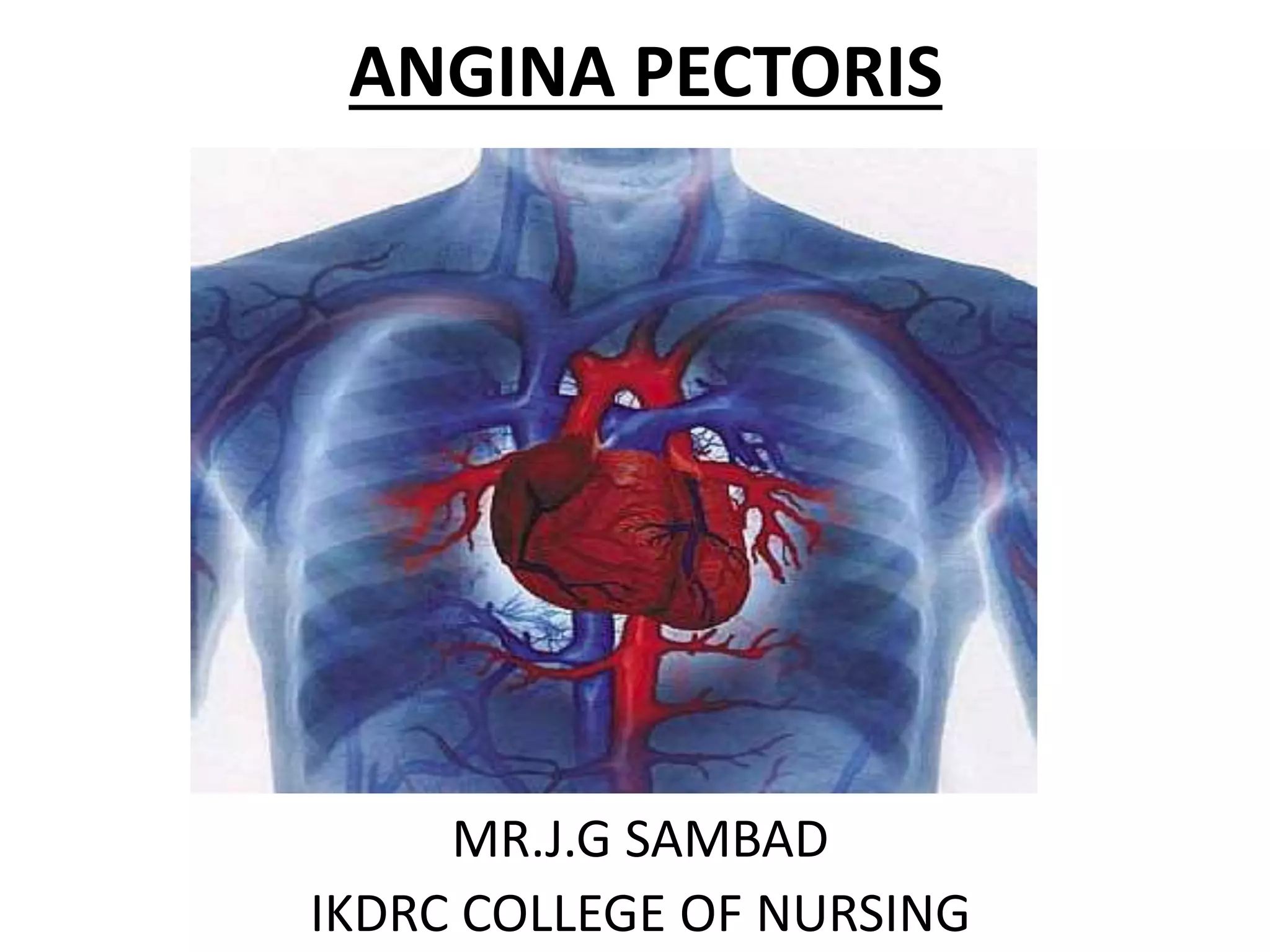
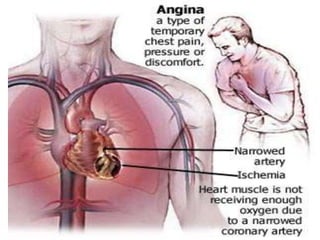
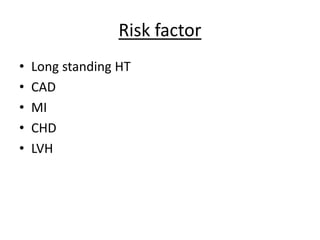
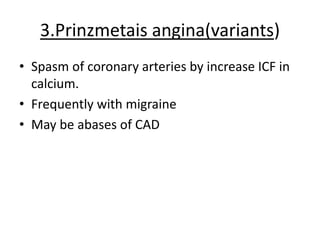
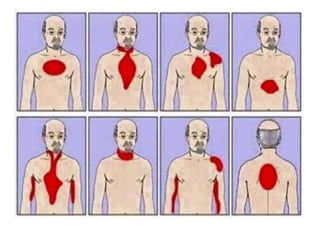
Angina pectoris, commonly known as chest pain, occurs when the heart muscle doesn't receive enough oxygen due to narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. It causes uncomfortable chest pressure or pain that may radiate to the shoulders, neck, or arms. There are different types of angina including stable angina brought on by exertion and unstable angina which occurs at rest with an unpredictable pattern. Diagnosis involves electrocardiograms and blood tests, while treatment focuses on nitroglycerin, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, exercising, and eating a healthy diet to prevent further risks.