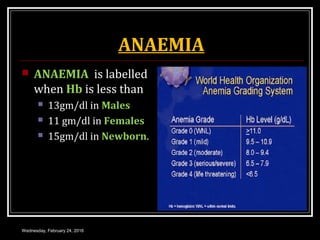
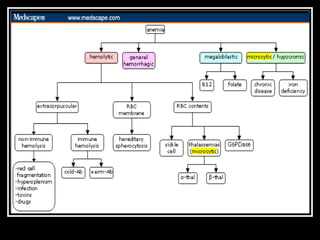
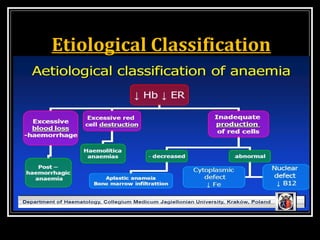
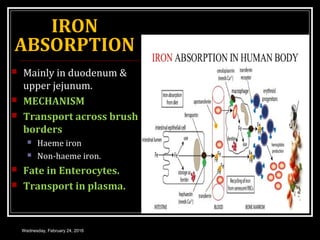
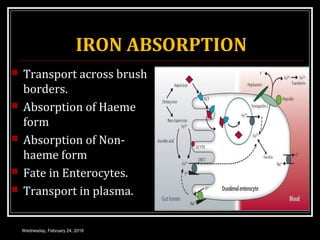
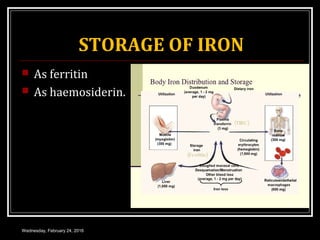
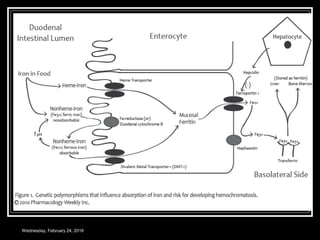
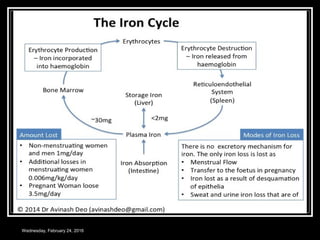
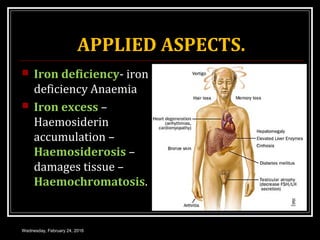
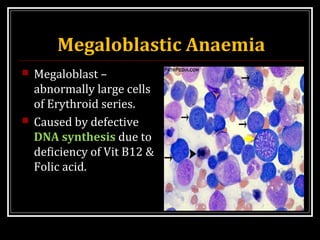
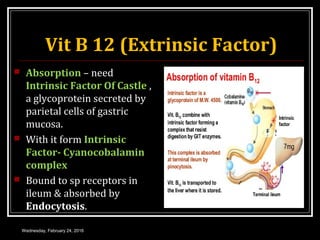
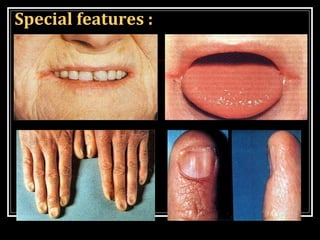
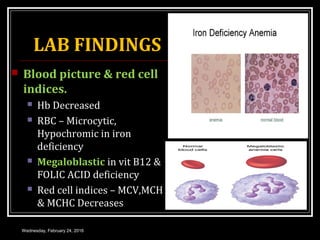
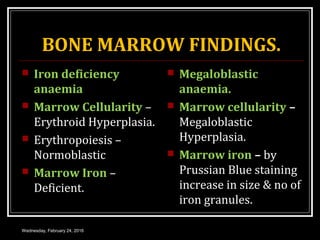
This document discusses anemia, specifically iron deficiency anemia and megaloblastic anemia. It defines anemia and provides classifications. It then describes iron metabolism, daily iron requirements, sources of iron, and factors affecting iron absorption. It discusses the causes, clinical features, laboratory findings, and management of iron deficiency anemia and megaloblastic anemia. Key points covered include the role of vitamin B12 and folic acid in megaloblastic anemia, and morphological and etiological classifications of anemia.