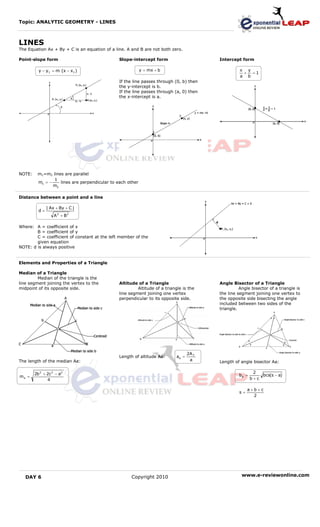
This document discusses fundamental concepts in analytic geometry related to lines. It defines key terms like slope, the different forms of a line equation, and how to find the distance from a point to a line. It also covers properties and elements of triangles, including how to calculate the length of a median, altitude, and angle bisector.
![Topic: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY - LINES
FUNDAMENTALS
RECTANGULAR OR CARTESIAN COORDINATES
Division of Line Segment
x1 + x 2
The x-coordinate is the abscissa, and the y-coordinate is the x=
2
ordinate.
Distance between two points y1 + y 2
y=
2
Slope and Inclination of a Line
The slope (m) of a line is the tangent of the inclination
2 2
The distance between P1 and P2: d = (x 2 − x1 ) + (y2 − y1 )
m = tan θ
Area of a Triangle Let P1 (x1, y1) and P2 (x2, y2) be two given points, and is
indicated by slope m
1 x1 x 2 x 3
A= y 2 − y1
2 y1 y 2 y 3 m = tan θ =
x 2 − x1
1
A = [(x1y2 + x 2 y3 + x3y1 ) − (y1x2 + y 2 x3 + y 3x1 )] Angle between Two Lines
2
Area of polygon of n-sides
1 x1 x2 x3 ... xn
A =
2 y1 y2 y3 ... yn
m2 − m1
tan θ =
1 + m2m1
Where: m1 = slope of line 1
m2 = slope of line 2
θ = angle from line 1 to line 2, measured
clockwise from line 1 to line 2
DAY 6 Copyright 2010 www.e-reviewonline.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdocumentsandsettingsm-edesktopantonfileswebsitemathematicsday32lectureshandoutslines6-100916044556-phpapp01/75/Day-06-1-2048.jpg)