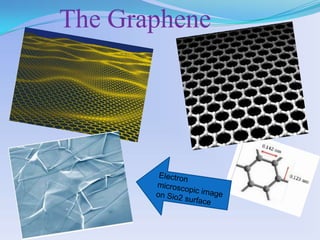
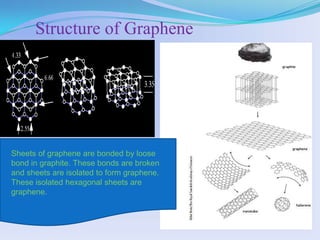
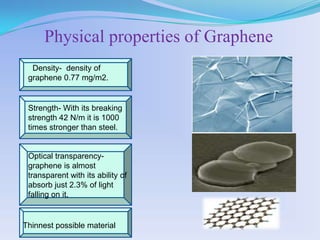
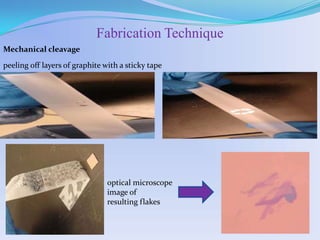
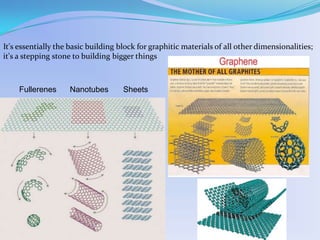
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. It is the thinnest material known and has remarkable properties such as strength, conductivity, and transparency. Graphene was first isolated in 2004 and has potential applications in electronics, solar cells, touchscreens, and more. It could replace silicon in transistors and integrated circuits due to its high electron mobility and thermal and electrical conductivity. Graphene is seen as an important material that will change electronics and enable new technologies in the future.