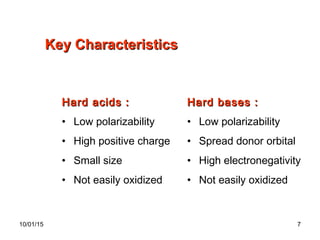
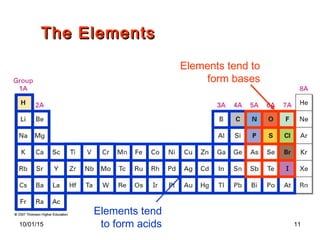
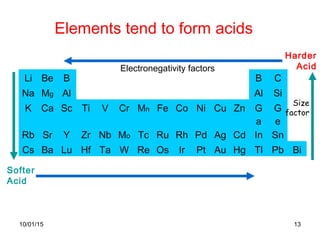
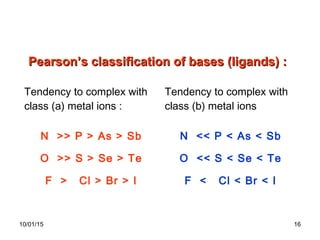
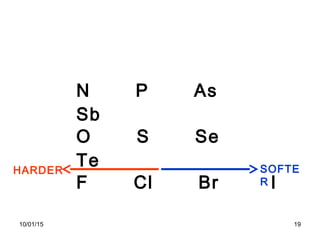
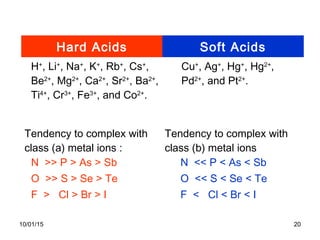
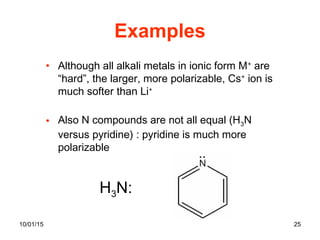
The document discusses the hard and soft acid and base (HSAB) theory introduced by Pearson in 1963. It explains that hard acids prefer to coordinate with hard bases, and soft acids prefer soft bases, due to their relative polarizabilities. Hard acids and bases are less polarizable, while soft species are more polarizable and form stronger bonds through electron sharing. The HSAB concept is used to understand stability, reactions, and reaction mechanisms based on qualitative descriptions of predominant factors like polarizability.