This document discusses bioinorganic chemistry and the roles of metal ions in biological systems. It begins by noting that the key elements that make up biomolecules are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur, with phosphorus playing a role in ATP and DNA and sulfur enabling cysteine coordination in proteins. Other essential elements include sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium which are involved in osmotic control, nerve action, chlorophyll, and structural functions. Trace metals like iron, cobalt, copper, zinc, and molybdenum are also required in small amounts. The document classifies the essential chemical elements into bulk elements, macrominerals and ions, and trace elements.


![4
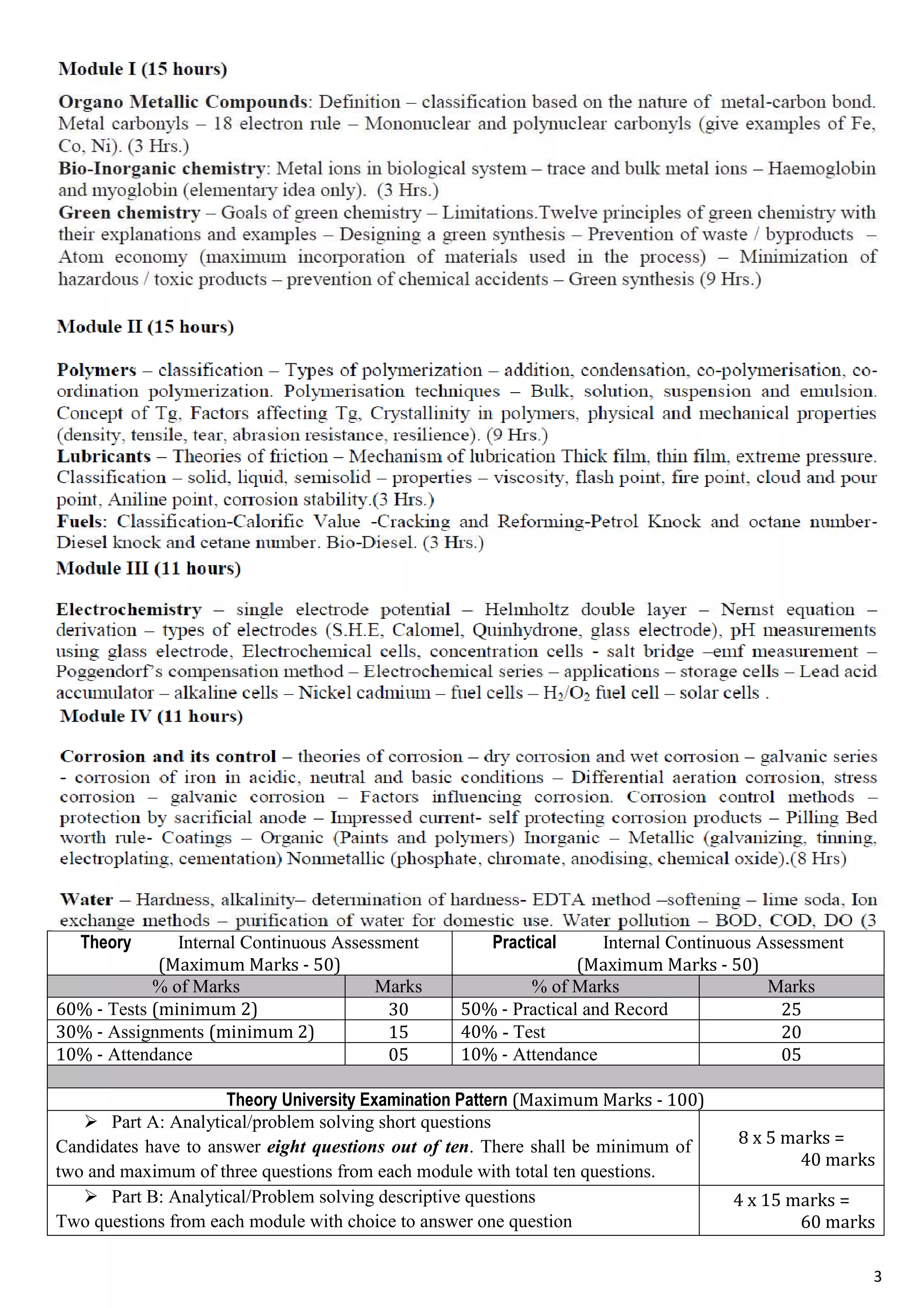
Organo Metallic CompoundsOrgano Metallic CompoundsOrgano Metallic CompoundsOrgano Metallic Compounds
Introduction
Organometallic chemistry, the chemistry of compounds containing metal-carbon bonds,
it encompasses a wide variety of chemical compounds and their reactions, including compounds
containing both σ and π bonds between metal atoms and carbon; many cluster compounds, containing
one or more metal-metal bonds. Aside from their intrinsically interesting nature, many organometallic
compounds form useful catalysts and consequently are of significant industrial interest.
Cr(CO)6 and [Ni(H2O)6]2+
example, are both octahedral. Both CO and H2O are σ donor ligands;
in addition, CO is a strong π acceptor. Other ligands that can exhibit both behaviors include CN-
, PPh3,
SCN-
, and many organic ligands. Cyclic organic ligands containing delocalized π systems can team up
with metal atoms to form sandwich compounds. A characteristic of metal atoms bonded to organic
ligands, especially CO, is that they often exhibit the capability to form covalent bonds to other metal
atoms to form cluster compounds. These clusters may contain only two or three metal atoms or as
many as several dozen; there is no limit to their size or variety. They may contain single, double,
triple, or quadruple bonds between the metal atoms and may in some cases have ligands that bridge
two or more of the metals.
The first organometallic compound to be reported was synthesized in 1827 by Zeise,
who obtained yellow needle-like crystals after refluxing a mixture of PtC14 and PtC12 in ethanol,
followed by addition of KC1. It is an ionic compound (Zeise's salt) of formula K[Pt(C2H4)Cl3]H2O.
In 1890, Mond reported the preparation of Ni(CO)4, a compound that became commercially useful for
the purification of nickel. Reactions between magnesium and alkyl halides, performed by Barbier in
1898 and 1899, and subsequently by Grignard led to the synthesis of alkyl magnesium complexes now
known as Grignard reagents. Kealy and Pauson reacted the Grignard reagent cyclo-CSH5MgBr with
FeC3, using anhydrous diethyl ether as the solvent. This reaction yield an orange solid of formula
(C5H5)2Fe, ferrocene. The structure of ferrocene consist of an iron atom sandwiched between two
parallel C5H5 rings.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-4-2048.jpg)
![5
Classification based on the nature of Metal-Carbon bond
The following five types of organometallic compounds can be distinguished depending
upon the nature of metal-carbon bond; [1] Ionic organometallic compounds [2] Organometallic compounds
containing metal-carbon sigma bond [3] Ylides [4] Organometallic compounds with multicentre bonds [5]
Organometallic compounds with pi bonded ligands.
[1] Ionic organometallic compounds: Most of the organometallic compounds of alkali metals fall in this
category. They have short life because of their high reactivity. Examples are Na+
(CH2=CH-CH2)-
, Na+
(CH2-
C6H5)-
, Na+
(C6H5)-
, Na+
(C5H5)-
, etc
[2] Organometallic compounds containing metal-carbon sigma bond: Metallic elements of Group II, III, IV
and V as well as transition metals form organometallic compounds in which the metal atoms are bonded to
carbon atoms by sigma bond.
OMC of Group II
Represented as R2M
OMC of Group III
Represented as R3M
OMC of Group IV
Represented as R4M
OMC of Group V
Represented as R3M
(CH3)2Hg, (CH3)2Cd,
(CH3)2Zn, (CH3)2Mg,
(CH3)3Ga, (C6H5)3Ga,
(CH3)3In,(CH3)3Tl,
(CH3)4Si, (CH3)4Ge,
(CH3)4Sn, (CH3)4Pb,
(CH3)3P, (CH3)3As,
(CH3)3Sb, (CH3)3Bi,
Organometallic compounds of transition metals: Very few examples of alkyl compounds of transition
metals are known because of their greater reactivity. But organic ligand does not contain any β hydrogen will
form stable complex, e.g., [CH3-CH2-Rh(NH3)5]. The alkynyl compounds [M-C≡C-R] are more stable than
alkyl or aryl complexes. The reason is that alkynyl group acts as σ donor as well as π acceptor. Similar
situation occurs in alkenyl compounds [M-CH=CR2]. Some other compounds are σ cyclopentadienyl
complexes containing (η1
-C5H5)M linkage.
[3] Ylides: These are the compounds in which the metal is doubly bonded with the carbon atom of the
ligand. Such compounds are formed by the main group elements as well as by the transition elements.
The example is Wittig reagent, Ph3P=CH2.
[4] Organometallic compounds with multicentre bonds: Organometallic compounds which are
loosely called electron-deficient and thus occur in polymeric forms fall under this category.
Examples are (Li-CH3)4, [Be(CH3)2]n, [Al(CH3)3]2, etc. These compounds are considered as intermediate
between ionic organometallic compounds of alkali metals and σ bonded organometallic compounds of Si, Sn,
Pb, etc. Elements which have highest tendency to form this complex are Li, Be, Mg, B and Al.
[5] Organometallic compounds with pi bonded ligands: This category includes organometallic compounds of
alkenes, alkynes and some other carbon-containing compounds having electrons in their π molecular orbitals.
Overlapping of these π orbitals with the vacant orbitals of the metal atom gives rise to an arrangement in which
the metal atom gets bound to all the carbon atoms over which the π molecular orbital of the organic ligand is
spread. The most important compound of this category is ferrocene or (bis-cyclopentadienyl)iron, represented
as (η5
-C5H5)2Fe. It is known to have a ‘sandwitch’ structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-5-2048.jpg)











![17
10. Chemical products should be designed so that at the end of their function they
do not persist in the environment and break down into innocuous degradation products:
It is extremely important that the products designed to be synthesized should be biodegradable.
They should not be persistent chemicals or persistent bio accumulators. It is now possible to place
functional groups in a molecule that will facilitate its biodegradation. Functional groups which are
susceptible to hydrolysis, photolysis or other cleavage have been used to ensure that products will be
biodegradable. It is also important that degradation products do not possess any toxicity and
detrimental effects to the environment.
11. Analytical methodologies need to be further developed to allow for real time,
in process monitoring and control prior to the formation of hazardous substances:
Methods and technologies should be developed so that the prevention or minimization of generation of
hazardous waste is achieved. It is necessary to have accurate and reliable reasons, monitors and other
analytical methodologies to assess the hazardous that may be present in the process stream.
These can prevent any accidents which may occur in chemical plants.
12. Substances and the form of a substance used in a chemical process should be chosen
so as to minimize the potential for chemical accidents, including releases, explosions and fires:
The occurrence of accidents in chemical industry must be avoided. It is well known that the incidents
in Bhopal (India) and Seveso (Italy) and many others have resulted in the loss of thousands of life.
It is possible sometimes to increase accidents potential inadvertently with a view to minimize the
generation of waste in order to prevent pollution. It has been found that in an attempt to recycle
solvents from a process (for economic reasons) increases the potential for a chemical accident or fire.
The principles of green chemistry and some examples of their applications to basic and applied
research are illustrated below:
Prevention of Waste: It is better to prevent waste than to treat or clean up waste after it is
formed. The ability of chemists to redesign chemical transformations to minimize the generation of
hazardous waste is an important first step in pollution prevention.
Maximize Atom Economy: Atom Economy is a concept that evaluates the efficiency of a
chemical transformation, and is calculated as a ratio of the total mass of atoms in the desired product
to the total mass of atoms in the reactants. Choosing transformations that incorporate most of the
starting materials into the product are more efficient and minimize waste. The examples are
[1] Diels–Alder reaction is 100%. Atom Economy reaction as all the atoms of the reactants are
incorporated in the cycloadduct. [2] Disinfection of water by chlorination. Chlorine oxidizes the
pathogens there by killing them, but at the same time forms harmful chlorinated compounds.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-17-2048.jpg)
![18
A remedy is to use another oxidant, such as O3 or supercritical water oxidation. [3] Production of allyl
alcohol CH2=CHCH2OH. Traditional route: Alkaline hydrolysis of allyl chloride, which generates the
product and hydrochloric acid as a by-product. CH2=CH-CH2-Cl + H2O → CH2=CH-CH2-OH +HCl
Greener route, to avoid chlorine: Two-step using propylene (CH2=CHCH3), acetic acid (CH3COOH)
and oxygen (O2). Step I. CH2=CH-CH3 + CH3-COOH +
ଵ
ଶ
O2 → CH2=CH-CH2-O-CO-CH3 + H2O
Step II. CH2=CH-CH2-O-CO-CH3 + H2O → CH2=CH-CH2-OH + CH3-COOH.
Added benefit: The acetic acid produced in the 2nd
reaction can be recovered and used again for the
1st
reaction, leaving no unwanted by-product.
Less Hazardous Chemical Syntheses: Synthetic methodologies should be designed to use and
generate substances that possess little or no toxicity to human health and environment.
Some toxic chemicals are replaced by safer ones for a green technology, when reagent choices exist
for a particular transformation. This principle focuses on choosing reagents that pose the least risk and
generate only benign by-products. Production of styrene (=benzene ring with CH=CH2 tail).
Traditional route: Two-step method starting with benzene, which is carcinogenic) and ethylene to
form ethylbenzene, followed by dehydrogenation to obtain styrene. Greener route: To avoid benzene,
start with xylene (cheapest source of aromatics and environmentally safer than benzene).
Another option, still under development, is to start with toluene. Phosgene, COCl2, is commonly used
as a starting material for polycarbonate. Phosgene is a highly toxic substance, and the by-products of
many of its reactions are undesirable. A superior alternative might be dimethyl carbonate
Designing Safer Chemicals for Accident Prevention: New products can be designed that are
inherently safer for the target application. Pharmaceutical products often consist of chiral molecules,
and the difference between the two forms can be a matter of life and death – for example, racemic
thalidomide when administered during pregnancy, leads to horrible birth defects in many new borns.
Evidence indicates that only one of the enantiomers has the curing effect while the other isomer is the
cause of severe defects. That is why it is vital to be able to produce the two chiral forms separately.
Catalysts that can catalyse important reactions that produce only one of the two mirror image forms
are developed. Design chemicals and their forms (solid, liquid, or gas) to minimize the chemical
accidents including explosions, fires and releases to the environment, e.g., manufacture of gold atom
nano particles used diborane (highly toxic and bursts into flame near room temperature) and cancer-
causing benzene. Now, diborane has been replaced by environmentally benign NaBH4 which also
eliminates the use of benzene. Nanoscience and nanotechnology is another important contribution to
green chemistry. Nanotechnology provides huge savings in materials by development of microscopic
and submicroscopic electronic and mechanical devices.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-18-2048.jpg)
![Atom Economy
Designing Safer Chemicals for Accident Prevention
very toxic compounds. It is this production that led to the disaster in Bophal in
Classical way of synthesis
Designing a Green Synthesis
Using “green catalyst” is that its action mimics nature in respect that all natural synthesis is
enzyme catalyzed reactions. This not only helps in designing a highly stereo specific, stereo selective
and enantio - selective product but also these reaction
Generally chloroform, DMC, carbon tetra chloride etc are used as a solvent in organic synthesis
which is not only costly but is very harmful for those who is handling them also. Among them carb
tetrachloride is worst solvent as it is highly environment destructive. In green chemistry an attempt has
been made to minimize or eliminate these effects by using water as a solvent. Not only this super
critical carbon dioxide which are obtained by ele
its critical temperature and pressure. Other super critical fluids used in green chemistry are ethane,
ethene, water, xenon etc.
A great attempt has been made to shift the usage of petroleum based produc
forms 95% of cases as a starting material for various chemicals required in tons per year.
On this basis shifting to biomass for such a vast need is the call of an hour. Researchers are now
finding new ways of converting biomass into starting material. E.g. converting D
acid using certain enzymes helps us to prepare aliphatic compounds from lactic acid.
Less Hazardous Chemical Syntheses
Polycarbonate Synthesis: Phosgene Process
[phosgene is highly toxic,
A superior alternative might be dimethyl
carbonate
Designing Safer Chemicals for Accident Prevention: The classical way of synthesis of carbaryl
It is this production that led to the disaster in Bophal in
Alternative reaction routes
Designing a Green Synthesis
Using “green catalyst” is that its action mimics nature in respect that all natural synthesis is
enzyme catalyzed reactions. This not only helps in designing a highly stereo specific, stereo selective
selective product but also these reactions takes place under ambient conditions.
Generally chloroform, DMC, carbon tetra chloride etc are used as a solvent in organic synthesis
which is not only costly but is very harmful for those who is handling them also. Among them carb
tetrachloride is worst solvent as it is highly environment destructive. In green chemistry an attempt has
been made to minimize or eliminate these effects by using water as a solvent. Not only this super
critical carbon dioxide which are obtained by elevating the temperature and pressure of the gas above
its critical temperature and pressure. Other super critical fluids used in green chemistry are ethane,
A great attempt has been made to shift the usage of petroleum based produc
forms 95% of cases as a starting material for various chemicals required in tons per year.
On this basis shifting to biomass for such a vast need is the call of an hour. Researchers are now
converting biomass into starting material. E.g. converting D
acid using certain enzymes helps us to prepare aliphatic compounds from lactic acid.
19
Less Hazardous Chemical Syntheses
Polycarbonate Synthesis: Phosgene Process
[phosgene is highly toxic, corrosive]
A superior alternative might be dimethyl
The classical way of synthesis of carbaryl involves
It is this production that led to the disaster in Bophal in India in 1984.
Alternative reaction routes
Using “green catalyst” is that its action mimics nature in respect that all natural synthesis is
enzyme catalyzed reactions. This not only helps in designing a highly stereo specific, stereo selective
s takes place under ambient conditions.
Generally chloroform, DMC, carbon tetra chloride etc are used as a solvent in organic synthesis
which is not only costly but is very harmful for those who is handling them also. Among them carbon
tetrachloride is worst solvent as it is highly environment destructive. In green chemistry an attempt has
been made to minimize or eliminate these effects by using water as a solvent. Not only this super
vating the temperature and pressure of the gas above
its critical temperature and pressure. Other super critical fluids used in green chemistry are ethane,
A great attempt has been made to shift the usage of petroleum based products which currently
forms 95% of cases as a starting material for various chemicals required in tons per year.
On this basis shifting to biomass for such a vast need is the call of an hour. Researchers are now
converting biomass into starting material. E.g. converting D-glucose into lactic
acid using certain enzymes helps us to prepare aliphatic compounds from lactic acid.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-19-2048.jpg)


![22
There are several ways of classification of polymers based on some special considerations.
The following are some of the common classifications of polymers: [1] by Source [2] by Backbone of
the chain [3] by Structure [4] by Compostion [5] by Mode of Polymerization [6] by Molecular force
Classification Based on Source: [1] Natural Polymers: These polymers are found in plants
and animals. Examples are proteins, cellulose, starch, resins and rubber.
[2] Semi-synthetic Polymers: Cellulose derivatives as cellulose acetate (rayon) and cellulose nitrate,
etc. are the usual examples of this sub category. [3] Synthetic Polymers: A variety of synthetic
polymers as plastic (polythene), synthetic fibres (nylon 6,6) and synthetic rubbers (Buna - S) are
examples of man-made polymers.
Classification Based on Backbone of the polymer chain: Organic and Inorganic Polymers:
A polymer whose backbone chain is essentially made of carbon atoms is termed as organic polymer.
The atoms attached to the side valencies of the backbone carbon atoms are, however, usually those of
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. The majority of synthetic polymers are organic. On the other hand,
generally chain backbone contains no carbon atom is called inorganic polymers. Glass and silicone
rubber are examples of it.
Classification Based on Structure of Polymers: [1] Linear Polymers: These polymers consist
of long and straight chains. The examples are high density polythen, PVC, etc. Linear polymers are
commonly relatively soft, often rubbery substances, and often likely to soften (or melt) on heating and
to dissolve in certain solvent. [2] Branched Polymers: These polymers contain linear chains having
some branches, e.g., low density polythene. [3] Cross-linked Polymers: These are usually formed from
bi-functional and tri-functional monomers and contain strong covalent bonds betweenvarious linear
polymer chains, e.g. vulcanized rubber, urea-formaldehyde resins, etc. Cross linked polymers are hard
and do not melt, soften or dissolve in most cases.
Linear Polymers Branched Polymers Cross-linked Polymers
Classification Based on Composition of Polymers: [1] Homopolymer: A polymer resulting
from the polymerization of a single monomer; a polymer consisting substantiallyof a single type of
repeating unit. [2] Copolymer: When two different types of monomers are joined in the same polymer
chain, the polymer is called a copolymer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-22-2048.jpg)

![24
Condensation Polymers: The condensation polymers are formed by repeated condensation
reaction between two different bi-functional or tri-functional monomeric units. In these polymerisation
reactions, the elimination of small molecules such as water, alcohol, hydrogen chloride, etc. take
place. The examples are terylene (dacron), nylon 6, 6, nylon 6, etc. For e.g., nylon 6, 6 is formed by
the condensation of hexamethylene diamine with adipic acid.
It is also possible, with three functional groups (or two different monomers at least one of
which is tri-functional), to have long linkage sequences in two (or three) dimensions and
such polymers are distinguished as cross linked polymers.
Classification Based on Molecular Forces: The mechanical properties of polymers
are governed by intermolecular forces, e.g., van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds,
present in the polymer. These forces also bind the polymer chains. Under this category,
the polymers are classified into the following groups on the basis of magnitude of intermolecular
forces present in them. They are (i) Elastomers (ii) Fibers (iii) Liquid resins
(iv) Plastics [(a) Thermoplastic and (b) thermosetting plastic].
Elastomers: These are rubber – like solids with elastic properties. In these elastomeric
polymers, the polymer chains are held together by the weakest intermolecular forces.
These weak binding forces permit the polymer to be stretched. A few ‘crosslinks’ are introduced in
between the chains, which help the polymer to retract to its original position after the force is released
as in vulcanised rubber. The examples are buna-S, buna-N, neoprene, etc.
Fibers: If drawn into long filament like material whose length is at least 100 times its diameter,
polymers are said to have been converted into ‘fibre’. Fibres are the thread forming solids which
possess high tensile strength and high modulus. These characteristics can be attributed to the strong
intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonding. These strong forces also lead to close packing of chains
and thus impart crystalline nature. Examples are polyamides (nylon 6, 6), polyesters (terylene), etc.
Liquid Resins: Polymers used as adhesives, potting compound sealants, etc. in a liquid form
are described liquid resins. Examples are epoxy adhesives and polysulphide sealants.
Plastics: A polymer is shaped into hard and tough utility articles by the application
of heat and pressure; it is used as a ‘plastic’. Typical examples are polystyrene, PVC
and polymethyl methacrylate. They are two types (a) thermoplastic and (b) thermosetting plastic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-24-2048.jpg)

![26
Types of PolymerizationTypes of PolymerizationTypes of PolymerizationTypes of Polymerization
There are four types of polymerisation reactions; (a) Addition or chain growth polymerisation
(b) Coordination polymerisation (c) Condensation or step growth polymerisation and
(d) Copolymerization
Addition Polymerisation: In this type of polymerisation, the molecules of the same monomer
or different monomers add together on a large scale to form a polymer. The monomers normally
employed in this type of polymerization contain a carbon-carbon double bond (unsaturated
compounds, e.g., alkenes and their derivatives) that can participate in a chain reaction.
A chain reaction consists of three stages, Initiation, Propagation and Termination.
In the Initiation step an initiator molecule is thermally decomposed or allowed to undergo a
chemical reaction to generate an "active species." This "active species," which can be
a free radical or a cation or an anion, then initiates the polymerization by adding to the monomer's
carbon-carbon double bond. The reaction occurs in such a manner that a new free radical or cation or
anion is generated. The initial monomer becomes the first repeat unit in the incipient polymer chain.
In the Propagation step, the newly generated "active species" adds to another monomer in the same
manner as in the initiation step. This procedure is repeated over and over again until the final step of
the process, termination, occurs. In the Termination step, the growing chain terminates through
reaction with another growing chain, by reaction with another species in the polymerization mixture,
or by the spontaneous decomposition of the active site. Under certain conditions, anionic can be
carried out without the termination step to generate so-called "living" polymers.
The following are several general characteristics of addition polymerization:
[1] Once initiation occurs, the polymer chain forms very quickly [2] The concentration of active
species is very low. Hence, the polymerisation mixture consists of primarily of newly-formed polymer
and unreacted monomer [3] Since the carbon-carbon double bonds in the monomers are, in effect,
converted to two single carbon-carbon bonds in the polymer, so energy is released making the
polymerization exothermic with cooling often required.
The mechanism of addition polymerisation can be divided broadly into two main classes,
free radical polymerization and ionic polymerization, although there are some others.
Ionic polymerisation was probably the earliest type to be noted, and is divided into
cationic and anionic polymerisations.
Free radical polymerization: A variety of alkenes or dienes and their derivatives are
polymerised in the presence of a free radical generating initiator (catalyst) like benzoyl peroxide,
acetyl peroxide, tert-butyl peroxide, etc. A free radical may be defined as an intermediate compound](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-26-2048.jpg)

![28
ii) Chain Propagation: Carbocation add to the C – C double bond of another monomer molecule to
from new carbocation.
iii) Chain Termination: Reaction is terminated by combination of carbocation with negative ion (or)
by loss of proton
Anionic polymerization depends on the use of anionic initiators which include reagents
capable of providing negative ions. Typical catalysts include sodium in liquid ammonia,
alkali metal alkyls, Grignard reagents and triphenylmethyl sodium [(C6H5)3C-Na].
They are effective with monomers containing electron withdrawing groups like nitrile (–CN) or
chloride (-Cl), etc. They include acrylonitrile [CH2=C(CN)], vinyl chloride [CH2=C(Cl)],
methyl methacrylate [CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3], etc.
i) Chain Initiation: Potassium amide (K+
NH2
-
) adds to C – C double bond of alkene to form stable
carbanion.
where W is electron withdrawing group
ii) Chain Propagation: Carbanion adds to the C – C double bond of another monomer molecule to
from new carbanion.
iii) Anionic polymerization has no chain termination reaction. So it is called living polymerization.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-28-2048.jpg)
![29
Coordination polymerization: It is also a subclass of addition polymerization. It usually
involve transition-metal catalysts. Here, the "active species" is a coordination complex, which initiates
the polymerization by adding to the monomer’s carbon-carbon double bond. The most important
catalyst for coordination polymerization is so-called Ziegler-Natta catalyst discovered to be effective
for alkene polymerization. Ziegler-Natta catalysts combine transition-metal compounds such as
chlorides of titanium with organometallic compounds [TiCl3 with Al(C2H5)3]. An important property
of these catalysts is that they yield stereoregular polymers when higher alkenes are polymerized,
e.g., polymerization of propene produces polypropene with high selectivity. Branching will not occur
through this mechanism since no radicals are involved; the active site of the growing chain is the
carbon atom directly bonded to the metal.
Zeigler-Nata catalysts: These are a special type of coordination catalysts, comprising two
components, which are generally referred to as the catalyst and the cocatalyst. The catalyst component
consists of chlorides of titanium (TiCl3 and TiCl4) and the cocatalysts are organometallic compound
such as triethyl aluminium (Al(C2H5)3).
Triethyl aluminium [Al(R)3] act as the electron acceptor whereas the electron donor is titanium
halides and the combination, therefore, readily forms coordination complexes (Fig. 1).
The complex formed, now acts as the active centre. The monomer is complexed with the metal ion of
the active centre in a way that the monomers attached towards the Ti—C bond (C from the
alkyl group R) in the active centre, when it forms a π complex with the Ti ion(Fig. 2).
Figure. 1 Figure. 2
The bonds between R and Ti opens up producing an electron deficient Ti and
a carbanion at R (Fig. 3). The Ti ion attracts the π electrons pair or the monomer and forms σ bond
(Fig. 4). This transition state now gives rise to the chain growth at the metal carbon bond, regenerating
the active centre (Fig. 5). Repeating the whole sequence, with the addition of second monomer
molecule, we will get the structure of the resultant chain growth as shown in Fig. 6.
Figure. 3 Figure. 4 Figure. 5 Figure. 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-29-2048.jpg)













![43
Hardness: The ability of a polymer to resist scratching, abrasion, cutting, or penetration. It is measured by its ability to
absorb energy under impact loads. It is also a measure of the wearing quality of a material and it is an indication of machinability
qualities of the polymer. Toughness: It is the amount of energy a polymer can absorb before actual fracture or failure takes place.
The ability of a polymer to withstand shock and vibrations. It is related to impact strength, i.e., resistance to shock loading.
It is the ability of a polymer to withstand both plastic and elastic deformation. Stiffness: The resistance of a polymer to elastic
deformation, i.e., a polymer which suffers slight deformation under load has a high degree of stiffness.
[1] Density: Mass per unit volume (at defined temperature). Relative Density is the mass of the
polymer with the mass of equal volume of a specific (reference) substance most often water.
Density is frequently measured as a quality control parameter. A specimen, with smooth surfaces
from crevices and dust, is weighed in air (W1) and then in freshly boiled water (W2),
then ρ୮୭୪୷୫ୣ୰ =
భ
భିమ
ρ୵ୟ୲ୣ୰
[2] Tensile Strength: The strength of a polymer is its capacity to withstand destruction under
the action of loads. It determines the ability of a polymer to withstand stress without failure.
Tensile strength or ultimate strength is the stress corresponding to the maximum load reached before
rupturing the polymer, Tensile strength or Stress =
୭୰ୡୣ ୭୰ ୟ୶୧୫୳୫ ୭ୟୢ
୰ୣୟ ୭ େ୰୭ୱୱ ୱୣୡ୲୧୭୬
[3] Abrasion Resistance: It is defined as the ability of a polymer to withstand mechanical action
(such as rubbing, scrapping, or erosion) that tends progressively to remove material from its surface.
Abrasion is closely related to frictional force, load and true area of contact. An increase in any one of
the three results in greater abrasion or wear. Abrasion process also creates oxidation on the surface
from the build up of localized high temperatures.
[4] Resilience: It is the capacity of a polymer to absorb energy elastically. When a body is loaded,
it changes its dimension, and on the removal of the load it regains its original dimensions.
In fact, the polymer behaves perfectly like a spring. So long as it remains loaded, it has stored energy
in itself. On removal of the load, the energy stored is given off exactly as in a spring when the load is
removed. Resilience gives capacity of the polymer to bear shocks and vibrations.
[5] Wear and Tear: It occurs when a steady rate of increase in the use of polymers in bearing
applications and in situations where there is sliding contact e.g. gears, piston rings, seals, cams, etc.
Wear and tear is characterized by fine particles of polymer being removed from the surface or
the polymer becomes overheated to the extent where large troughs of melted polymer are removed.
The wear and tear of polymers is extremely complex subjects which depend markedly on the nature of
the application and the properties of the material. Hence it is characterized by adhesion and
deformation which results in frictional forces that are not proportional to load but rather to speed.
The mechanism of wear and tear is complex; the relative rates may change depending on specific
circumstance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-43-2048.jpg)





![49
(4) Aniline Point: Aniline point of the lubricant oil is defined as the minimum equilibrium
solution temperature for equal volumes of aniline and lubricant oil samples. It gives an indication of
the possible deterioration of the lubricant oil in contact with rubber sealing; packing, etc.
Aromatic hydrocarbons have a tendency to dissolve natural rubber and certain types of synthetic
rubbers. Consequently, low aromatic content in the lubricant oil is desirable. A higher aniline point
means a higher percentage of paraffinic hydrocarbons and hence, a lower percentage of aromatic
hydrocarbons. Aniline point is determined by mixing mechanically equal volumes of the lubricant oil
samples and aniline in a test tube. The mixture is heated, till homogenous solution is obtained.
Then, the tube is allowed to cool at a controlled rate. The temperature at which the two phases
(the lubricant oil and aniline) separate out is recorded at the aniline point.
(5) Corrosion Stability: Corrosion stability of the lubricant oil is estimated by carrying out
corrosion test. A polished copper strip is placed in the lubricant oil for a specified time at a particular
temperature. After the stipulated time, the strip is taken out and examined for corrosion effects.
If the copper strip has tarnished, it shows that the lubricant oil contains any chemically active
substances which cause the corrosion of the copper strip. A good lubricant oil should not effect the
copper strip. To retard corrosion effects of the lubricant oil, certain inhibitors are added to them.
Commonly used inhibitors are organic compounds containing P, As, Cr, Bi or Pb.
Essential requirements or characteristics of a good lubricant are as follows:
[1] It should have a high viscosity index [2] It should have flash and fire points higher than the
operating temperature of the machine [3] It should have high oiliness [4] The cloud and pour points of
a good lubricant should always be lower than the operating temperature of the machine
[5] The volatility of the lubricating oil should be low [6] It should deposit least amount of carbon
during use [7] It should have higher aniline point [8] It should possess a higher resistance towards
oxidation and corrosion [9] It should have good detergent quality
Syllabus
Lubricants ––– Theories of friction ––– Mechanism of lubrication (thick film,
thin film and extreme pressure) ––– Classification (solid, liquid and semisolid) –––
Properties (viscosity, flash point and fire point, cloud and pour point, aniline point,
and corrosion stability)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-49-2048.jpg)
![50
Fuels
CLASSIFICATION OF FUEL
Fuels are classified as follows: [1] Primary fuels which occur in nature, e.g. coal, petroleum
and natural gas [2] Secondary fuels which are derived from the primary fuels, e.g. coke, gasoline and
coal gas. Both primary and secondary fuels may be further classified based upon their physical state as
(a) solid fuels, (b) liquid fuels and (c) gaseous fuels
CHARACTERISTICS OF A GOOD FUEL
The following are the characteristics of a good fuel: [1] A good fuel should be cheap and
readily available [2] It should have a high calorific value [3] A good fuel should have a moderate
ignition temperature. If the ignition temperature is low, the fuel can catch fire easily and the risk of fire
hazards is high. If the ignition temperature is very high, it is very difficult to ignite the fuel.
Ignition temperature is defined as the minimum temperature at which the substance ignites and bums
without further addition of external heat [4] The moisture content of the fuel should be very low
because the moisture content reduces the calorific value [5] A good fuel should have low non-
combustible matter content or ash content because the ash content reduces the calorific value or
heating value of the fuel. The disposal of ash is also a big problem and it increases the cost of
operation [6] The products of combustion should not pollute the atmosphere. Gases like CO, SO2 and
H2S are some of the harmful gases [7] Combustion should be easily controllable, i.e. combustion of
the fuel should start easily or stop when required [8] It should not undergo spontaneous combustion
[9] It should be safe, convenient and economical for storage and transport.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-50-2048.jpg)
![51
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF SOLID, LIQUID AND GASEOUS FUELS
Solid Fuels: The following are the advantages of solid fuels: [1] Solid fuels occur widely and
they are cheap [2] They can be handled and transported very easily [3] No complex mechanism is
required for their burning [4] They can be stored conveniently without any problem like explosion
[5] They have a moderate ignition temperature.
The disadvantages of solid fuels are as follows: [1] Solid fuels form a lot of ash during burning
and disposal of ash is very difficult [2] A lot of labour is required to transport solid fuels
[3] The burning process of solid fuels is not as clear as that of liquid and gaseous fuels
[4] A large space is required for storage of solid fuels and sometimes they may undergo spontaneous
ignition. [5] Since a lot of air is necessary for complete combustion of solid fuels, the thermal
efficiency is not so high.
Liquid Fuels: The advantages of liquid fuels are as follows: [1] Liquid fuels occupy less storage
space than solid fuels [2] As compared to solid fuels; they have a high calorific value
[3] They can be easily transported through pipes. 4. Liquid fuels do not yield any ash or residue during
burning [5] The burning process of liquid fuels is clear [6] The combustion is uniform and very easily
controllable [7] For complete combustion of liquid fuels, less air is required than that of the solid fuels
and hence their thermal efficiency is high [8] They can be used in IC engines, boilers and gas turbines
[9] They do not undergo spontaneous combustion.
The disadvantages of liquid fuels are as follows: [1] When the liquid fuels undergo incomplete
combustion, they give unpleasant odour [2] In comparison with solid fuels they are costly
[3] Risk of fire hazards is more in the case of inflammable and volatile liquid fuels. Thus, they should
be stored and transported more carefully [4] Some amount of liquid fuels may escape due to
evaporation during storage [5] Special type of burners and sprayers are required for effective
combustion.
Gaseous Fuels: The following are the advantages of gaseous fuels: [1] Gaseous fuels on
burning do not produce any ash or smoke [2] They can be very easily transported to any place as they
can flow through the pipes [3] They have a high calorific value and produce high temperature
[4] Burning of fuels can be controlled and the nature of flame can be easily made oxidizing or
reducing [5] Gaseous fuels can be produced by the poorest quality of solid fuels [6] Gaseous fuels can
be used in IC engines, boilers and gas turbines [7] Compared to solid and liquid fuels, they have a high
thermal efficiency.
The following are the disadvantages of gaseous fuels: [1] Since gases occupy a large volume,
they require large storage tank s[2] Gaseous fuels are highly inflammable and the Possibility of fire
hazards is very high](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-51-2048.jpg)



![55
Fixed Bed Catalytic Cracking Moving Bed Catalytic Cracking
Reforming is a process used to improve the anti-knock characteristics of a gasoline by bringing
about structural modifications in the components of gasoline either thermally or in the presence of
catalyst. The main reactions in the reforming process are as follows: [1] Dehydrogenation
[2] Hydrocracking [3] Isomerization
Dehydrogenation Hydrocracking Isomerization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-55-2048.jpg)

![57
process and thus stop the chain growth. When this leaded petrol is used as a fuel, lead and lead oxide
vapours formed may contaminate the atmosphere. To avoid this, ethylene dibromide is added along
with TEL. This ethylene dibromide reacts with Pb and PbO to give PbBr2 which will escape into the
atmosphere.
Improving the octane number of a fuel: The octane number of a fuel may be improved by the
following: [1] The addition of anti-knock compounds like TEL [2] Low octane petrol is blended with
high octane compounds like alcohol, e.g. straight· run petrol is mixed with reformed petrol,
benzol and alcohol [3] Reforming.
Diesel Oil
Diesel oil is a fraction obtained between 2S0-320°C and is a mixture of C15H32 and C18H38
hydrocarbons, Its calorific value is about 11000 kcal/kg. It is used as a diesel engine fuel.
Diesel knock: In a diesel engine, air is first drawn into the cylinder and compressed,
this compression is accompanied by a rise in temperature to about 500°C. Near the completion of the
compression stroke, oil is sprayed into the heated air; Droplets of the oil in the atomized form get
vaporized and ignited. This raises temperature as well as pressure, the piston is pushed by the
expanding gases and this constitutes a power stroke.
The combustion of a fuel in a diesel engine is not instantaneous and the interval between the
start of fuel injection and its ignition is called ignition delay and is an important quality of the diesel
fuel. This delay is due to the time taken for the vaporization of individual droplets and rising of the
vapour to its ignition temperature. Long ignition delays lead to accumulation of more vapours in the
engine and when ignited an explosion results as the combined effect of increased temperature and
pressure. This is responsible for diesel knock. In order to avoid diesel knock, the ignition delay period
should be as short as possible. The cetane number decreases in the following order: straight chain
paraffins > cycloparaffins > olefins > brandied paraffins > aromatics
The diesel fuels are graded by means of cetane rating. Cetane, i.e. n-hexadecane
[CH3(CH2)14CH3] having a very short ignition delay is given the value of 100 in the rating scale.
α-methylnaphthalene having a longer ignition delay represents zero of the scale,
The percentage of cetane in the cetane-α-methylnaphthalene mixture which has the same ignition
delay as the fuel under test is the cetane number of the fuel. High cetane number fuels eliminate diesel
knock. The cetane number of a diesel fuel may be increased by the addition of ethyl nitrite,
amyl nitrite, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-57-2048.jpg)






![64
Cell potential or emf
In a Zn-Cu voltaic cell, electrons are released at the anode and it becomes negatively charged.
The negative electrode pushes electrons through the external circuit by electrical repulsions.
The copper electrode gets positive charge due to the discharge of Cu2+
ions on it. Thus electrons from
the outer circuit are attracted into this electrode. The flow of current through the circuit is determined
by the ‘push’, of electrons at the anode and ‘attraction’ of electrons at the cathode.
These two forces constitute the ‘driving force’ or ‘electrical pressure’ that sends electrons through the
circuit. This driving force is called the electromotive force (abbreviated emf) or cell potential.
The emf of cell potential is measured in units of volts (V) and is also referred to as cell voltage.
Calculating the emf of a cell
The emf of a cell can be calculated from the half-cell potentials of the two cells
(anode and cathode) by using the following formula, ۳ܔܔ܍܋ = ۳܍܌ܗܐܜ܉܋ − ۳܍܌ܗܖ܉ = ۳܀ − ۳ۺ
where ER and EL are the reduction potentials of the right-hand and left-hand electrodes respectively.
It may be noted that absolute values of these reduction potentials cannot be determined. These are
found by connecting the half-cell with a standard hydrogen electrode whose reduction potential has
been arbitrarily fixed as zero.
Measurement of emf of a cell [Poggendorf’s compensation method]
The emf of an unknown cell can be measured with the help of a potentiometer (Fig. 4).
It consists of a wire AB which is about one metre long. The two ends of this wire are connected to a
working battery W. A standard cell C1 (i.e., a cell of known emf) is connected to the end A.
At the other end, the cell C1 is connected to a galvanometer through a key K1. The galvanometer is
then joined to a sliding contact that moves on the wire AB. The cell C2 whose emf is to be measured is
similarly connected to the key K2, the galvanometer and then the sliding contact. By using the key K1,
the cell C1 is put into the circuit and the contact is moved to and fro along AB. When no current flows
through the galvanometer, the point of contact X1 is recorded. Then by using the key K2, the cell C2 is
put into the circuit and the procedure is repeated to find the corresponding point X2. The emf of the
cell C2 is calculated by using the following equation:
Fig. 4: Measuring the emf of a cell with a potentiometer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-64-2048.jpg)
![65
Potential differences at interfaces
The transition region between two phases consists of a region of charge unbalance known as the
electric double layer [Helmholtz double layer]. As its name implies, this consists of an inner
monomolecular layer of adsorbed water molecules and ions, and an outer diffuse region that
compensates for any local charge unbalance that gradually merges into the completely random
arrangement of the bulk solution. In the case of a metal immersed in pure water, the electron fluid
within the metal causes the polar water molecules to adsorb to the surface and orient themselves so as
to create two thin planes of positive and negative charge. If the water contains dissolved ions,
some of the larger (and more polarizable) anions will loosely bond (chemisorb) to the metal, creating a
negative inner layer which is compensated by an excess of cations in the outer layer.
Electrochemistry is the study of reactions in which charged particles (ions or electrons) cross
the interface between two phases of matter, typically a metallic phase (the electrode) and a conductive
solution, or electrolyte. A process of this kind can always be represented as a chemical reaction and
is known generally as an electrode process. Electrode processes take place within the double layer and
produce a slight unbalance in the electric charges of the electrode and the solution.
Single electrode potential
An electrochemical cell consists of two half-cells. With an open-circuit, the metal electrode
in each half-cell transfers its ions into solution. Thus an individual electrode develops a potential
with respect to the solution. The potential of a single electrode in a half-cell is called the
Single electrode potential. Thus in a Daniel cell in which the electrodes are not connected externally,
the anode Zn/Zn2+
develops a negative charge and the cathode Cu/Cu2+
, a positive charge.
The amount of the charge produced on individual electrode determines its single electrode potential.
The single electrode potential of a half-cell depends on: (a) concentration of ions in solution;
(b) tendency to form ions; and (c) temperature.
Standard emf of a cell [E°]
The emf generated by an electrochemical cell is given by the symbol E. It can be measured with
the help of a potentiometer. The value of emf varies with the concentration of the reactants
and products in the cell solutions and the temperature of the cell. When the emf of a cell is determined
under standard conditions, it is called the standard emf. The standard conditions are (a) 1 M solutions
of reactants and products; and (b) temperature of 25°C. Thus standard emf may be defined as:
the emf of a cell with 1 M solutions of reactants and products in solution measured at 25°C.
Standard emf of a cell is represented by the symbol E°. With gases 1 atm pressure is a standard
condition instead of concentration. For a simple Zn-Cu voltaic cell, the standard emf, E°, is 1.10 V.
This means that the emf of the cell operated with [Cu2+
] and [Zn2+
] both at 1 M and 25°C is 1.10 V.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-65-2048.jpg)


![68
Electrochemical Series
The standard electrode potentials (reduction) of a number of electrodes are given in Table.
These values are said to be on the hydrogen scale since in these determinations, the potential of the
standard hydrogen electrode used as the reference electrode has been taken as zero. When the various
electrodes are arranged in the order of their increasing values of standard reduction potentials on the
hydrogen scale, then this arrangement is called electrochemical series.
Applications of Electrochemical Series or Electrode Potentials: The following are the
applications of electrochemical series:
[1]The standard emf of a cell can be calculated if the standard electrode potential values are
known. ۳ܔܔ܍܋
= ۳ܜܐܑ܀
− ۳ܜ܍ۺ
[2] The relative tendencies of metals to go into solution can be noted by the help of electrochemical
series. Metals on the top are more easily ionized into solution.
[3] The metal with negative reduction potential will displace hydrogen from an acid solution:
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 EZn
0 = -0.76 volt
The metal with positive reduction potential will not displace hydrogen from an acid solution.
Ag + H2SO4 → no reaction EAg
0 = +0.80 volt
[4] Metals which lie higher in the series can displace from the solution those elements which lie below
them in the series. Thus, zinc can displace copper from the solution.
[5] The anodic or more active metals in the series are more prone to corrosion. The cathodic or more
noble metals are less prone to corrosion. The galvanic series is used for this purpose.
Galvanic Series: the galvanic series is used to provide sufficient information in predicting the
corrosion behaviour in a particular set of environmental conditions. Oxidation potential measurements
of various metals and alloys have been made using the standard calomel electrode as the reference
electrode and immersing the metals and alloys in sea water. These are arranged in decreasing order of
activity and this series is known as the galvanic series. The galvanic series gives more practical
information on the relative corrosion tendencies of the metals and alloys. The speed and severity of
corrosion depends upon the difference in potential between the anodic and cathodic metals in contact.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-68-2048.jpg)


![71
Applications of the Nernst Equation
[1] Calculation of Half-cell potential: For an oxidation half-cell reaction when the metal
electrode M gives Mn+
ion, M → Mn+
+ ne-
. The Nernst equation takes the form
۳ = ۳
−
. ܂܀
۴ܖ
ܗܔ
ሾۻܖାሿ
ሾۻሿ
The concentration of solid metal [M] is equal to zero. Therefore, the Nernst equation can be written as
۳ = ۳
−
. ܂܀
۴ܖ
ܗܔሾۻܖାሿ
Substituting the values of R, F and T at 25°C, the quantity 2.303 RT/F comes to be 0.0591.
Thus the Nernst equation can be written in its simplified form as
۳ = ۳
−
. ૢ
ܖ
ܗܔሾۻܖାሿ
This is the equation for a half-cell in which oxidation occurs. In case it is a reduction reaction,
the sign of E will have to be reversed.
[2] Calculation of Cell potential: The Nernst equation is applicable to cell potentials as well. Thus,
۳ܔܔ܍܋ = ۳ܔܔ܍܋
−
. ૢ
ܖ
ܗܔ ۹
K is the equilibrium constant of the redox cell reaction.
[3] Calculation of Equilibrium constant for the cell reaction: The Nernst equation for a cell is
۳ܔܔ܍܋ = ۳ܔܔ܍܋
−
. ૢ
ܖ
ܗܔ ۹
At equilibrium, the cell reaction is balanced and the potential is zero. The Nernst equation becomes
= ۳ܔܔ܍܋
−
. ૢ
ܖ
ܗܔ ۹ , ܍܋ܖ܍ܐ ܗܔ ۹ =
۳ܖܔܔ܍܋
. ૢ
Concentration Cells
A concentration cell is an electrochemical cell which produces electrical energy by the transfer
of material from a system of higher concentration to a system of lower concentration. The difference
in concentration may be due to the difference in concentration of the electrodes or electrolytes. Based
on this, concentration cells are divided into two categories; (i) Electrode Concentration Cells and
(ii) Electrolyte Concentration Cells
Electrode Concentration Cells
In electrode concentration cells, two electrodes of the same metal with different concentrations
are dipped in the same solution of the electrolyte, e.g. amalgam concentration cells. Amalgam
electrodes are produced by mixing various proportions of any metal and mercury. Depending on the
amount of metal taken during the preparation of amalgam, the concentration of electrodes will vary.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-71-2048.jpg)

![73
Types ofTypes ofTypes ofTypes of ElectrodesElectrodesElectrodesElectrodes (S.H.E, Calomel, Quinhydrone, glass electrode)
[1] Gas electrode {Pt/H2, H+
}: It contains an inert electrode like platinum dipped in a solution
containing ions (H+
ions) to which the gas (H2 gas) is bubbled continuously.
The electrode is represented as Pt (s)/H2 (P = x atm), H+
(aq). The electrode reaction can be written as
2H+
(aq) + 2e-
→ H2 (g). The electrode potential is ۳۶/ܜ۾/۶శ = ۳۶/ܜ۾/۶శ
−
܂܀
۴ܖ
۱۶
൫۱۶శ൯
Example is Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). It consists of a platinum electrode immersed
in a 1 M solution of H+
ions maintained at 25°C. Hydrogen gas at one atmosphere enters the glass
hood and bubbles over the platinum electrode.
[2] Metal-metal insoluble salt electrode {M (s) /MX (s)/X-
(aq)}: It consists of a pure metal
[M (s)] coated by a layer of its sparingly soluble salt [MX (s)] and kept immersed in a solution
containing a common anion [X-
(aq)]. It is represented as M (s) /MX (s)/X-
(aq). The electrode reaction
can be written as MX (s) + ne-
→ M (s) + X-
(aq). Electrode potential is
۳܆/܆ۻ/ۻష = ۳܆/܆ۻ/ۻష
−
܂܀
۴ܖ
۱ۻ. ۱܆ష
۱܆ۻ
Example is Calomel electrode: The standard calomel electrode, SCE, consists of a wide glass-
tube with a narrow side-tube. It is set up as illustrated in Fig. 10. A platinum wire is dipping into
liquid mercury covered with solid mercurous chloride (Hg2Cl2, calomel). The tube is filled with a 1 M
solution of KCl (or saturated KCl solution). The side-tube containing KCl solution provides the salt
bridge which connects the electrode to any other electrode. The calomel electrode is represented as
The half-cell reaction is Hg2Cl2 + 2e-
→ 2Hg + 2Cl-
Calomel electrode Fig. 10: The calomel electrode coupled with zinc electrode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-73-2048.jpg)
![74
[3] Quinhydrone Electrode: It is a widely used secondary standard electrode.
It involves the redox reaction between quinine (Q) and hydroquinone (QH2), represented in Figure 1.
The hydroquinone half-cell consists of a platinum strip immersed in a saturated
solution of quinhydrone at a definite H+
ion concentration (buffered solution).
Quinhydrone is a molecular compound which gives equimolar amounts of quinone and hydroquinone
in solution represented in Figure 2. The potential developed is measured against a hydrogen electrode
or calomel electrode. The emf with respect to a standard hydrogen electrode is 0.2875 V at 25°C.
The electrode system may be represented in Figure 3
Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3
[4] Glass electrode: It consists of a glass tube having a thin-walled bulb at the lower end.
The bulb contains a 1M HCl solution. Sealed into the glass-tube is a silver wire coated with silver
chloride at its lower end. The lower end of this silver wire dips into the hydrochloric acid, forming
silver-silver chloride electrode. The glass electrode may be represented as
When placed in a solution, the potential of the glass electrode depends on the H+
ion
concentration of the solution. The potential develops across the glass membrane as a result of a
concentration difference of H+
ions on the two sides of the membrane. This happens much in the same
way as the emf of a concentration cell develops. A commonly used secondary standard electrode is
the so-called glass electrode. Its emf is determined by coupling with a standard calomel electrode
(SCE). The glass electrode provides one of the easiest methods for measuring the pH of a given
solution. A simple type of glass electrode is shown Fig. 11.
Fig. 11: Glass electrode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-74-2048.jpg)
![75
The pH of solutions
A knowledge of the concentration of hydrogen ions (more specifically hydronium ions) is of the
greatest importance in chemistry. Hydrogen ion concentrations are typically quite small numbers.
Therefore, chemists report the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution in terms of pH. It is defined as
the negative of the base-10 logarithm (log) of the H+
concentration. Mathematically it may be
expressed as pH = – log [H+
] where [H+
] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per litre.
Alternative and more useful forms of pH definition are:
The pH concept is very convenient for expressing hydrogen ion concentration.
It was introduced by Sorensen in 1909. It is now used as a general way of expressing other quantities
also, for example,
pH Scale: In order to express the hydrogen ion concentration or acidity of a solution, a pH
scale was evolved. The pH is defined as
The hydrogen ion concentration of different acidic solutions were determined experimentally.
These were converted to pH values using the above relations. Then these pH values were computed on
a scale taking water as the reference substance. The scale on which pH values are computed is called
the pH scale.
Thus the H+
ion and OH–
ion concentrations in pure water are both 10–7 mol l– 1 at 25°C and it
is said to be neutral. In acidic solution, however, the concentration of H+
ions must be greater than
10–7 mol l–1. Similarly in a basic solution, the concentration of OH–
ions must be greater than
10–7 mol l–1. Thus we can state:
Expressing the [H+] in terms of pH for the different solutions cited above, we get what we call
the pH scale. On this scale the values range from 0 to 14. Since pH is defined as – log [H+
] and the
hydrogen ion concentration of water is 10– 7, the pH of water is 7. All solutions having pH less than 7
are acidic and those with pH greater than 7 are basic. pH decreases with the increase of [H+
].
The lower the pH, higher is the [H+
] or acidity.
In any aqueous solution, the product of [H+
] and [OH–
] is always equal to Kw. This is so
irrespective of the solute and relative concentrations of H+
and OH–
ions. However, the value of Kw
depends on temperature. At 25°C it is 1.0 × 10– 14. Thus,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-75-2048.jpg)
![76
Determination of pH of a solution using glass electrode: A half-cell is set up with the test
solution as electrolyte. The emf of the cell depends on the concentration of H+
ions or pH of the
solution. The emf of the half-cell is determined by coupling it with another standard half-cell and
measuring the emf of the complete cell. The commonly used standard electrode is the glass electrode.
A glass electrode is immersed in the solution of unknown pH. It is coupled with a standard calomel
electrode (SCE) as shown in Figure. The emf of the complete cell can be determined experimentally.
Glass electrode
A glass electrode coupled with standard
calomel electrode for determining pH
Calomel electrode
Calculations: The potential of the glass electrode, EG, at 25°C is given by equation
The value of the potential of calomel electrode is known while Ecell can be found
experimentally. Therefore, we can find pH of a given solution if E°
G is known. It can be determined by
using a solution of known pH in the cell and measuring Ecell. This value of E°
G is constant for a
particular glass electrode and can be used for any subsequent determinations of pH of unknown
solutions with the help of equation. The potential of the cell, Ecell, cannot be measured using ordinary
potentiometer or voltmeter as the resistance of the glass membrane is very high and the current small.
Therefore, an electronic voltmeter is required which reads pH directly.
Merits and demerits of Glass electrode: A glass electrode is universally used because
[1] It is simple to operate. [2] It is not easily poisoned. [3] Its activity is not affected by strong
oxidising and reducing agents. [4] Since E°
G depends on a particular glass electrode used, it is not a
universal constant and also changes with time. Hence a glass electrode only compares pH values while
the hydrogen electrode measures pH absolutely.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-76-2048.jpg)

![78
Chemistry: As the cell is discharged zinc is oxidized and manganese dioxide is reduced:
Figure 1: Interior section of a dry cell
Drawbacks of dry cells: The following are the drawbacks of dry cells:
[1] Dry cells do not have an indefinite life period. Since the electrolyte medium is acidic,
zinc metal dissolves slowly there by reducing the life time even if it is not in use.
[2] When current is rapidly drawn from the cell, due to the building up of products on the electrodes
there is a drop in voltage.
Alkaline Battery: An alkaline battery is an improved form of the dry cell.
In this cell, the electrolyte is a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide (35-52%).
As the electrolyte in this cell is an alkali, it is called alkaline battery. The cathode is made from a
mixture of manganese dioxide and carbon. The anode mix consists of alkaline electrolyte, zinc powder
and small quantity of gelling agent (starch) to immobilize the electrolyte and suspend the zinc powder.
The alkaline cell derives power from the oxidation of zinc anode and the reduction of MnO2 cathode.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-78-2048.jpg)
![79
The emf of the cell is 1.5 volt. The advantages of this battery over a dry battery are as follows:
[1] As potassium hydroxide is used as an electrolyte, zinc does not readily dissolve.
[2] Since there is no corrosion of zinc, the life of alkaline battery will be longer.
[3] Its output capacity is high.
Secondary Batteries or Storage Batteries or Accumulators
Lead-acid Accumulator or Acid Battery: A storage cell is one which can operate both as a
voltaic cell and as an electrolytic cell. When it acts as a voltaic cell it supplies electrical energy. On
recharging it acts as an electrolytic cell.
An acid battery consists of a negative electrode of porous lead (lead sponge) as the anode and a
positive electrode of lead dioxide as the cathode. A number of such electrode pairs are immersed in an
aqueous solution of 20% sulphuric acid (specific gravity: 1.15 at 25°C) which is the electrolyte
(Figure 2).
Figure 2: Lead-acid storage cell
Discharging: The electrode reactions that occur during the discharge of the cell, i.e. when
current is drawn from the cell are as follows:
Anode Cathode
The overall cell reaction is as follows:
The PbSO4 formed gets precipitated on the cathode and in the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-79-2048.jpg)
![80
Charging: When both anode and cathode become covered with PbSO4, the cell stops its
functioning. Recharging is done by applying a voltage across the electrodes that is slightly higher than
the voltage that the battery can deliver. The net reaction during discharging is as follows:
During the discharge process the consumption of sulphuric acid is replaced by an equivalent
quantity of water and the sulphuric acid concentration decreases. On charging the reverse reaction
takes place. During the reverse reaction water is consumed and sulphuric acid is regenerated. Hence
the original strength of acid is restored. Since both of these changes are associated with variations in
the specific gravity of the acid, the extent of charge or discharge of the cell at any time can be
determined by testing the specific gravity of the acid.
Uses: The following are the uses of lead-acid storage cells: [1] Lead-acid storage cells are used
in automobiles, hospitals, telephone exchanges, etc. [2] As it is rechargeable it is used in UPS
(uninterrupted power supply) a power system which maintains current flow without even a momentary
break in the event of current failure.
Maintenance: If the lead-acid batteries are properly maintained in the following ways,
they can function for long periods: [1] Avoid over discharging of the battery. [2] Maintain the
electrolyte at the proper level by adding water (whenever required). [3] Keep the battery clean.
[4] Avoid overheating of the battery.
Nickel-Cadmium Battery or Nicad Battery: A nickel-cadmium battery is a type of alkaline
storage battery. This battery consists of a cadmium anode, nickel oxyhydroxide cathode and an
alkaline electrolyte (potassium hydroxide).
During discharge cadmium metal oxidizes to cadmium hydroxide at the anode:
By accepting the electrons, nickel oxyhydroxide [NiO(OH)] is reduced to nickel hydroxide [Ni(OH)2]
at the cathode:
The overall cell reaction is:
The emf of the cell is 1.3 volt. This is a rechargeable battery. When the discharged battery is
connected to an external voltage source, the cell reaction is reversed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-80-2048.jpg)

![82
The cell reaction is the same as combustion of hydrogen in air or oxygen. Generally a large
number of these cells are stacked together in series to make a battery called fuel cell battery
or fuel battery.
In the fuel cells, gaseous fuels used are hydrogen, alkanes and co. Among the liquid fuels
methanol, ethanol, etc. are very important. Oxygen, air, hydrogen peroxide, etc. are some of the
oxidants used.
Advantages of fuel cells: The following are the advantages of fuel cells:
[1] The energy conversion efficiency is very high (75-83%). [2] They are used as power sources in
spacecrafts. [3] The product of a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell is pure water which can be used for
drinking purpose. [4] Noise and thermal pollution are very low. [5] The maintenance cost is very low.
[6] It saves fossil fuels.
Limitations: The following are the limitations of fuel cells: [1] The cost of power from a fuel
cell is high as result of the cost of electrodes and pure hydrogen gas. [2] As the fuels used are gases,
they have to be stored in big tanks under high pressures
Solar Cells or Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells convert solar energy directly into electrical energy.
Description of solar cells: The conventional solar cells made up of p-type doped semiconductor
(i.e., silicon doped with boron) and n-type doped semiconductor (i.e., silicon doped with phosphorus)
is shown in Figure 4
Figure 4: Solar cell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-82-2048.jpg)
![83
The surface layer is made up of n-type semiconductor and it is extremely thin (~ 0.2 µm) so
that sun light can penetrate through it. The bottom layer is made up of p-type semiconductor. The
electrodes made of Ti-Ag solder are attached to both the sides to provide electrical contact. The
electrode on the top surface is in the form of a metal grid with fingers which permit sun light to pass
through. On the back side, the electrode completely covers the surface. An anti-reflection coating of
silicon oxide having a thickness of 0.1 µm is also put on the top surface.
Working: When p-type and n-type semiconductors are placed together, electrons from
n-type side diffuse across p-n junction to combine with holes present in p-type semiconductor side.
As a result positive ions (on n-type side) and negative ions (on p-type side) are created near
the junction to certain thickness. The separation of charges produces an electric field across
p-n junction which is about 0.6-0.7 volt. This potential at p-n junction prevents the charges moving
across it further.
When light strikes on the p-n junction, electron-hole pair is produced. As the potential barrier
resists the flow of charge carriers across it, they flow through the conductor/load connected externally
to produce electric current. Since the emf of a single solar cell is about 0.6 V, they are arranged into
larger groupings called arrays in solar panels.
Applications: The following are the application of solar cells: [1] Solar cells are used to
provide power supply for space satellites. [2] They are used for the distillation of water to get pure
drinking water. [3] Solar cells provide thermal energy for solar cookers, solar furnaces, etc.
[4] They provide electricity for street lighting in remote areas, and to run water pumps and radios in
desert areas. [5] Solar cells provide electric power to light houses.
Chemical sensors
A chemical sensor is a transducer which provides direct information about the chemical
composition of its environment. It can warn occupants of potentially toxic agents in air. It consists of a
physical transducer and a chemically selective layer.
Actually, it contains an array of tiny micro-hot-plates in conjunction with thin metalized films
such as tin, titanium, or zinc oxides. Both the hot plates and sensing films are incorporated into an
integrated circuit device. Sensitive films create a sensitive surface for detecting ambient chemicals.
If a specific chemical of interest is present, the resistance of the device changes. It produces a type of
“signature” for a specific chemical that can be matched up against a library of chemical signatures to
identify both the type and concentration of the gas in the ambient air. Metal-oxide semiconductors
(MOS) structures are of particular interest for chemical sensors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-83-2048.jpg)
![84
CorrosionCorrosionCorrosionCorrosion
Introduction
Metals and alloys are used as construction and fabrication materials in engineering. If the metal
or alloy structure is not properly maintained, they deteriorate slowly by the action of atmospheric
gases, moisture and other chemicals. This phenomenon of metals and alloys to undergo destruction by
the act of environment is known as corrosion.
Corrosion is defined as the gradual eating away or deterioration of a metal by chemical or
electrochemical reactions with its environment.
Due to corrosion the useful properties of a metal such as malleability, ductility and electrical
conductivity are lost. The most familiar example of corrosion is rusting of iron when exposed to
atmospheric conditions. During this, a layer of reddish scale and powder of oxide (Fe3O4) is formed
and the iron becomes weak. Another example is the formation of green film or basic carbonate
[CuCO3 + Cu(OH)2] on the surface of copper when exposed to moist air containing CO2.
It has been roughly assessed that the amount of iron wasted due to corrosion is one fourth of
world production. The direct loss due to corrosion in India amounts to Rs. 200 crore/annum while the
money spent annually in controlling corrosion is of the order of Rs. 50 crore. It is better to control
rather than to prevent corrosion, since it is impossible to eliminate corrosion.
Cause of Corrosion
In nature, most metals are found in a chemically combined state known as an ore. All the metals
except gold, platinum and silver exist in nature in the form of their oxides, carbonates, sulphides,
sulphates, etc. These combined forms of the metals represent their thermodynamically stable state (low
energy state). The metals are extracted from these ores after supplying a large amount of energy.
Metals in the uncombined condition have a higher energy and are in an unstable state. It is their natural
tendency to go back to the low energy state, i.e., combined state by recombining with the elements
present in the environment. This is the main reason for corrosion.
Effects of corrosion: The following are the effects of corrosion: [1] Lost production during a
shut down [2] Replacement of corroded equipment [3] High maintenance costs such as repainting
[4] Loss of efficiency [5] Contamination of the product.
Theories of Corrosion: [1] Direct chemical attack or Chemical or Dry corrosion
[2] Electrochemical theory or Wet corrosion [3] Differential aeration or
Concentration cell corrosion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-84-2048.jpg)
![85
Theories of CorrosionTheories of CorrosionTheories of CorrosionTheories of Corrosion
[1] Direct Chemical Attack or Chemical or Dry Corrosion
Whenever corrosion takes place by direct chemical attack by gases like' oxygen, nitrogen and
halogens, a solid film of the corrosion product is formed on the surface of the metal which protects the
metal from further corrosion. If a soluble or volatile corrosion product is formed, then the metal is
exposed to further attack. For example, chlorine and iodine attack silver generating a protective film of
silver halide on the surface. On the other hand, stannic chloride formed on tin is volatile and so
corrosion is not prevented.
Oxidation corrosion is brought about by direct action of oxygen at low or high temperatures on
metals in the absence of moisture. Alkali metals (Li, Na, K, etc.) and alkaline earth metals
(Mg, Ca, Sn, etc.) are readily oxidized at low temperatures. At high temperatures, almost all metals
except Ag, Au and Pt are oxidized. Alkali and alkaline earth metals on oxidation produce oxide
deposits of smaller volume. This results in the formation of a porous layer through which oxygen can
diffuse to bring about further attack of the metal. On the other hand, aluminium, tungsten and
molybdenum form oxide layers of greater volume than the metal from which they were produced.
These non-porous, continuous and coherent oxide films prevent the diffusion of oxygen and hence the
rate of further attack decreases with increase in the thickness of the oxide film.
The protective or non-protective nature of the oxide film is determined by a rule known as the
Pilling-Bedworth rule. The ratio of the volume of the oxide formed to the volume of the metal
consumed is called the Pilling-Bedworth rule. According to it, if the volume of the oxide layer is
greater than the volume of the metal, the oxide layer is protective and non-porous. On the other hand,
if the volume of the oxide layer formed is less than the volume of the metal, the oxide layer is non-
protective and porous.
[2] Electrochemical Theory or Wet Corrosion
According to the electrochemical theory, the corrosion of a metal in aqueous solution may be a
two-step process, one involving oxidation and another reduction. It is known that two metals having
different electrode potentials form a galvanic cell when they are immersed in a conducting solution.
The emf of the cell is given by the difference between the electrode potentials. When the electrodes are
joined by a wire, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. The oxidation reaction occurs at the
anode, i.e. at the anode the metal atoms lose their electrons to the environment and pass into the
solution in the form of positive ions. Fe → Fe2+ + 2e-. Thus, there is a tendency at the anode to
destroy the metal by dissolving it as ions. Hence corrosion always occurs at anodic areas. The
electrons released at the anode are conducted to the cathode and are responsible for various cathodic
reactions such as electroplating (deposition of metals), hydrogen evolution and oxygen absorption:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-85-2048.jpg)
![86
(i) Electroplating: The metal ions at the cathode collect the electrons and deposit on the cathode
surface. Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
(ii) Liberation of hydrogen: In an acid solution, (in the absence of oxygen) hydrogen ions
accept electrons and hydrogen gas is formed. 2H+ + 2e- → H2
In a neutral or alkaline medium, (in the absence of oxygen) hydrogen gas is liberated with the
formation of OH- ions. 2H2O + 2e- → H2 + 2OH-
(iii) Oxygen absorption: In the presence of dissolved oxygen and in an acid medium, oxygen
absorption reaction takes place. 4H+ + O2 + 4e- → 2H2O
In the presence of dissolved oxygen and in a neutral or weakly alkaline medium, OH-
ions are
formed. 2H2O + O2 + 4e- → 4OH- Thus it is clear that the essential requirements of electrochemical
corrosion are as follows: (a) Formation of anodic and cathodic areas. (b) Electrical contact between the
cathodic and anodic parts to enable the conduction of electrons. (c) An electrolyte through which the
ions can diffuse or migrate. This is usually provided by moisture.
[3] Differential Aeration or Concentration Cell Corrosion
Anodic and cathodic areas may be generated even in a perfectly homogeneous and pure metal
due to different amounts of oxygen reaching different parts of the metal which form oxygen
concentration cells. In such circumstances, those areas which are exposed to greater amount of air
become cathodic while the areas which are little exposed or not exposed to air become anodic and
suffer corrosion. Figure shows the part of a metal surface covered with dirt which is less accessible to
air than the rest of the metal.
Hence, the area covered with dirt becomes anodic and suffers corrosion. The anodic
reaction is Fe → Fe2+
+ 2e-
The most common reactions taking place at the cathode are
which is further oxidized to Fe(OH)3. Since the anodic area is small and the cathodic area is large,
corrosion is more concentrated at the anode. Thus, a small hole is formed on the surface of the metal.
This type of intense local corrosion is called pitting. Figure shows a wire fence in which the areas
where the wires cross are less accessible to air than the rest of the fence and hence corrosion takes
place at the wire crossings which are anodic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-86-2048.jpg)
![87
In a similar way, iron corrodes under drops of water or salt solution. Areas covered by droplets,
having less access of oxygen become anodic with respect to the other areas which are freely exposed
to air. Differential aeration corrosion occurs when one part of metal is exposed to a different air
concentration from the other part. This causes a difference in potential between differently aerated
areas. It is experimentally found that poor oxygenated parts are anodic. Consequently, differential
aeration of a metal causes a flow of current.
Factors influencing corrosionFactors influencing corrosionFactors influencing corrosionFactors influencing corrosion: The rate and extent of corrosion depend mainly on
(a) the nature of the metal and (b) the nature of the environment.
Nature of the Metal
[I] Position in the galvanic series: The extent of corrosion depends upon the position of the
metal in the galvanic series. Greater the oxidation potential, the greater is the rate of corrosion.
When two metals are in electrical contact, the metal higher up in the galvanic series becomes anodic
and suffers corrosion. Further, the rate and severity of corrosion depend upon the difference in their
positions in the galvanic series. The greater is the difference, the faster is the corrosion
of anodic metal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-87-2048.jpg)
![88
[2] Relative areas of the anode and cathode: The rate of corrosion is more when the area of the
cathode is larger. When the cathodic area is larger, the demand for electrons will be more,
and this results in increased rate of dissolution of metals at anodic regions.
[3] Purity of the metal: The impurities present in a metal create heterogeneity and thus galvanic
cells are set up with distinct anodic and cathodic areas in the metal. The higher the percentage of
impurity present in a metal, the faster is the rate of corrosion of the anodic metal. For instance,
impurities such as Pb and Fe in zinc lead to till formation of tiny electrochemical cells at the exposed
part of the impurity and the corrosion of zinc around the impurity takes place due to local action.
It is evident that the corrosion resistance of a metal may be improved by increasing impurity.
[4] Physical state of the metal: Metal components subjected to unevenly distributed stresses are
easily corroded. Even in a pure metal, the areas under stress tend to be anodic and suffer corrosion.
Caustic embrittlement takes place in stressed parts such as bends, joints and rivets in boilers.
[5] Nature of the oxide film: Metals such as Mg, Ca and Ba form oxides whose volume is less
than the volume of the metal. Hence, the oxide film formed will be porous, through which oxygen can
diffuse and bring about further corrosion. On the other hand, metals like AI, Cr and Ni form oxides
whose volume is greater than that of the metal and the nonporous oxide film so formed will protect the
metal from further corrosion.
[6] Solubilities of the products of corrosion: Solubility of the corrosion product formed is an
important factor in corrosion. If the corrosion product is soluble in the corroding medium, the
corrosion of the metal will proceed faster. On the other hand, if the corrosion product is insoluble, then
the protective film formed tends to suppress corrosion.
Nature of the Environment
[1] Temperature: The rate of chemical reactions and the rate of diffusion of ions increase with
temperature. Hence, corrosion increases with temperature. A passive metal may become active at a
higher temperature.
[2] Humidity: Atmospheric corrosion of iron is slow in dry air but increases rapidly in the
presence of moisture. This is due to the fact that moisture acts as the solvent for the oxygen in the air
to furnish the electrolyte essential for setting up a corrosion cell. Rusting of iron increases when the
relative humidity of air reaches from 60 to 80%.
[3] Effect of pH: The possibility of corrosion with respect to pH of the solution and the
electrode potential of the metal can be correlated with the help of a Pourbaix diagram.
The Pourbaix diagram for iron in water is shown in Figure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-88-2048.jpg)
![89
.
The diagram shows clearly the zones of corrosion, immunity and passivity.
In the diagram x is a point where pH is 7 and the electrode potential is -0.4 V.
It is present in the corrosion zone. This shows that iron rusts in water under those conditions.
This is noticed to be true in actual practice also.
From figure, it is seen that the rate of corrosion can be altered by shifting the point x into
immunity or passivity regions. The iron would be immune to corrosion if the potential is changed to
about -0.8 V and this can be achieved by applying external current. On the other hand, the corrosion
rate of iron can also be reduced by moving into the passivity region by applying positive potential. The
diagram clearly indicates that the corrosion rate can also be reduced by increasing the pH of the
solution by the addition of alkali without disturbing the potential.
[4] Nature of the electrolyte: The nature of the electrolyte also influences the rate of corrosion.
If the electrolyte consists of silicate ions, they form insoluble silicates and prevent further corrosion.
On the other hand, if chloride ions are present, they destroy the protective film and the surface is
exposed for further corrosion. If the conductance of electrolyte is more, the corrosion current is easily
conducted and hence the rate of corrosion is increased.
[5] Concentration of oxygen and formation of oxygen concentration cells:
The rate of corrosion increases with increasing supply of oxygen. The region
where oxygen concentration is lesser becomes anodic and suffers corrosion.
Corrosion often takes place under metal washers where oxygen cannot diffuse readily.
Similarly, buried pipelines and cables passing from one type of soil to another suffer corrosion due to
differential aeration, e.g. lead pipeline passing through clay and then through sand. Lead pipeline
passing through clay get corroded because it is less aerated than sand.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-89-2048.jpg)
![90
Types of Corrosion:Types of Corrosion:Types of Corrosion:Types of Corrosion: The following are the different types of corrosion:
[1] Galvanic corrosion: Galvanic corrosion is a type of electrochemical corrosion in which two
different types of metals in contact are jointly exposed to corrosive atmosphere. Here the metal with
more negative electrode potential will become the anode and goes into solution or corrode, e.g. (a)
zinc and copper metals and (b) steel pipe connected to copper plumbing. This corrosion can be
minimized by (a) avoiding galvanic couples and (b) providing an insulating material between the two
metals.
[2] Stress corrosion cracking: Corrosion of metals is also influenced by some physical
differences like internal stresses in the metals. Such differences result during manufacture, fabrication
and heat treatment. Metal components are subjected to unevenly distributed stresses during their
manufacturing process. The electrode potential thus varies from one point to another. Areas under
great stress act as the anode while areas not under stress act as the cathode. Various treatments of
metals and alloys such as cold working or quenching, bending and pressing introduce uneven stress
and lead to stress corrosion. Corrosion takes place so as to minimize the stress. Most of the time it
ends in breaking of the components into pieces. Corrosion of head and point portions of a nail
indicates that they have been acting as anode to the middle portion. Actually the head and the point
portions were put under stress during their manufacture. In the case of iron-wire hammered at the
middle, corrosion takes place at the hammered part and results in breaking of the wire into two pieces.
Caustic embrittlement takes place in stressed parts such as bends, joints and rivets in boilers.
Corrosion Control:Corrosion Control:Corrosion Control:Corrosion Control: Corrosion can be controlled by the following ways:
[1] By selection of the material: Selection of the right type of the material is the main factor for
corrosion control. Thus, noble metals are used for surgical instruments and ornaments as they are most
immune to corrosion. [2] By using pure metals: Pure metals have higher corrosion resistance. Even
minute amount of impurities may lead to severe corrosion, e.g. 0.02% iron in aluminium decreases its
corrosion resistance. [3] By alloying: Both corrosion resistance and strength of many metals can be
improved by alloying, e.g. stainless steels containing chromium produce a coherent oxide film which
protects the steel from further attack. [4] By annealing: Heat treatment like annealing helps to reduce
internal stresses and reduces corrosion. [5] By eliminating galvanic action: If two metals have to be in
contact, they should be so selected that their oxidation potentials are as near as possible. Further, the
area of the cathode metal should be smaller than that of the anode, e.g. copper nuts and bolts on large
steel plate. The corrosion can also be reduced by inserting an insulating material between the two
metals. [6] By cathodic protection: The principle involved in cathodic protection is to force the metal
behave like a cathode. Since there will not be any anodic area on the metal, corrosion does not occur.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-90-2048.jpg)
![91
There are two types of cathodic protection. (a) Sacrificial anodic protection. (b) Impressed current
cathodic protection.
(a) Sacrificial anodic protection: In this technique, a more active metal is connected to the
metal structure to be protected so that all the corrosion is concentrated at the more active metal and
thus saving the metal structure from corrosion. This method is used for the protection of sea going
vessels such as ships and boats. Sheets of zinc or magnesium are hung around the hull of the ship. Zinc
and magnesium being anodic to iron get corroded. Since they are sacrificed in the process of saving
iron (anode) they are called sacrificial anodes. The corroded sacrificial anode is replaced by a fresh
one, when consumed completely. Important applications of sacrificial anodic protection are as follows:
[i] Protection from soil corrosion of underground cables and pipelines (Figure a). [ii] Magnesium
sheets are inserted into domestic water boilers to prevent the formation of rust water (Figure b).
Sacrificial anodic protection
Figure a Figure b
(b) Impressed current cathodic protection: In this method, an impressed current is applied in
an opposite direction to nullify the corrosion current and converting the corroding metal from anode to
cathode. This can be accomplished by applying sufficient amount of direct current from a battery to an
anode buried in the soil and connected to the corroding metal structure which is to be protected.
The anode is in a backfill (composed of gypsum) so as to increase the electrical contact with the soil.
Since in this method current from an external source is impressed on the system, this is called
impressed current method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-91-2048.jpg)
![92
[8] By modifying the environment: The corrosion rate can be reduced by
modifying the environment. The environment can be modified by the following:
(a) Deaeration: The presence of increased amounts of oxygen is harmful since it increases the
corrosion rate. Deaeration aims at the removal of dissolved oxygen. Dissolved oxygen can be removed
by deaeration or by adding some chemical substances like Na2SO3 (b) Dehumidification: In this
method, moisture from air is removed by lowering the relative humidity of surrounding air. This can
be achieved by adding silica gel which can adsorb moisture preferentially on its surface.
(c) Inhibitors: In this method, some chemical substances known as inhibitors are added to the
corrosive environment in small quantities. These inhibitors substantially reduce the rate of corrosion.
(i) Anodic inhibitors: Anodic inhibitors include alkalis, molybdates, phosphates. chromates, etc.
When these inhibitors are added, they react with the ions of the anode and produce insoluble
precipitates. The so formed precipitate is adsorbed on the anode metal forming a protective film
thereby reducing corrosion. (ii) Cathodic inhibitors: In an electrochemical corrosion, the cathodic
reactions are of two types depending on the environment. In acidic solution, the cathodic reaction is
2H+ + 2e- → H2. In acidic solution; the corrosion can be controlled by slowing down the diffusion of
H+
ions through the cathode. This can be done by adding organic inhibitor like amines and pyridine.
They adsorb over the cathodic metal surface and act a protective layer. In neutral solution,
the cathodic reaction is H2O + 1/2O2 + 2e-
→ 2OH-
The formation of OH-
ions is only due to the
presence of oxygen. By elimination the oxygen from the medium, the corrosion rate can be reduced.
Oxygen can be removed by adding some reducing agents (Na2SO3) or by deaeration.
(iii) Vapour phase inhibitors: Vapour phase inhibitors (VPIs) are organic inhibitor which readily
sublime and form a protective layer on the metal surface, e.g., dicyclohexylammoniumnitrite. They are
used in the protection of machinery, sophisticated equipment, etc. which are sent by ships. The
condensed inhibitor can be easily wiped off from the metal surface.
[9] By Passivation: Passivation is a phenomenon of converting an active surface of a metal into
passive i.e. more corrosion resistant by forming a thin, non-porous and highly protective film over the
surface. When the metals like aluminium and tin are exposed to the atmosphere or to the oxidizing
environment, their surfaces rapidly get converted into oxides. The non-porous nature of these oxide
layers prevents further corrosion. In other words, the metals are passivated. Similarly, metals which
are susceptible to corrosion are made passive by alloying with one or more metals which are passive or
resist corrosion. For example, iron is rendered passive by alloying it with any of the transition metals
such as chromium, nickel and molybdenum.
[10] By applying protective coating: The surface of engineering material can be protected from
corrosion by covering it by a protective coating. This coating may be of organic or inorganic material.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-92-2048.jpg)

![94
Metallic CoatingsMetallic CoatingsMetallic CoatingsMetallic Coatings
Surface coatings made up of metals are known as metallic coatings. These coatings separate the
base metal from the corrosive environment and also function as an effective barrier for the protection
of base metals. Metallic coatings are mostly applied on iron and steel because they are cheap and
commonly used. Metallic coatings are usually imparted by the following methods.
Hot Dipping: In the process of hot dipping, the metal to be coated is dipped in the molten bath
of the coating metal and the thickness of the coating is adjusted by squeezing out the excess of the
coating metal with rollers. Such hot dip coatings are generally non-uniform. The common examples of
hot dip coatings are galvanizing and tinning.
[1] Galvanizing: The process of coating a layer of zinc on steel is called galvanizing.
The steel article is first pickled with dilute sulphuric acid to remove traces of rust, dust, etc, at 60-
90°C for about 15-20 minutes. Then this metal is dipped in a molten zinc bath maintained at 430°C.
The surface of the bath is covered with ammonium chloride flux to prevent oxide formation on the
surface of molten zinc. The coated base metal is then passed through rollers to correct the thickness of
the film. It is used to protect roofing sheets, wires, pipes, tanks, nails, screws, etc.
[2] Tinning: The coating of tin on iron is called tin plating or tinning. In tinning, the base is
first pickled with dilute sulphuric acid to remove surface impurities. Then it is passed through molten
tin covered with zinc chloride flux. The tin coated article is passed through a series of rollers
immersed in a palm oil bath to remove the excess tin. Tin-coated utensils are used for storing
foodstuffs, oils, etc. Galvanizing is preferred to tinning because tin is cathodic to iron, whereas zinc is
anodic to iron. So, if the protective layer of the tin coating has any cracks, iron will corrode. If the
protective layer of the zinc coating has any cracks, iron being cathodic does not get corroded. The
corrosion products fill up the cracks, thus preventing corrosion.
Cementation: In cementation, the base metal is heated with the coating metal in the form of
fine powder in order to promote the diffusion of the coating metal into the base metal.
The coatings obtained are of uniform thickness. The base metal is generally steel and the coating
metals used is zinc, chromium and aluminium. When the coating metal is zinc, the process is called
sherardizing. When the coating metal is chromium, the process is called chromizing. When the coating
metal is aluminium, the process is called calorizing.
[1] Sherardizing: Cementation with zinc powder is called sherardizing. The base metal is
heated with zinc dust in a metal drum maintained at a temperature of 350-370°C. The drum is closed
tightly and rotated with constant heating for two to three hours. During this process zinc gets diffused
into iron forming an alloy of Fe-Zn on the surface. Sherardized coatings are used for protecting small
steel parts such as nuts and bolts against atmospheric corrosion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-94-2048.jpg)
![95
[2] Chromizing: The base metal is heated with a powdered mixture of 55 per cent chromium
and 45 per cent alumina at a temperature of 1300-1400°C for about 3-4 hours in a closed drum.
The purpose of using alumina is to prevent the coalescing of chromium particles. The outermost
surface of the base metal is converted into a chrome alloy which protects the metal against corrosion.
This method is used to protect gas turbine blades. [3] Calorizing: Here the base metal is heated with a
powdered mixture of aluminium and alumina in a drum at a temperature of 840-930°C for 4-6 hours.
Electroplating or Electrodeposition: Electroplating is a process in which metals are deposited
or plated on base metals from solutions containing metallic ions by means of electrolysis.
The objectives of electroplating are as follows: (1) To obtain improved resistance to corrosion and
chemical attack (2) To get better appearance (3) To get increased hardness (4) To change the surface
properties of metals and non-metals. In the electroplating process, the freshly cleaned base metal
which is to receive the coat is made the cathode in a suitable electrolyte bath containing (a) a solution
of the salt of the metal 10 be electrodeposited, (b) buffer solution to control the pH, and (c) additional
reagents to enhance conductivity and to aid the formation of smooth, dense and coherent coating.
The concentration of the salt solution is maintained by the addition of the metal salt at regular intervals
or by the use of continuously dissolving anode of the metal. The plating is usually done at a high
current density. The nature of the deposit depends upon the current density, pH and the concentration
of the bath. A typical electroplating process is shown in Figure.
Organic Coatings:Organic Coatings:Organic Coatings:Organic Coatings: Organic coatings are inert organic barriers applied to the surface of
base metals for corrosion resistance and decoration. Paints, varnish, lacquers and enamels are the main
organic coatings. Paints: Paint is a viscous suspension of finely divided solid pigment in a fluid
medium which on drying yields an impermeable film having considerable hiding power.
When paint is applied to a metal surface, the thinner evaporates, while the drying oil slowly oxidizes
forming a dry pigmented film. Requirements of a good paint: A good paint should essentially have
the following: [1] A good paint should fonn a good impervious and uniform film on the metal surface.
[2] It should have a high hiding (covering) power. [3] The film should not crack on drying.
[4] A good paint should adhere well to the surface. [5] It should spread on the metal surface easily.
[6] It should give a glossy film. [7] It should be corrosion resistant. [8] A good paint should give a
stable and decent colour on the metal surface.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-95-2048.jpg)

![97
Water and Its Treatment
Rain water is almost pure (may contain some dissolved gases from the atmosphere).
Being a good solvent, when it flows on the surface of the earth, it dissolves many salts. Presence of
calcium and magnesium salts in the form of bicarbonate, chloride and sulphate [Cations are Ca2+
ion
and Mg2+
ion and Anions are HCO3
-
ion, Cl-
ion, and SO4
2-
ion] in water makes water ‘hard’.
Hard water does not give ready and permanent lather with soap. Water free from soluble salts of
calcium and magnesium is called Soft water. It gives lather with soap easily.
Hardness of Water: Hardness was originally defined as the soap consuming capacity of a
water sample. Soap is the sodium salt of higher fatty acids, e.g. sodium stearate. The sodium salt is
soluble in water, but the corresponding calcium and magnesium ions are insoluble in water.
When soap is added to soft water, it dissolves and lathers readily.
On adding soap solution to a sample of hard water which contains calcium or magnesium ions,
soap is precipitated as insoluble salts which prevent the formation of lather. This reaction causes the
loss of soap. No lather is obtained until all the ions are removed. So, large amount of soap is consumed
unnecessarily before lather is formed.
2C17H35COONa (sodium stearate) + CaCl2 → (C17H35COO)2Ca [ppt of calcium stearate] + 2NaCI
The hardness of water is of two types: (i) Temporary Hardness, and (ii) Permanent Hardness.
Temporary Hardness is due to the presence of magnesium and calcium bicarbonates
[Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg(HCO3)2]. It is also called carbonate hardness (CH). It can be removed by
Boiling. During boiling, the soluble Mg(HCO3)2 is converted into insoluble Mg(OH)2 and Ca(HCO3)2
is changed to insoluble CaCO3. These insoluble precipitates can be removed by filtration.
Filtrate thus obtained will be soft water.
MgሺHCOଷሻଶ
ୌୣୟ୲୧୬
ሱ⎯⎯⎯⎯ሮ MgሺOHሻଶ ↓ + 2COଶ ↑ and CaሺHCOଷሻଶ
ୌୣୟ୲୧୬
ሱ⎯⎯⎯⎯ሮ CaCOଷ ↑ + COଶ ↑ + HଶO
Permanent Hardness is due to the presence of soluble salts of magnesium and calcium in the
form of chlorides and sulphates in water (CaCl2, CaSO4, MgCl2 and MgSO4). Permanent hardness is
not removed by boiling. It is also called non-carbonate hardness (NCH).
Total Hardness: Temporary hardness and permanent hardness constitute the
total hardness which is also expressed as the sum of the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions.
Total Hardness = Temporary Hardness + Permanent Hardness or = [Ca2+
] + [Mg2+
]
Units of hardness: The following are the common units used in hardness measurements.
[1] Parts per million (ppm): It is defined as the number of parts by weight of CaCO3 present in million parts by weight of water. 1 ppm = 1 part of CaCO3
equivalent hardness in 106
parts of water, so 1 ppm =
ଵ ୮ୟ୰୲ ୭ ୦ୟ୰ୢ୬ୣୱୱ
ଵల ୮ୟ୰୲ୱ ୭ ୵ୟ୲ୣ୰
. Both temporary and permanent hardness is expressed in ppm as CaCO3. The choice of CaCO3
because is due to the fact that it is the most insoluble salt in water.
[2] Milligram per litre: It is defined as the number of milligrams of CaCO3 present in one litre of water.1 mg/l = 1 mg of CaCO3 equivalent hardness in one
litre of water Since weight of 1 litre of water = 1 kg = 1000 g = 1000 x 1000 mg = 106
mg so 1 mg/l = 1 mg of CaCO3 per 106
mg of water = 1 part of CaCO3 per
106
parts of water = 1 ppm. Thus, mathematically both units are equal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-97-2048.jpg)
![98
Determination of Total Hardness of Water by Complexometric Titration
[EDTA Method]: Eriochrome Black-T [EBT] is the indicator used in the determination of hardness
by complexometric titration with EDTA. Here, Eriochrome Black-T is a complex organic compound
[sodium-1-(1-hydroxy 2-naphthylato)-6-nitro-2-naphthol-4-sulphonate] and EDTA is a hexadentate
ligand [disodium salt of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid].
OH
N N
NO2
HO
SO3Na
Eriochrome Black-T [EBT]
N
H2
C
H2
CN
HOOCH2C
NaOOCH2C CH2COOH
CH2COONa
EDTA
[Disodium salt of ethylenediamine
tetraacetic acid]
Principle: Estimation of hardness by EDTA method is based on the principle that EDTA forms
metal complexes with hardness producing metal ions in water. These complexes are stable when the
pH is maintained between 8 and 10 and also the indicator becomes effective only at this pH range.
In order to maintain the pH, buffer solution (NH4Cl and NH4OH mixture) is added. The completion of
the complexation reaction is indicated by Eriochrome Black-T indicator. When this indicator is added
to the sample water it forms indicator-metal complexes of wine red colour.
Ca2+
/ Mg2+
+ EBT → [Ca2+
/ Mg2+
EBT]
from hard water Wine red coloured unstable complex
Now when this wine red-coloured solution is titrated against EDTA solution,
EBT in the unstable complex is replaced by EDTA to form a stable metal-EDTA complex and
liberates the free Eriochrome Black-T. At this point, the colour of the solution changes from wine red
to original blue colour which showing the end point of the titration.
[Ca2+
/ Mg2+
EBT] + EDTA → [Ca2+
/ Mg2+
EDTA] + free EBT
Wine red coloured Stable metal-EDTA complex Blue colour
unstable complex (Colourless)
The temporary hardness is removed by boiling and after the removal of precipitate by filtration;
the permanent hardness in the filtrate is determined by titration with EDTA as before.
Therefore, total hardness - permanent hardness - temporary hardness
Experimental procedure: A known volume of the sample of hard water (V ml) is treated with
about 10 ml of a buffer solution and 5 drops of Eriochrome Black-T indicator. This solution is then
titrated against the standard EDTA reagent (standardized such that 1 ml of the reagent corresponds to
1 mg of CaCO3). The end point is the colour change from wine red to blue.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-98-2048.jpg)






![105
Alkalinity: The alkalinity of water is due to the presence of a wide variety of salts of weak
acids such as carbonates, bicarbonates, phosphates, etc., and also due to the presence of weak and
strong bases (due to contamination with industrial wastes). The major portion of alkalinity in natural
water is caused by the presence of bicarbonates that are formed when water containing free carbon
dioxide percolates through soils containing calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate.
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2
The alkalinity of natural water may be taken as an indication of the concentration of hydroxides,
carbonates and bicarbonates.
Caustic Embrittlement: It is the phenomenon during which the boiler material becomes brittle
due to the accumulation of caustic substances. It is a very dangerous form of stress corrosion occurring
in mild steel boiler metals exposed to alkaline solution at high temperatures, resulting in the failure of
the metal. Stressed parts like bends, joints and rivets are severely affected. Boiler water usually
contains a small proportion of Na2CO3. In high pressure boilers, this breaks up to give NaOH and
makes the boiler water more alkaline: Na2CO3 + H2O → 2NaOH + CO2
This very dilute alkaline boiler water flows into the minute hair cracks and crevices by capillary
action. There the water evaporates and the concentration of caustic soda increases progressively.
The concentrated alkali dissolves iron as sodium ferroate in crevices, cracks, etc. where the metal is
stressed. This causes brittlement of boiler parts particularly stressed parts like: bends, joints and rivets
causing even failure of the boiler. Highly alkaline water may lead to caustic embrittlement.
Caustic embrittlement can be avoided (a) by using sodium phosphate as softening reagent instead of
Na2CO3 and (b) by adding tannin or lignin to boiler water which blocks the hair cracks.
Dissolved Oxygen (D.O): Oxygen is poorly soluble in water. The solubility of oxygen of air in
fresh water varies from 7.5 - 14.5 mg/Lit. Dissolved oxygen is needed for living organism
to maintain their biological process. It is an important factor in corrosion. Dissolved oxygen in water is
mainly responsible for the corrosion of a boiler. The dissolved oxygen in water attacks the boiler
material at high temperatures.
2Fe + 2H2O + O2 → 2Fe(OH)2
4Fe(OH)2 + O2 + 2H2O → 2[Fe2O3·3H2O] (rust)
Determination of Dissolved Oxygen present in a given Water Sample by Iodometric Method
(Winkler’s Method): The principle involved in the determination of dissolved oxygen is to bring about
the oxidation of potassium iodide (KI) to iodine (I2) with the dissolved oxygen present in the water
sample after adding MnSO4, KOH and KI, the basic manganic oxide formed act as an oxygen carrier
to enable the dissolved oxygen in the molecular form to take part in the reaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-105-2048.jpg)

![107
Impurities in water: The impurities present in water may be broadly classified as follows.
[1] Dissolved impurities: The dissolved impurities are mainly the carbonates, bicarbonates, chlorides
and sulphates of calcium, magnesium, iron, sodium and potassium. The presence of these salts imparts
hardness to water. The dissolved impurities also include dissolved gases like oxygen
and carbon dioxide.
[2] Suspended impurities: The following are the types of suspended impurities:
(a) Inorganic: Clay and sand (b) Organic: Oil globules, vegetable and animal matter.
The above suspended impurities impart turbidity, colour and odour to water.
[3] Colloidal impurities: They are finely-divided silica and clay, organic waste products,
complex protein amino acids, etc.
[4] Microorganisms: They are algae, fungi and bacteria.
Potable Water (water for domestic supply): Municipalities have to supply potable water,
i.e., It is a water of sufficiently high quality that it can be consumed or used without risk of immediate
or long term harm. The following are characteristics of potable water
[1] It should be sparking clear, soft, pleasant in taste, perfectly cool and odourless
[2] Its turbidity should not exceed 10 ppm [3] Its alkanity should not be high (pH = 8.0)
[4] Its dissolved solids should be less than 500 ppm [5] It should be free from objectionable minerals
such as lead, arsenic, chromium and manganese salts and also free from objectionable dissolved gases
like hydrogen sulphide [6] It should be free from disease producing micro-organisms.
Drinking water comes from two major sources: (a) Surface water such as lakes, rivers, and
reservoirs, but it requires both filtration and disinfection in order to use as drinking water.
(b) Ground water, which is pumped from wells, it is considered to be the purest source of water.
Rivers, lakes and wells are the most common sources of water used by municipalities.
The actual treatment methods depend directly on the impurities present. For removing various types of
impurities the following treatment processes are employed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-107-2048.jpg)

![109
Sterilization: The complete removal of harmful bacteria is known as sterilization.
The following sterilizers are generally used for sterilizing water.
[1] Sterilization by chlorine or bleaching powder: Chlorine is the most common sterilizing
agent in water treatment. Chlorine may be added in the form of bleaching powder or directly as a gas
or in the form of concentrated solution in water.
When bleaching powder is added to water, HOCI which acts as a powerful germicide is
produced. It is believed that HOCI reacts with bacteria and inactivate the enzymes present in the cells
of bacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the metabolic activities of microorganisms.
Since these enzymes are inactivated, microorganisms become dead.
CaOCl2 + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + Cl2; Cl2 + H2O → HCI + HOCI; HOCI + Bacteria → Bacteria are killed
[2] Sterilization by ultraviolet radiations: Ultraviolet radiations emanating from electric mercury
vapour lamp is capable of sterilizing water. This process is particularly useful for sterilizing swimming
pool water. This process is highly expensive.
[3] Sterilization by ozone: Ozone is a powerful disinfectant and is readily absorbed by water.
Ozone is highly unstable and decomposes to give nascent oxygen which is capable of destroying the
bacteria. O3 → O2 + [O]. This process is relatively expensive.
Break point chlorination
In break point chlorination a sufficient amount of chlorine is added to oxidize (a) organic matter,
(b) reducing substances (Fe2+
, H2S, etc.) and (c) free ammonia in raw water leaving behind mainly free chlorine
which destroys pathogenic bacteria. When chlorine is added to water, initially it reacts with ammonia and there
will formation of chloramines (See equations). Thus the amount of combined residual chlorine (chloramines)
increases with increasing dosage. Then the oxidation of chloramines and other impurities start and there is a
fall in combined chlorine content. Thus combined residual chlorine decreases to a minimum at which oxidation
of chloramines and other organic compounds complete. This minimum is the breaking point of chlorine (Fig)
The reason for such behaviour is due to the fact that some organic compounds which defy oxidation at
lower chlorine concentration get oxidized when the break point chlorine concentration is reached.
Since, it is these organic compounds which are generally responsible for bad taste and odour in water, it is clear
that break point chlorination eliminates bad taste and odour. Further chlorination increases the free residual
chlorine (CI2, HOCI, OCI-
). Hence, it use chlorine as a good disinfectant, the chlorine dosage has to be given
more than the break point.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-109-2048.jpg)



![113
Module IIModule IIModule IIModule II ---- PolymerPolymerPolymerPolymer
NoNoNoNo QuestionsQuestionsQuestionsQuestions MarksMarksMarksMarks
1
What are the classifications of polymers?
Give one example for addition and condensation polymers
8
2 How would you classify polymers based on source and applications? 5
3
Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic.
Give two examples of each type
5
4 Discuss the various types of polymerization with suitable examples 5
5
Distinguish between polymerization by addition and condensation
processes
5
6 Discuss the mechanism of addition polymerization 8
7 Explain free radical, cationic and anionic mechanism of polymerization 8
8 Discuss the mechanism of coordination [or Ziegler-Natta] polymerization 5
9 Briefly explain the techniques of polymerization 8
10
What is glass transition temperature? Discuss the factors affecting Tg.
What is its significance?
8
11 Write notes about crystallinity in polymers and the factors affecting it 7
Module IIModule IIModule IIModule II ---- LubricantsLubricantsLubricantsLubricants
NoNoNoNo QuestionsQuestionsQuestionsQuestions MarksMarksMarksMarks
1 What are lubricants? Discuss the classification of lubricants with examples 7
2 Explain the classification of liquid lubricants 5
3 What are lubricating oils? Give their properties and uses 5
4 Write a note on grease as a lubricant 5
5 Write a note on the term solid lubricants 5
6
Draw and explain the structure of graphite and molybdenum disulphide.
How are they used as lubricants?
7
7 Outline the mechanism of lubrication 8
8 Discuss in detail the properties of lubricants highlighting their importance 8
9
How do viscosity and viscosity index influence the selection of lubricants for
a particular purpose? 5
10
Write short notes on: (i) Solid lubricants (ii) Flash and Fire point
(iii) Aniline point (iv) Cloud and Pour point
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-113-2048.jpg)




![118
COMBINED FIRST AND SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH. (ENGINEERING)
MODEL EXAMINATION, APRIL – 2016
(2014 Scheme)
EN 14 104 Engineering Chemistry
Time: Three hours Maximum: 100 marks
Part A
Answer any eight questions
Each question carries 5 marks
I [1] Discuss the 18-electron rule with two examples
[2] What is the importance of bulk and trace metal ions in biological systems
[3] Discuss about green synthesis
[4] Write about the concept of Tg and crystallinity in polymers
[5] Write a note on the term solid lubricants
[6] What is cracking and what for it used? What are the types of cracking?
[7] What is electrochemical series? What are its applications?
[8] How pH is measured by using glass electrode?
[9] Describe the various factors influencing the corrosion
[10] Among BOD and COD, which is greater? Why?
Part B
Answer one full question from each module
Module I
II (A) (i) What are organometallic compounds? Explain the classification of
organometallic compounds with examples {8 marks}
(ii) Explain the twelve principles of green chemistry {7 marks}
Or
(B) (i) Give elementary idea about hemoglobin and myoglobin{7 marks}
(ii) What are metal carbonyls? Discuss the nature of bonding involved in it and
write examples for mononuclear and polynuclear carbonyls {8 marks}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-118-2048.jpg)

![120
COMBINED FIRST AND SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH. (ENGINEERING)
MODEL EXAMINATION, APRIL – 2016
(2014 Scheme)
EN 14 104 Engineering Chemistry
Time: Three hours Maximum: 100 marks
Part A
Answer any eight questions
Each question carries 5 marks
I [1] What are organometallic compounds? How are they classified?
[2] Write short notes on atom economy
[3] Distinguish between polymerization by addition and condensation processes
[4] Explain the classification of lubricants
[5] Write informative notes on biodiesel
[6] Differentiate between electrochemical cell and concentration cell?
[7] Explain the construction and functioning of solar cells
[8] Distinguish between chemical and electrochemical corrosion
[9] Discuss the phosphate and chromate coatings
[10] How is water softened by soda lime process?
Part B
Answer one full question from each module
Module I
II (A) (i) What are metal carbonyls? Discuss the nature of bonding involved
in it and write examples for mononuclear and polynuclear carbonyls {8 marks}
(ii) Discuss about the prevention of waste, minimization of toxic products and
prevention of chemical accidents in green chemistry {7 marks}
Or
(B) (i) Give elementary idea about hemoglobin and myoglobin{7 marks}
(ii) Explain the twelve principles of green chemistry {8 marks}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allchaptersofengineeringchemistry-151021024229-lva1-app6891/75/All-chapters-of-engineering-chemistry-120-2048.jpg)
