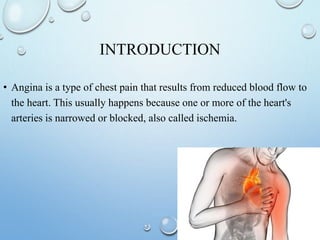
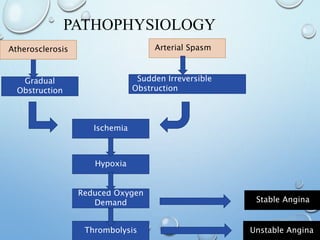
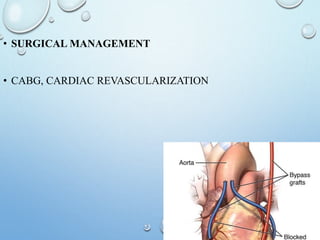
Angina pectoris, or angina, is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. There are different types of angina that vary based on factors like when the pain occurs and how long it lasts. Risk factors include obesity, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes. Treatment involves medications like nitroglycerin to relieve symptoms as well as procedures like CABG to restore blood flow if needed. Nurses manage angina by addressing pain, activity tolerance, and providing patient education.