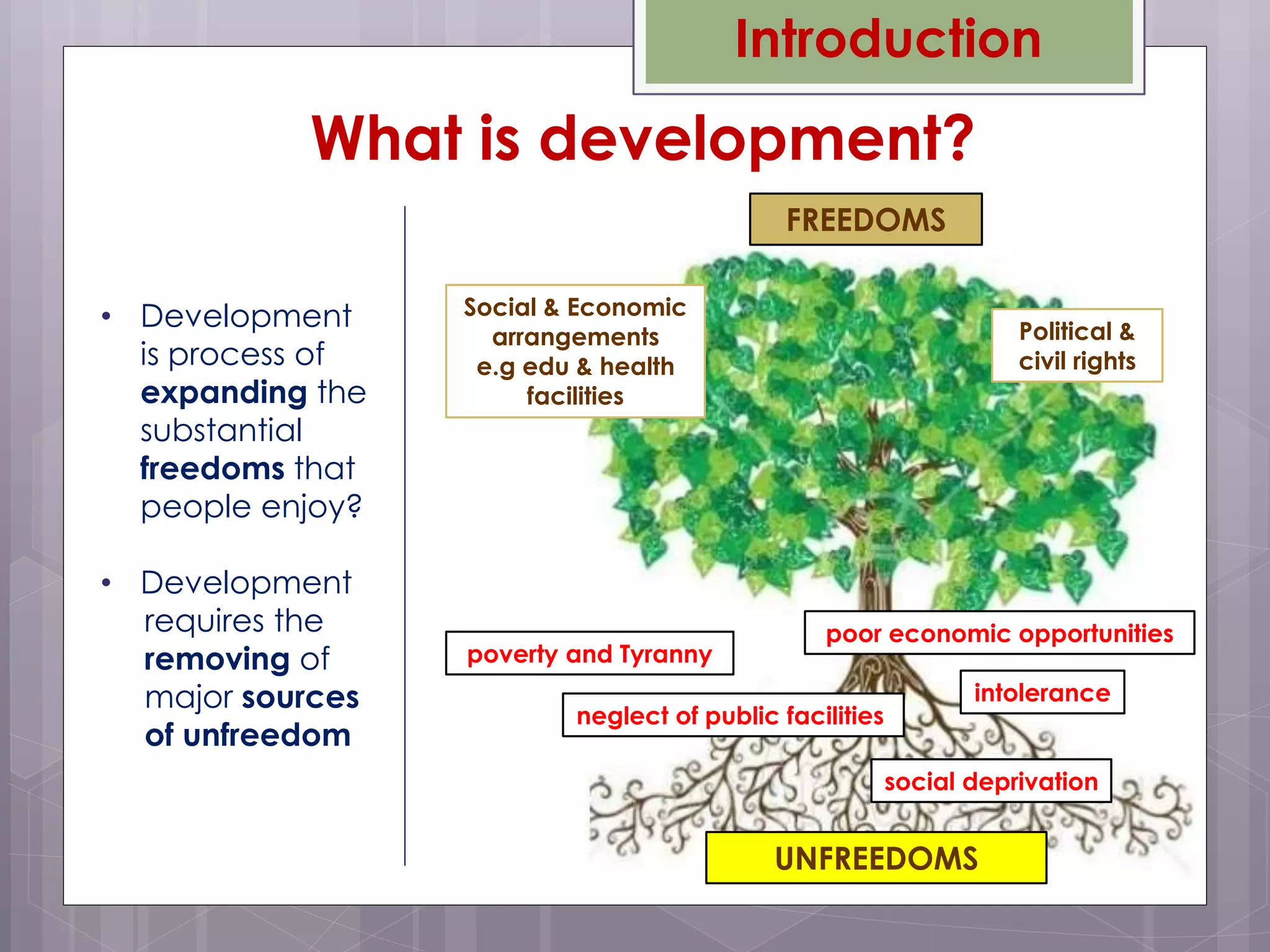
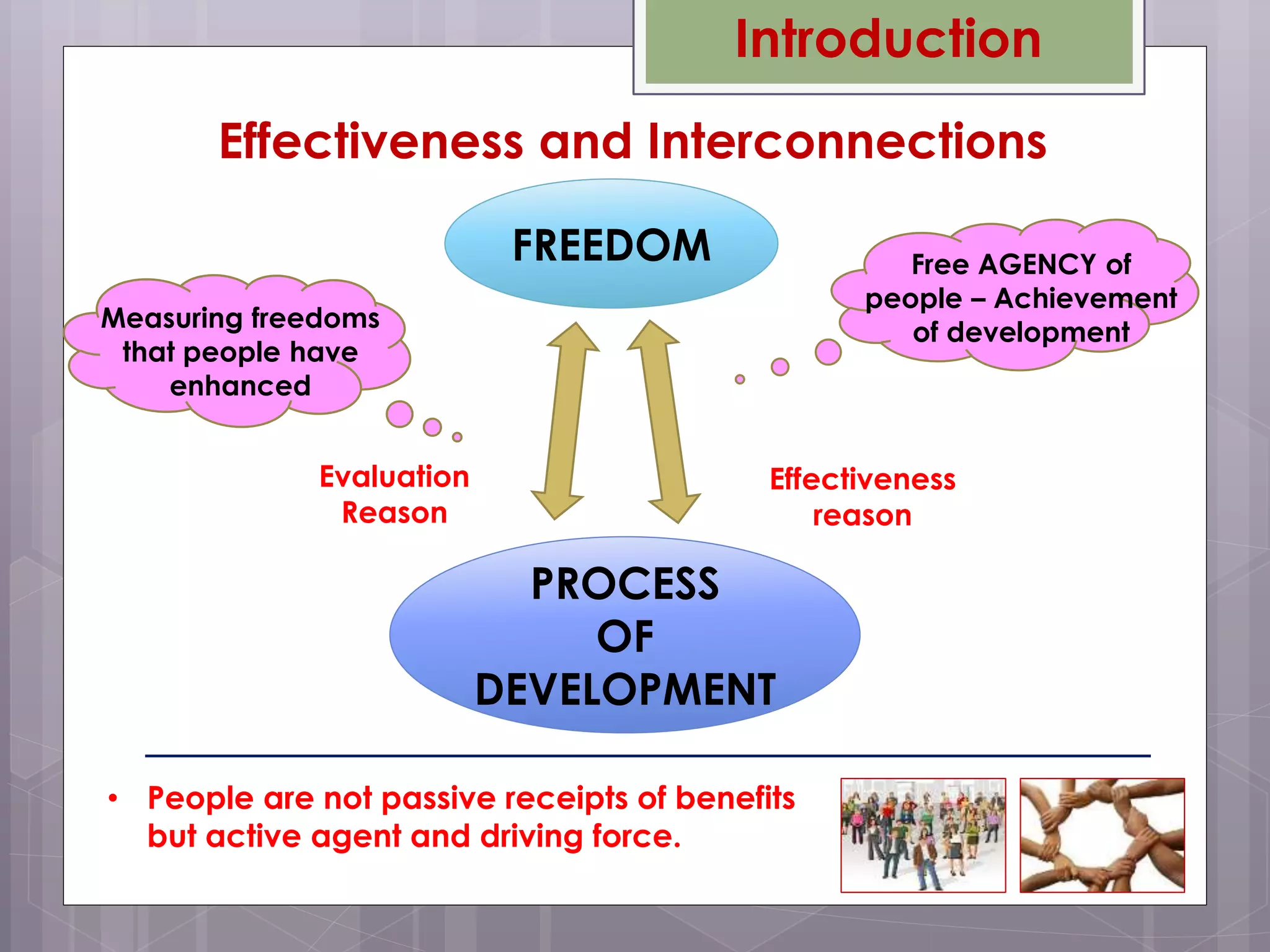
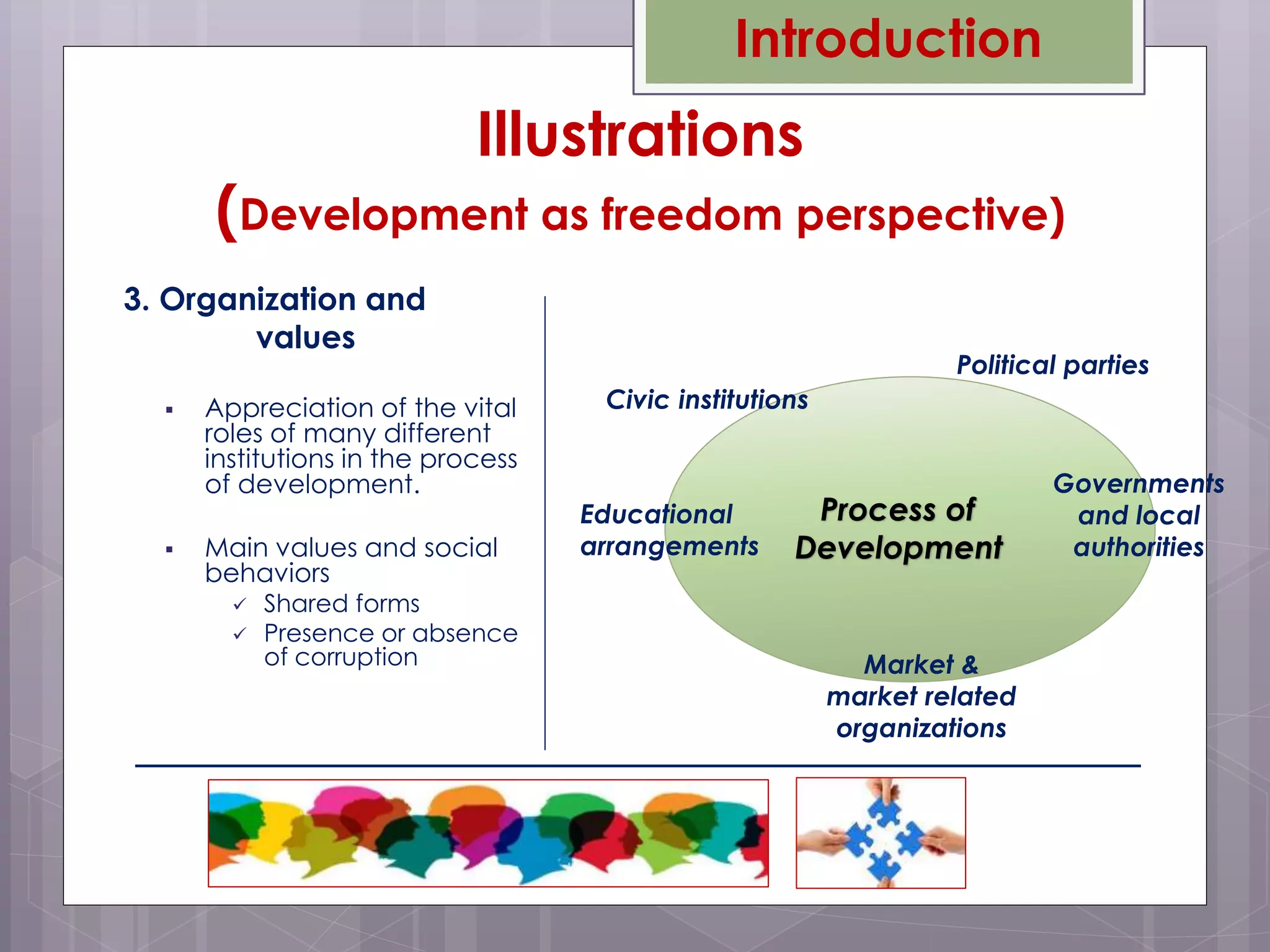
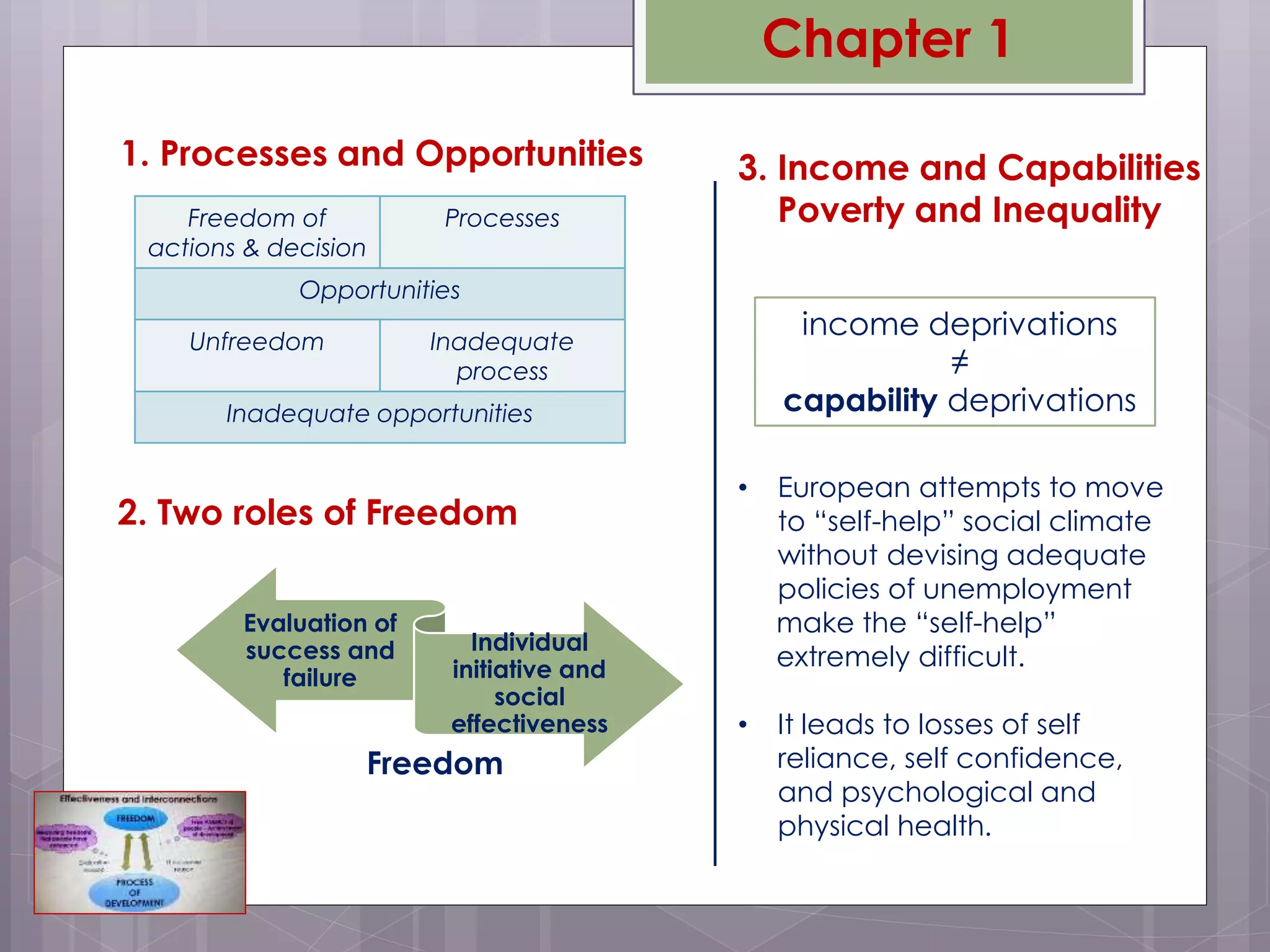
Amartya Sen's 1999 book "Development as Freedom" argues that development should be understood as expanding the freedoms and capabilities of individuals. Sen defines freedom as both the processes that allow freedom of actions and decisions, as well as the opportunities available to individuals. True development requires removing major sources of unfreedom like poverty, tyranny, and lack of economic opportunity. Sen discusses five types of instrumental freedoms - political freedoms, economic facilities, social opportunities, transparency guarantees, and protective security - that interact and can strengthen one another in the development process.