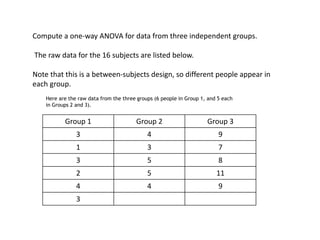
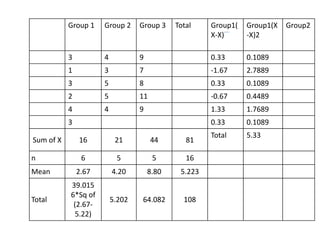
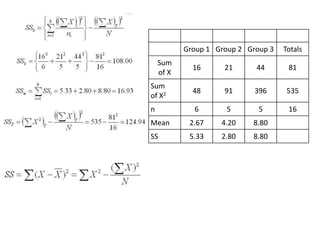
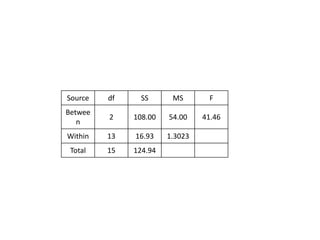
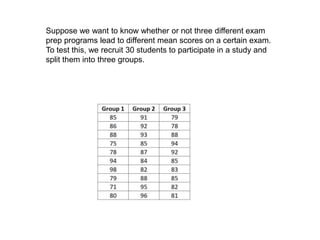
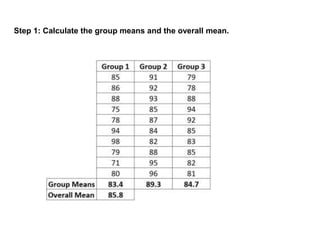
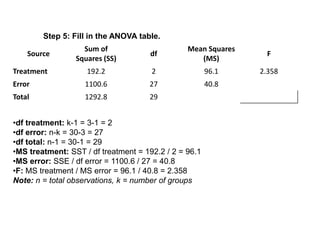
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a statistical technique used to compare the means of three or more groups. It compares the variance between groups with the variance within groups to determine if the population means are significantly different. The key assumptions of ANOVA are independence, normality, and homogeneity of variances. A one-way ANOVA involves one independent variable with multiple levels or groups, and compares the group means to the overall mean to calculate an F-ratio statistic. If the F-ratio exceeds a critical value, then the null hypothesis that the group means are equal can be rejected.