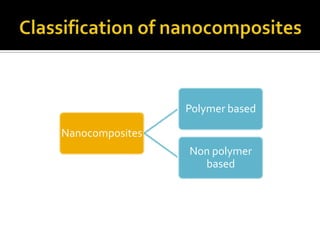
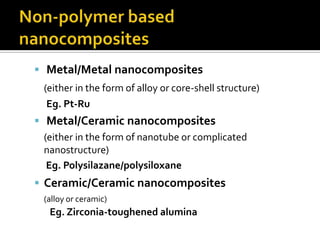
1) A nanocomposite is a multiphase solid material where one of the phases has dimensions less than 100 nm.
2) Nanocomposites consist of a continuous matrix phase and one or more discontinuous reinforcement phases distributed within the matrix.
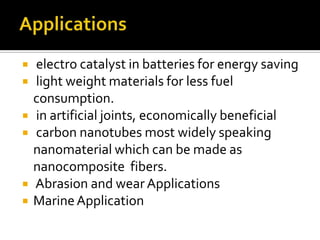
3) Polymer nanocomposites can have ceramic, metal, or polymer reinforcements and find applications in packaging, marine uses, and more due to properties like increased strength and melting temperature.