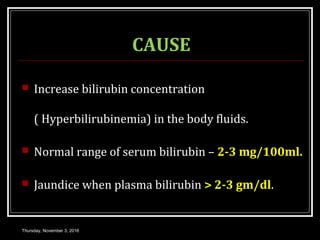
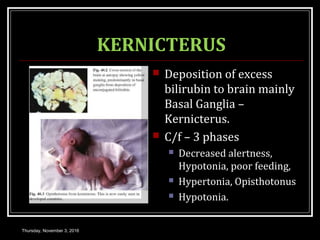
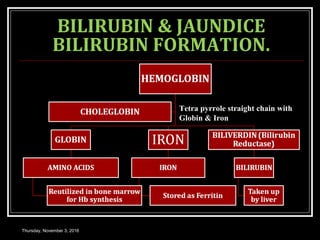
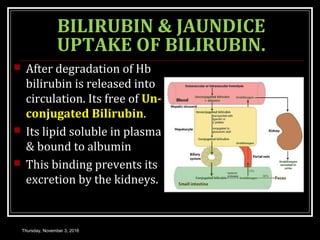
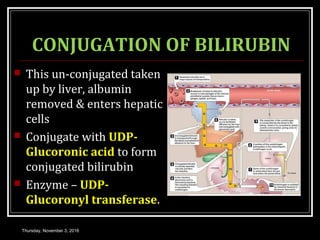
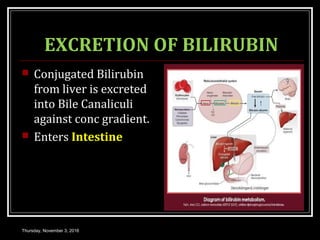
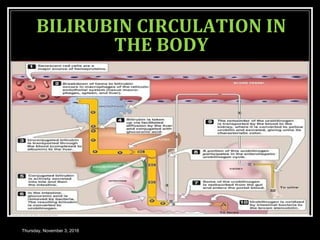
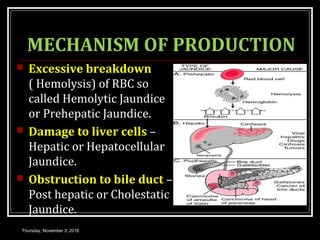
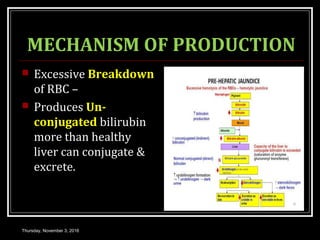
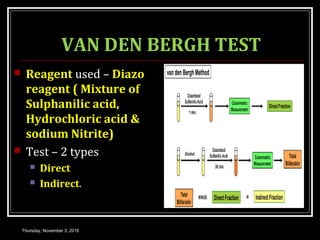
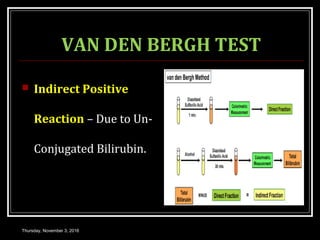
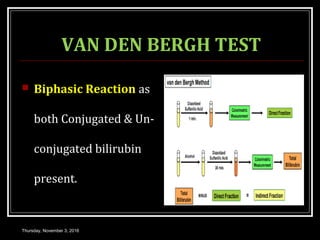
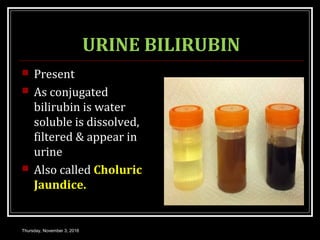
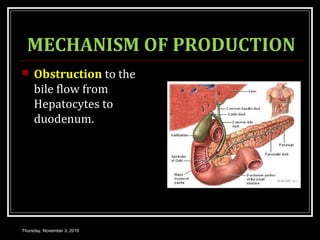
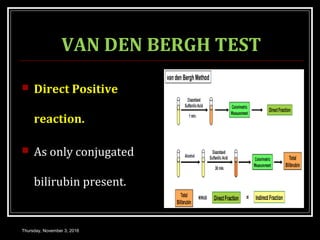
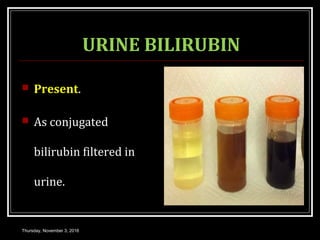
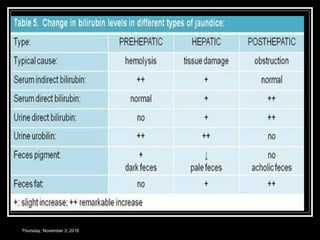
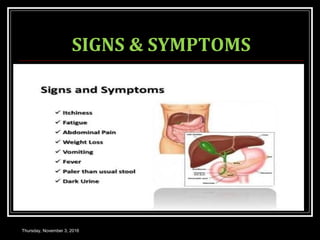
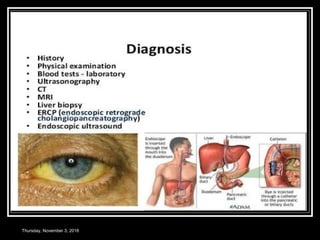
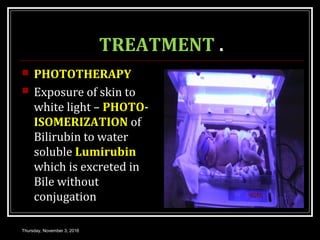
This document provides an overview of jaundice, including its definition, causes, types, and characteristics. Jaundice is caused by an increase in bilirubin levels and results in a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. There are three main types of jaundice - hemolytic, hepatocellular, and cholestatic. The document describes the mechanisms, clinical features, and diagnostic tests for each type in detail. Physiological jaundice in newborns is also discussed. Treatment focuses on phototherapy for neonatal jaundice and addressing the underlying cause for pathological jaundice in adults.