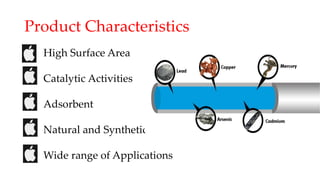
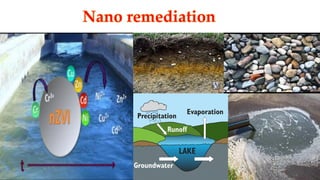
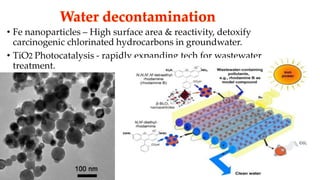
The document discusses the fundamentals and applications of nanotechnology, particularly in environmental sciences, detailing its characteristics, tools, and potential benefits for pollution remediation. It highlights various applications such as air and water pollution management, oil spill cleanup, and advancements in filtration systems using nanoparticles. The conclusion emphasizes the rapid growth of nanotechnology while noting the need for increased funding in its environmental impact research.