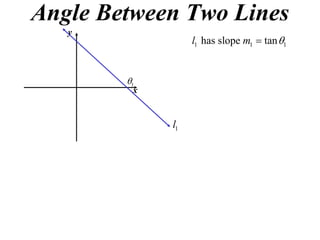
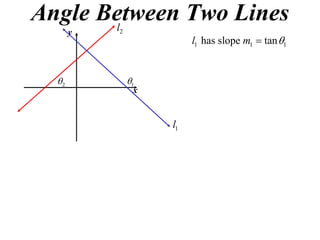
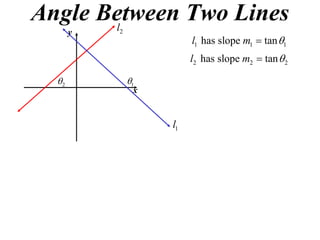
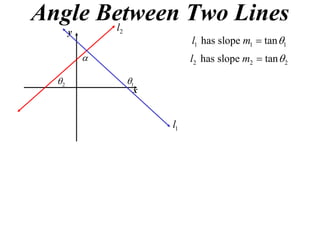
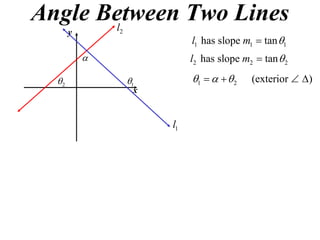
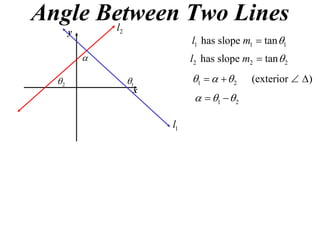
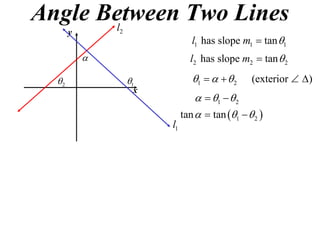
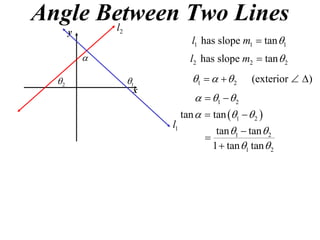
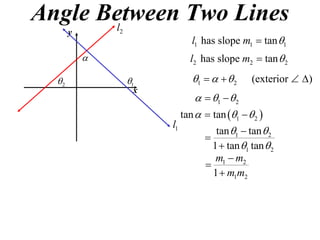
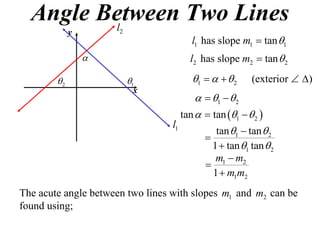
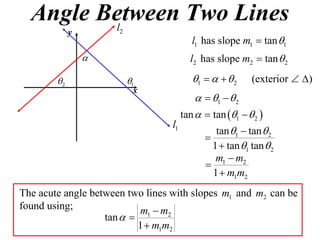
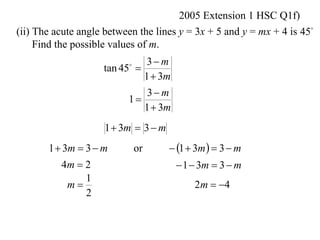
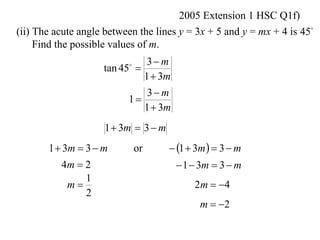
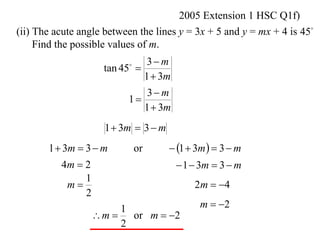
The document shows how to find the acute angle between two lines given their slopes. It provides examples that demonstrate using the formula tan(α) = (m1 - m2) / (1 + m1m2) to calculate the angle. For lines with slopes m1 and m2, this formula can be used to find the acute angle between them.