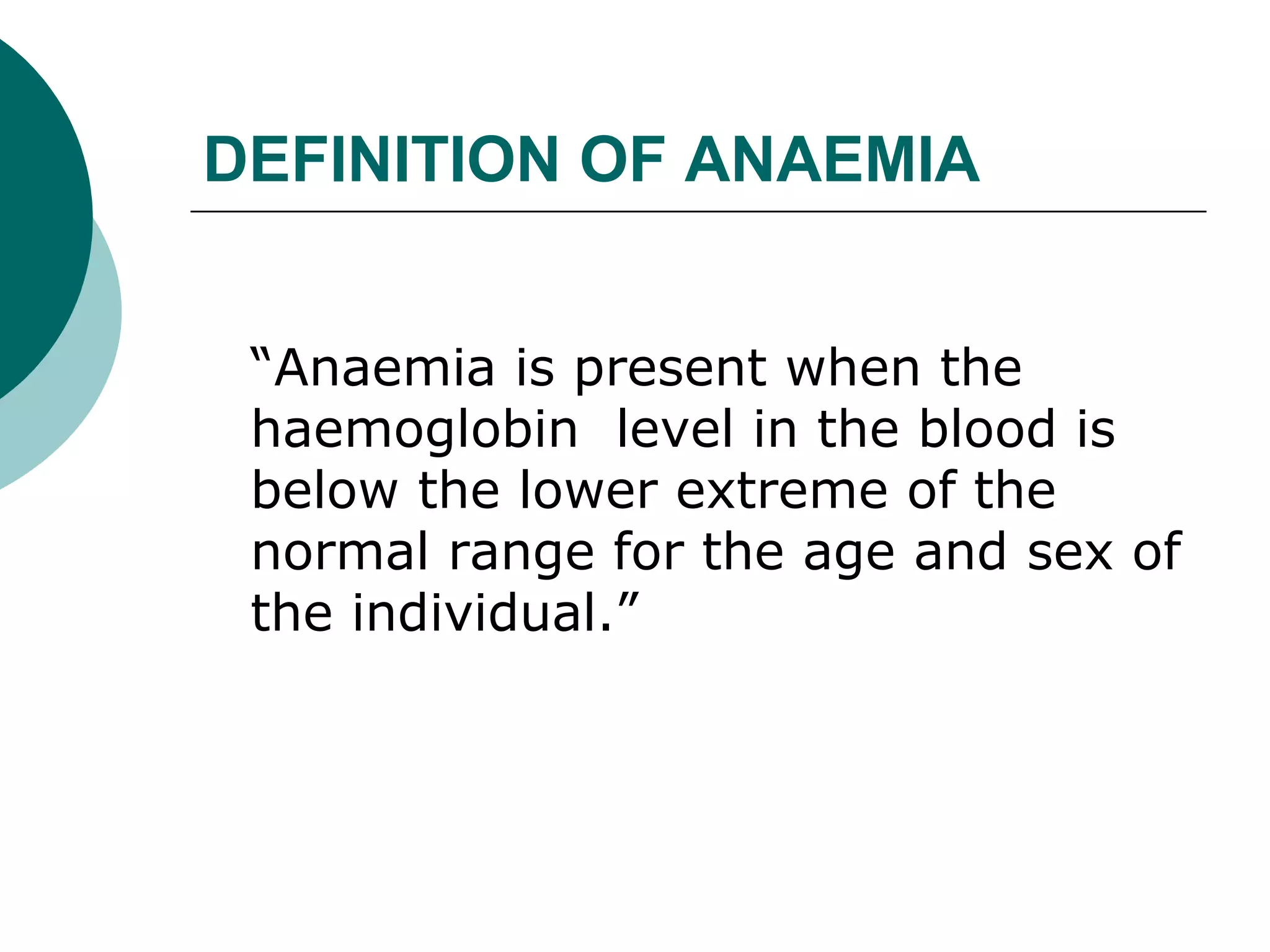
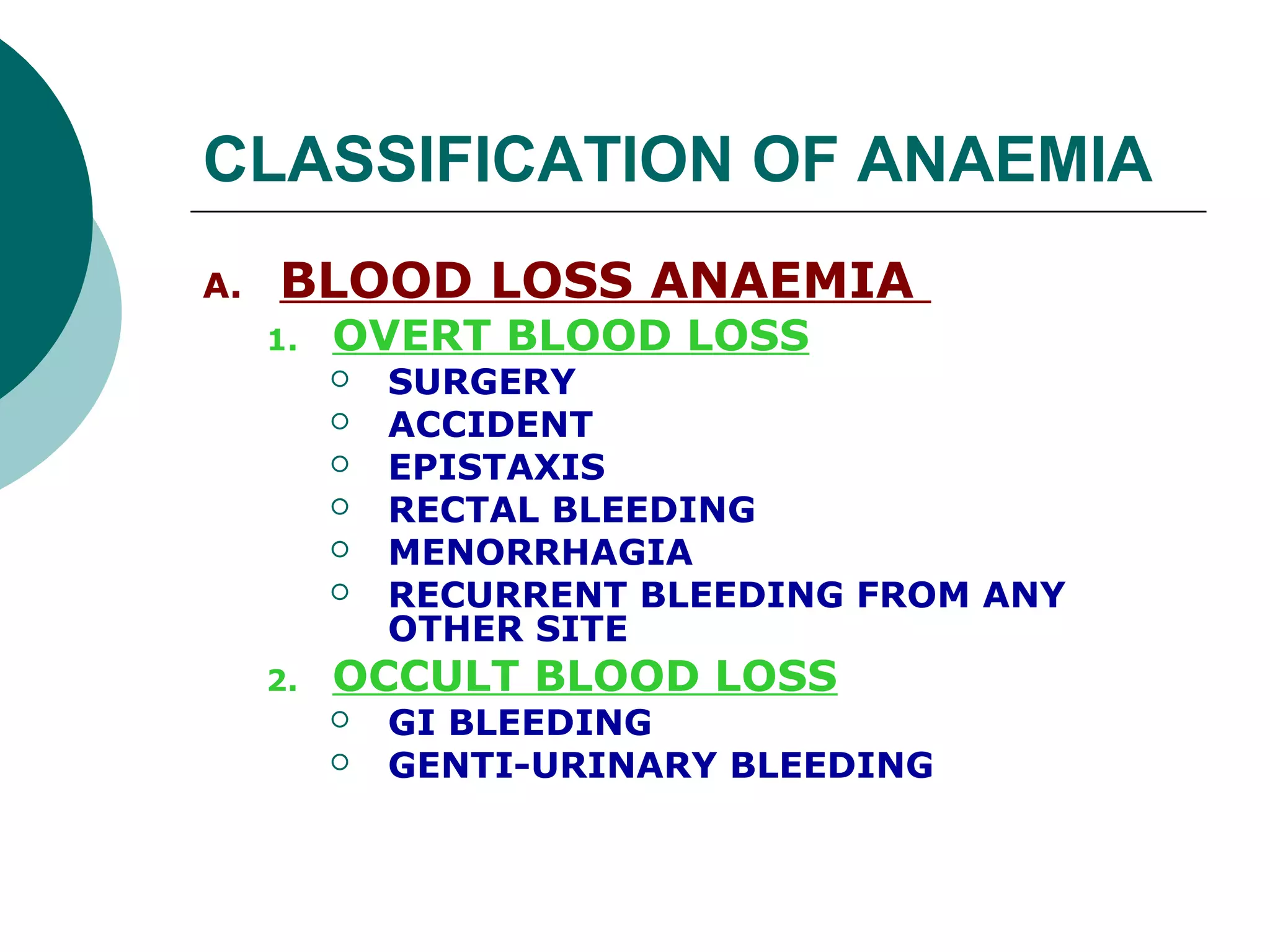
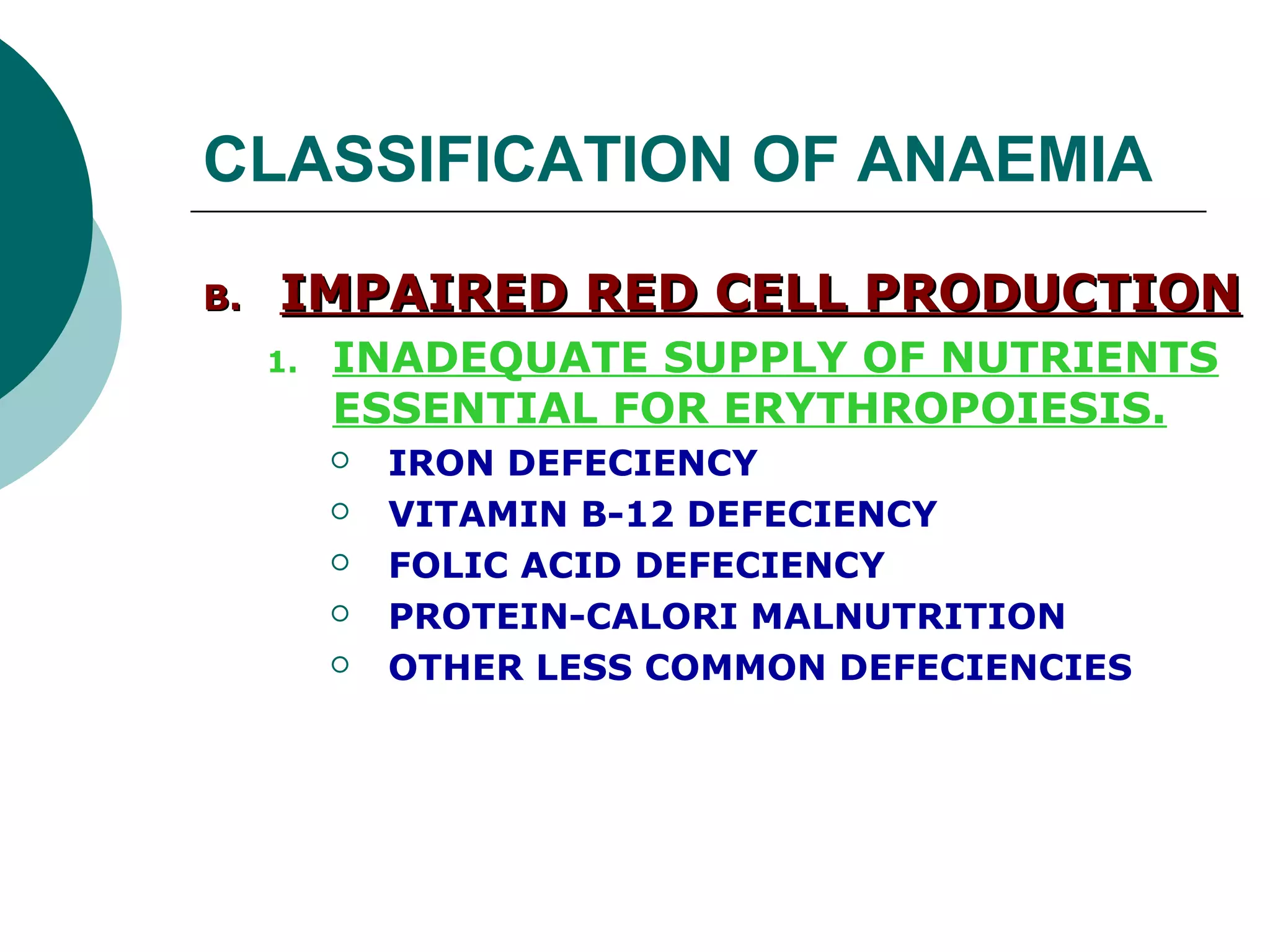
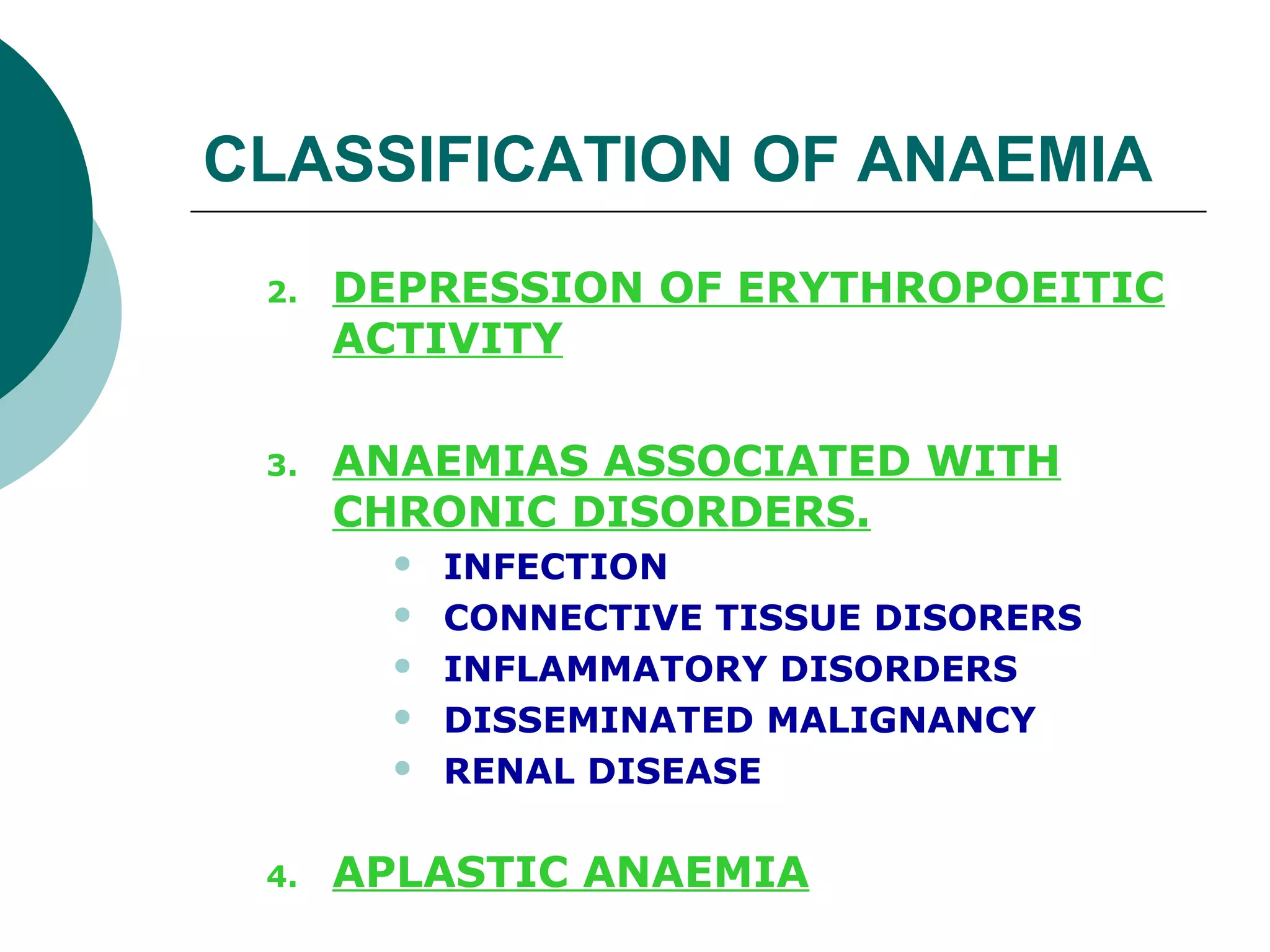
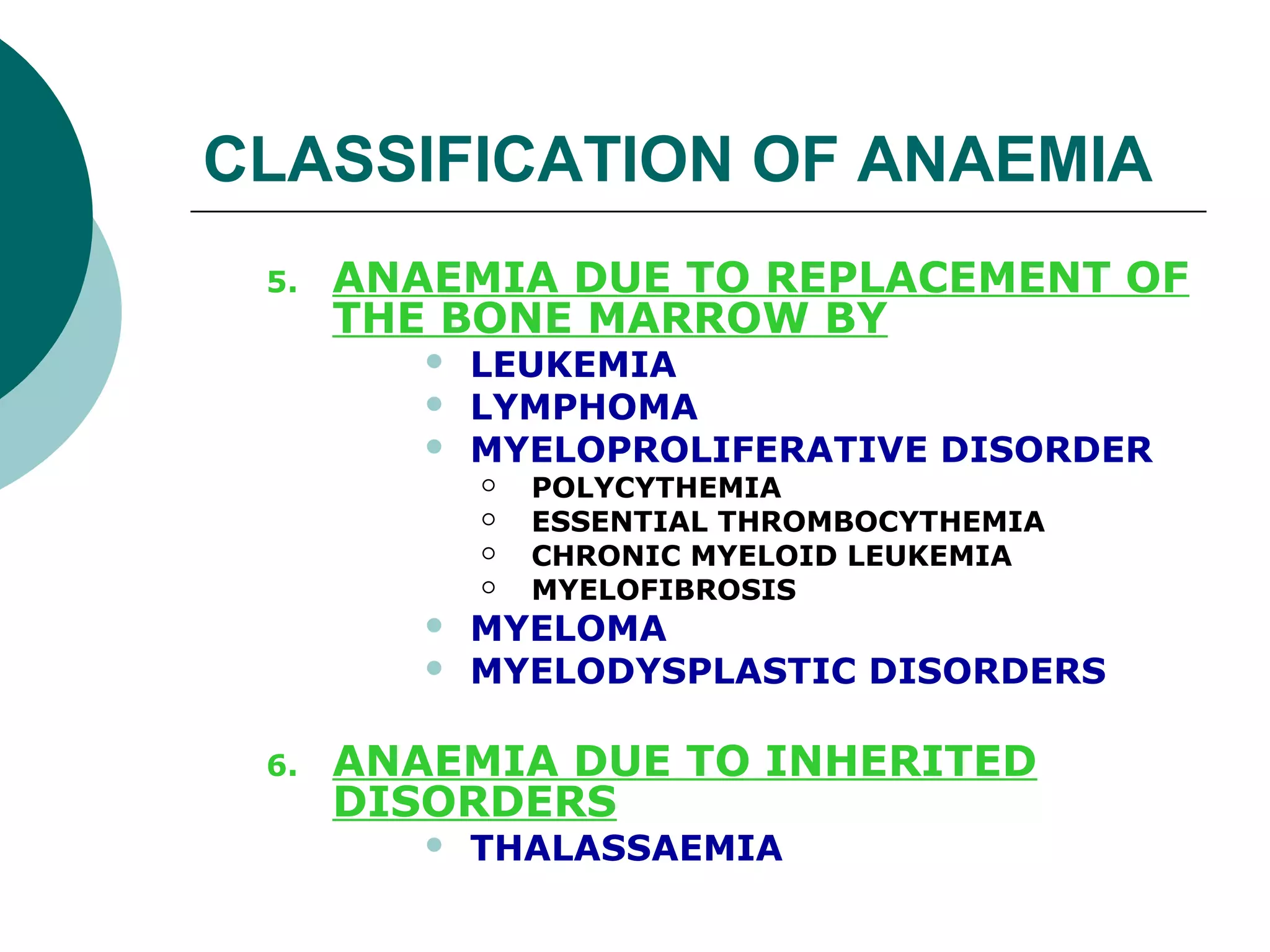
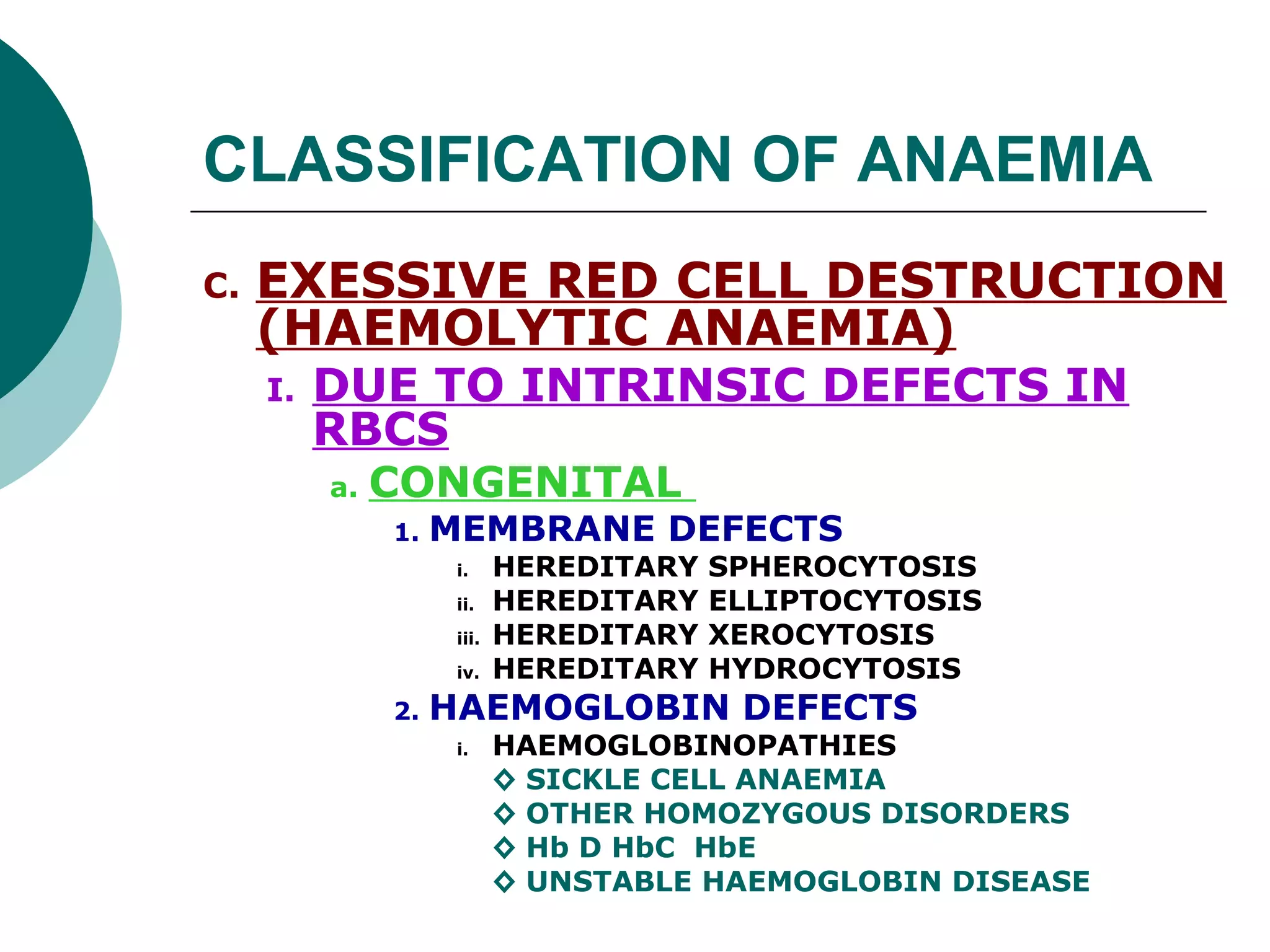
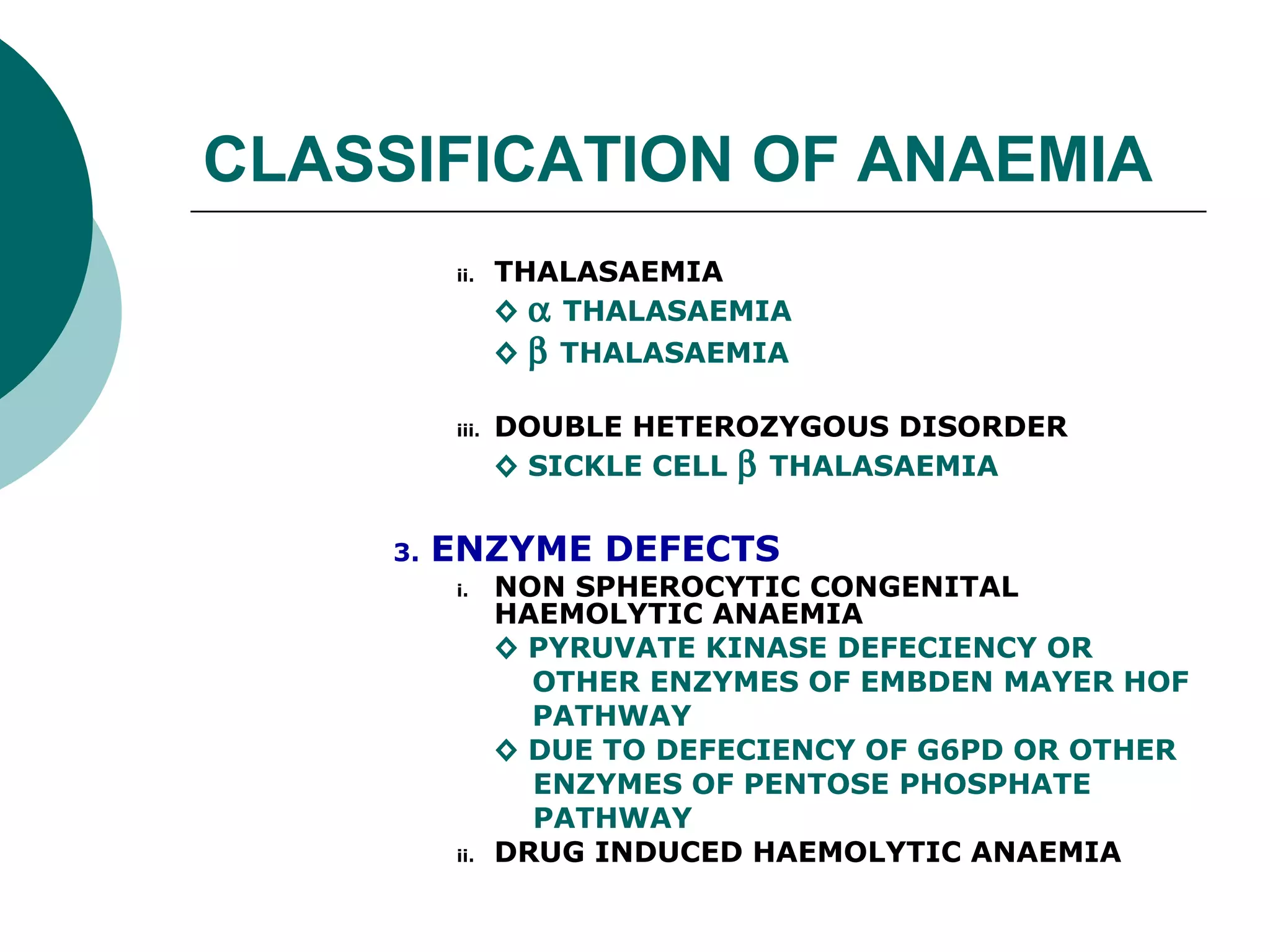
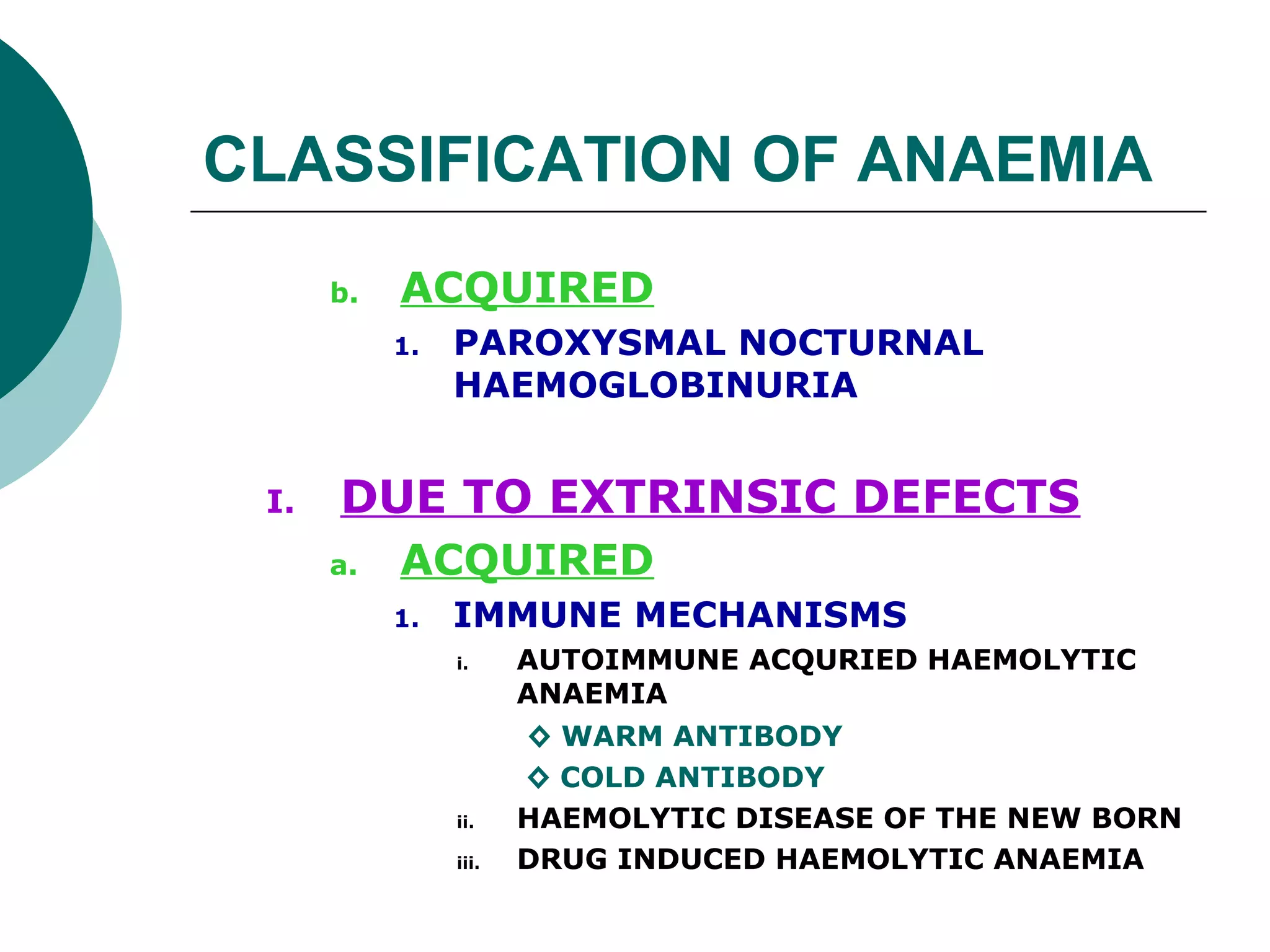
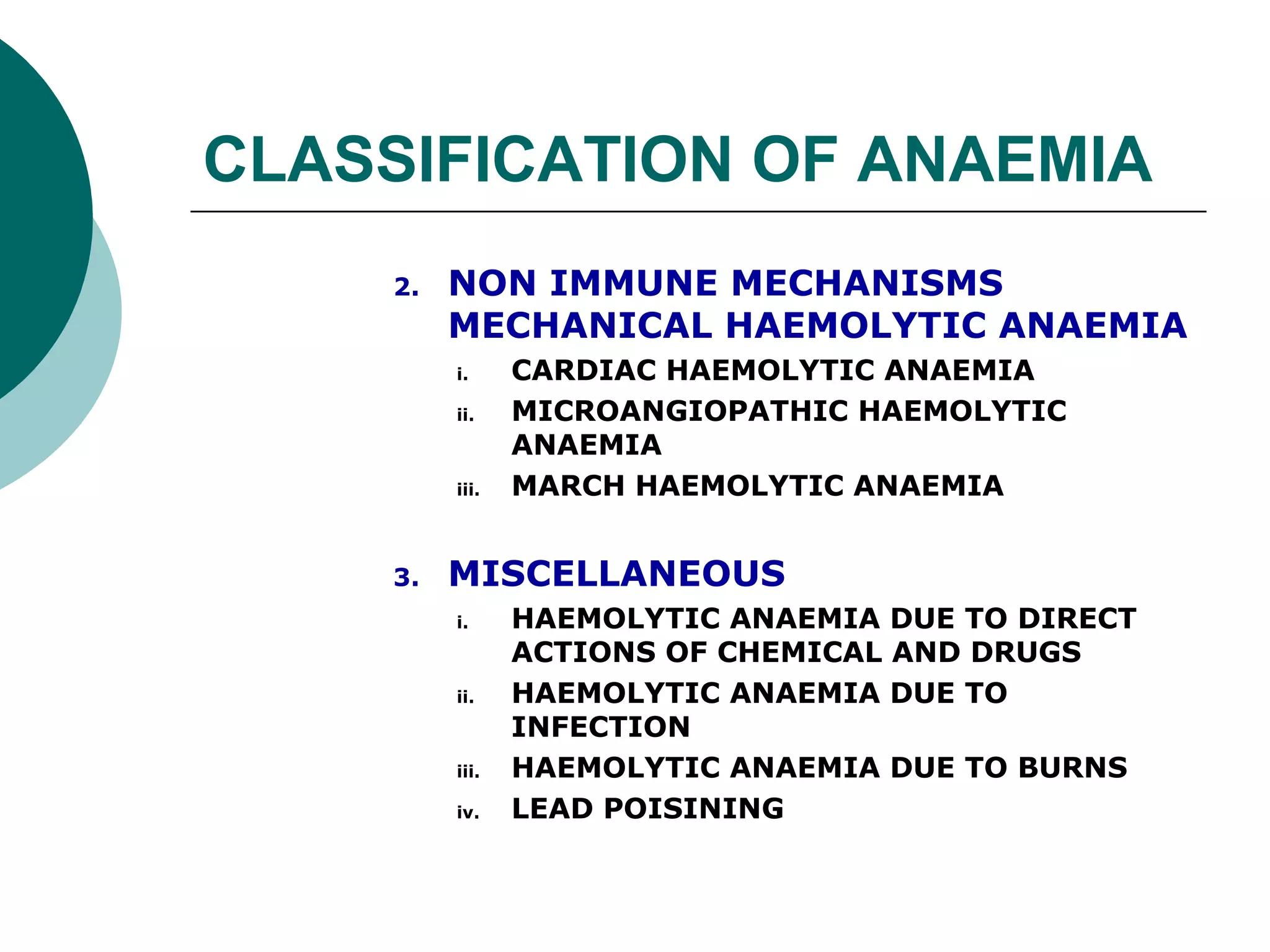
The document classifies anaemia into three main categories: blood loss anaemia, impaired red blood cell production, and excessive red blood cell destruction (haemolytic anaemia). Blood loss anaemia includes overt blood loss from injuries or procedures and occult bleeding from the GI or GU tract. Impaired production is due to nutrient deficiencies like iron, B12, and folate or conditions that suppress red blood cell formation. Excessive destruction includes hereditary defects affecting red blood cell membranes or haemoglobin as well as acquired immune or non-immune causes.