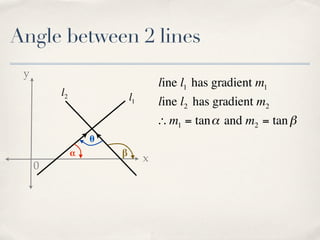
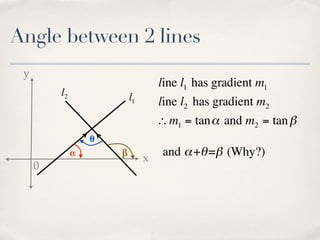
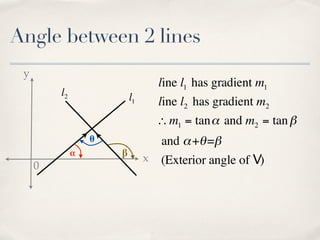
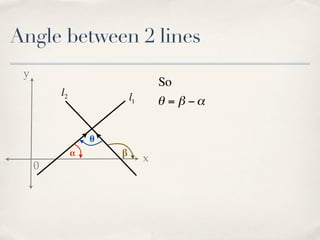
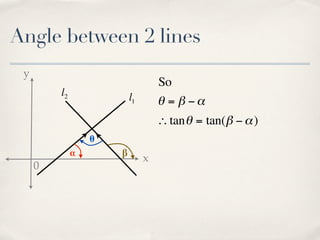
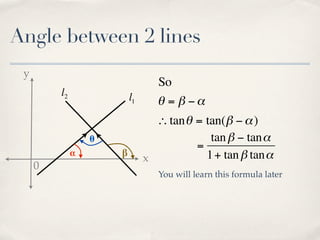
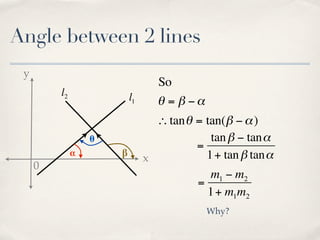
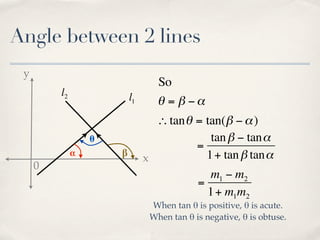
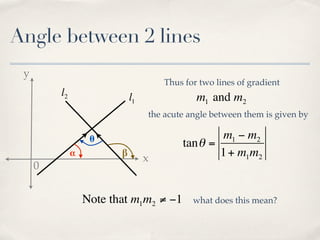
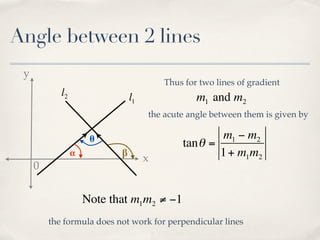
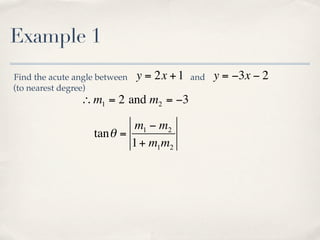
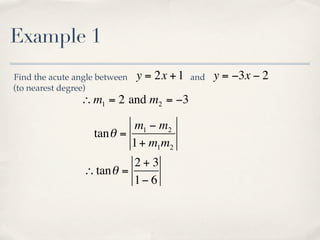
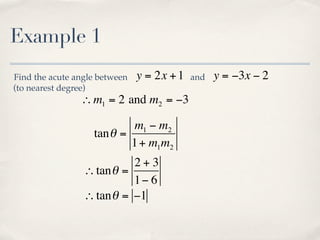
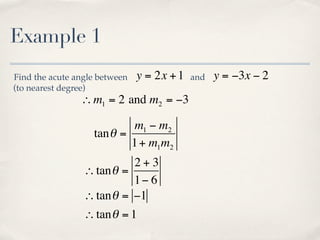
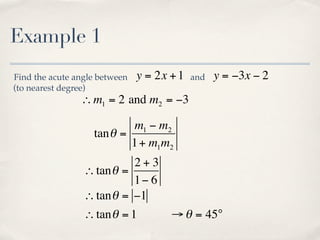
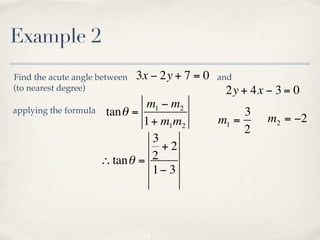
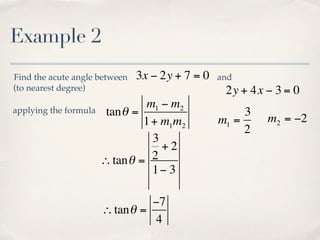
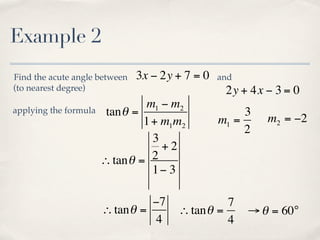
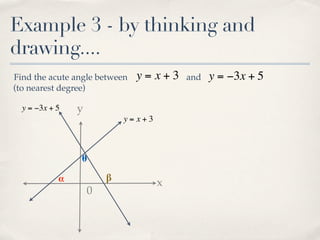
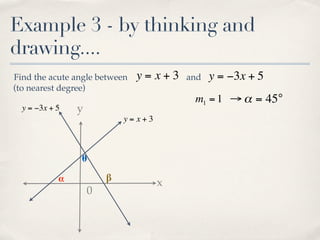
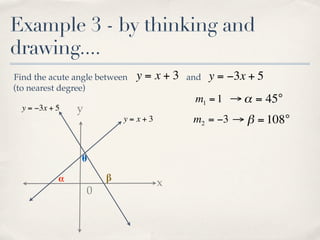
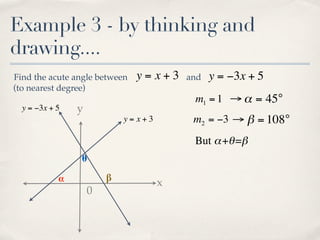
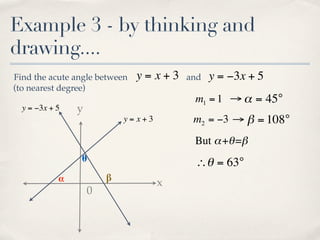
The document discusses finding the angle between two lines given by their gradients (slopes). It provides the formula for calculating the tangent of the acute angle between the lines as (m1 - m2) / (1 + m1m2), where m1 and m2 are the gradients of the two lines. It then works through three examples of applying the formula to find the acute angle between pairs of lines.