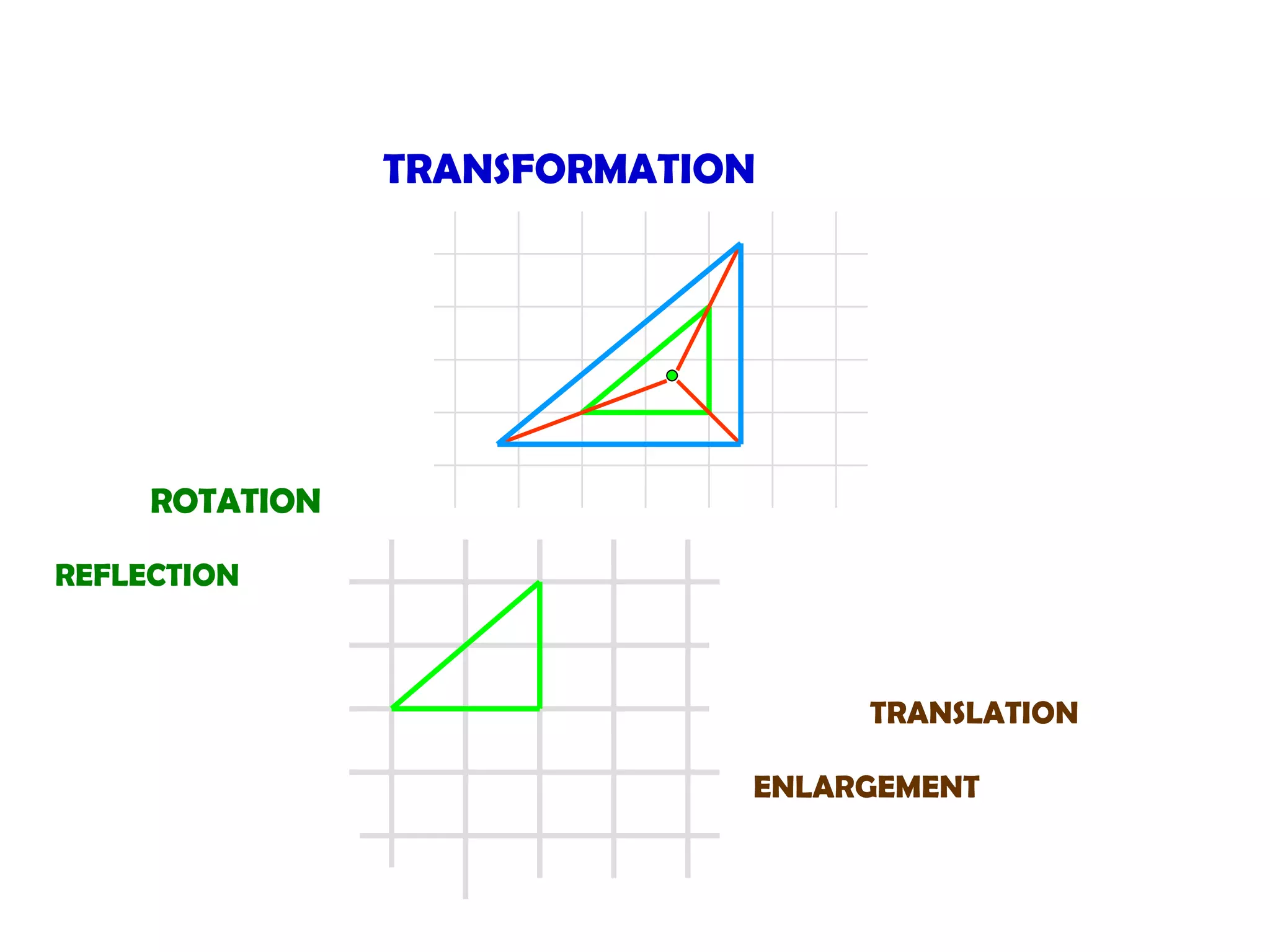
The document discusses different types of geometric transformations including:
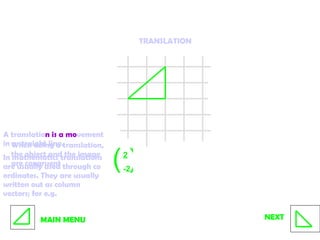
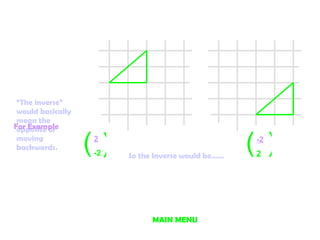
1. Translations move objects in a straight line and are written as column vectors. The inverse is the opposite movement.
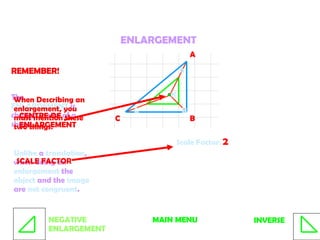
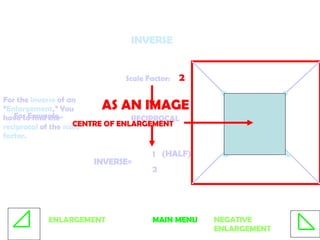
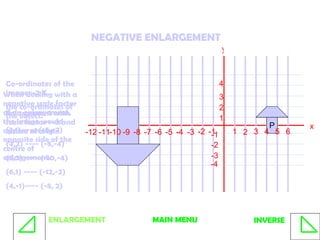
2. Enlargements change the size of shapes. The image and object are not congruent and the scale factor and center of enlargement must be specified. The inverse has a reciprocal scale factor.
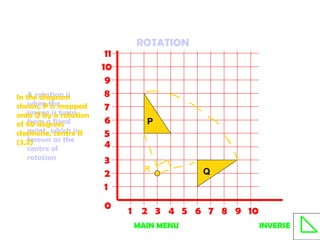
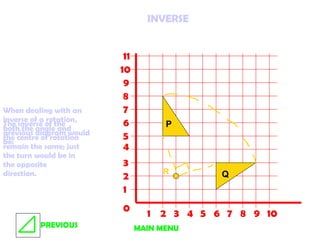
3. Rotations turn objects around a fixed point, the center of rotation. The inverse rotation is in the opposite direction.
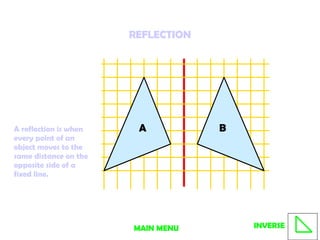
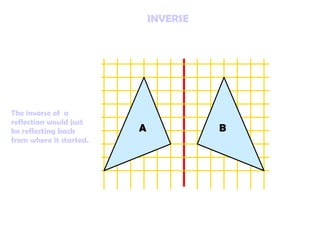
4. Reflections move points to the opposite side of a fixed line. The inverse reflects back to the original position.
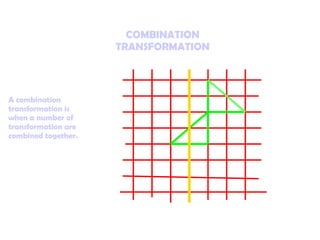
5. Combination transformations apply multiple transformations sequentially.