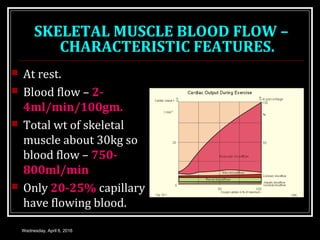
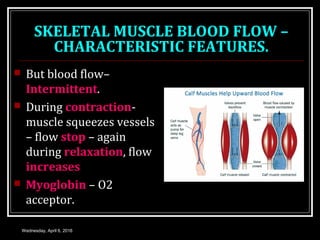
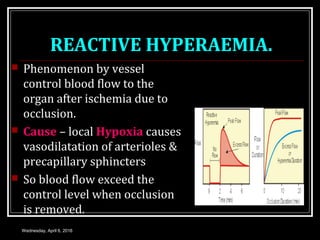
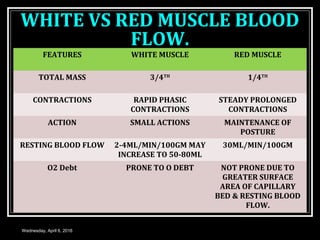
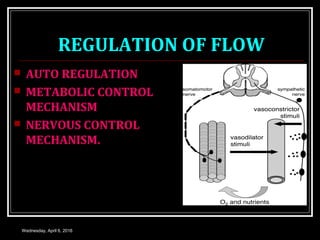
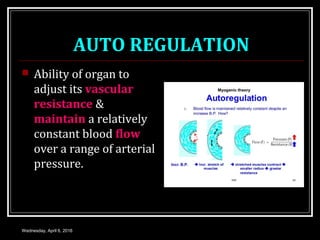
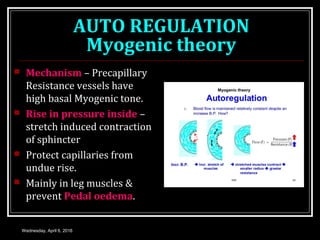
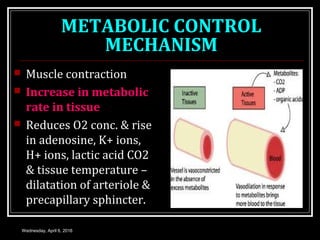
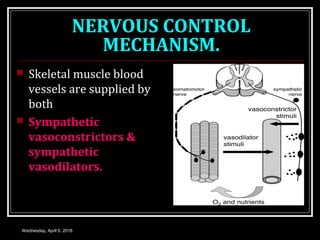
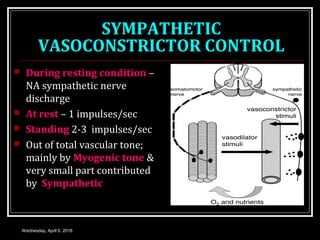
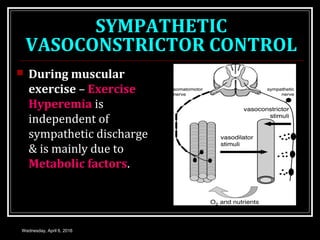
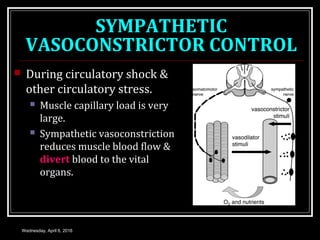
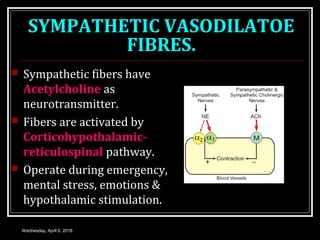
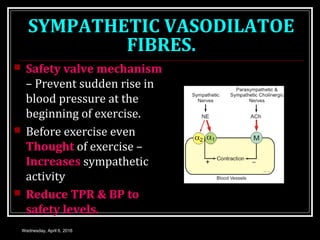
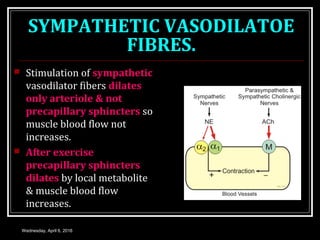
This document discusses skeletal muscle circulation and blood flow regulation. It notes that at rest, skeletal muscle blood flow is relatively low at 2-4 ml/min/100gm but increases up to 20 times during exercise due to arteriole and precapillary sphincter dilation from local metabolites. Blood flow is intermittent during muscle contraction and cessation. Regulation of skeletal muscle blood flow involves auto-regulation via myogenic tone in precapillary vessels, metabolic control from factors like oxygen levels and sympathetic nervous control with both vasoconstrictor and vasodilator fibers.