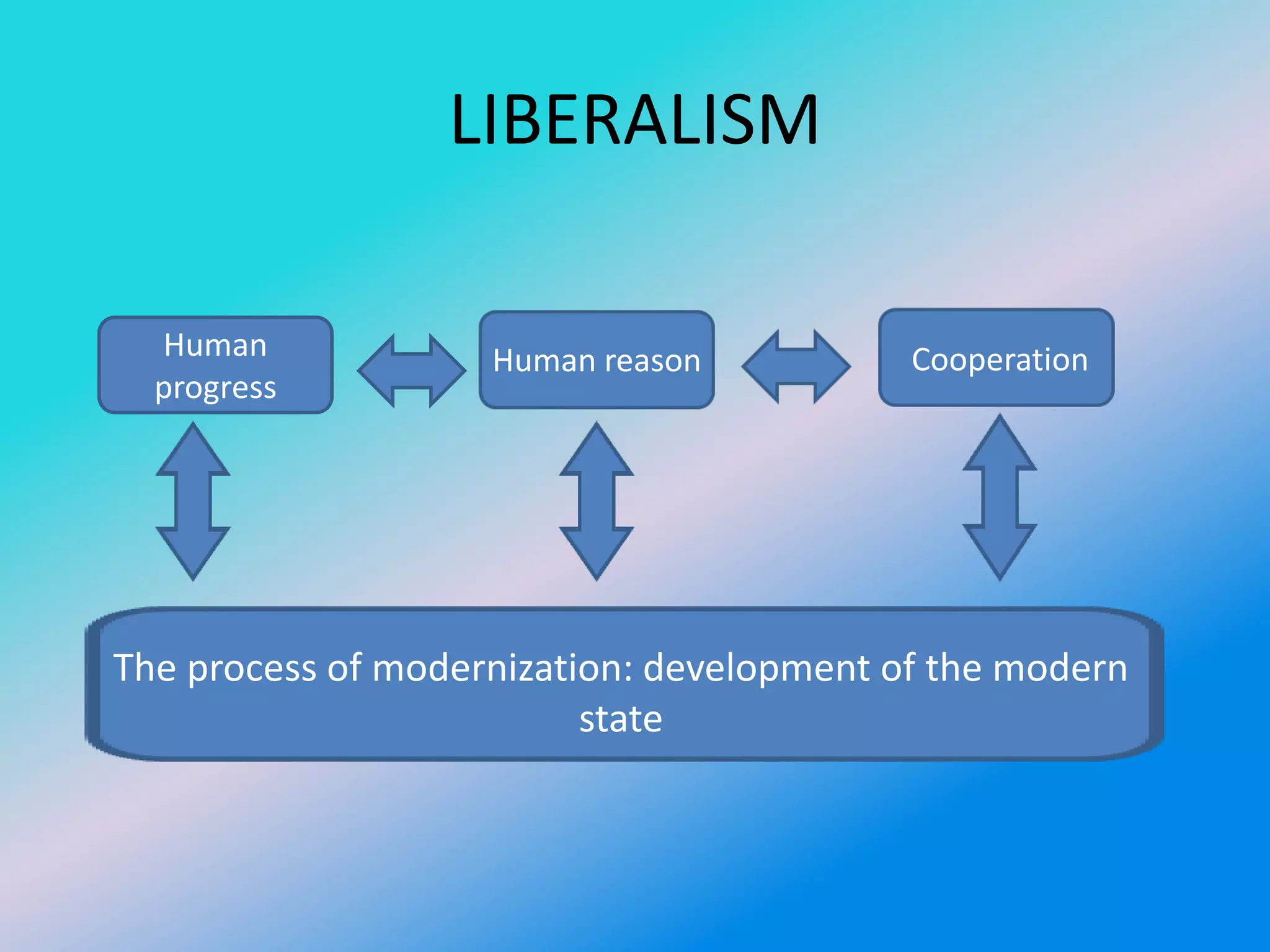
Liberalism is a political philosophy founded on ideas of liberty and equality. It emphasizes individual freedom and sees international relations as potentially cooperative rather than conflictual. Liberalism emerged with thinkers like John Locke in the 17th century who saw potential for progress in civil society, capitalism, and individual liberty guaranteed by states. The four main strands of liberal thought are institutional liberalism, which underscores organized state cooperation through institutions; interdependence liberalism, which focuses on economic interdependence reducing conflict; sociological liberalism, highlighting non-governmental ties between societies; and republican liberalism, arguing liberal democracies induce peaceful relations.