical significance and is similar to multiple t-tests but with less type I error. It requires continuous dependent variables and categorical independent variables. There are different types of ANOVA including one-way, factorial, repeated measures, and multivariate ANOVA. Key assumptions of ANOVA include normality, homogeneity of variance, and independence of observations. The F-test statistic follows an F-distribution and is used to evaluate the null hypothesis that population means are equal.