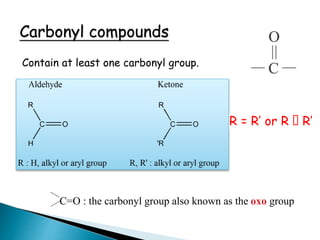
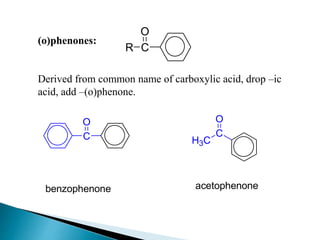
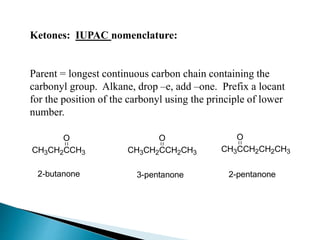
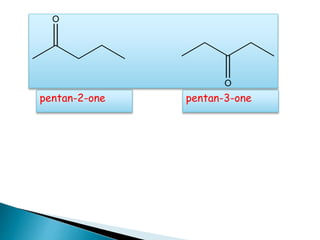
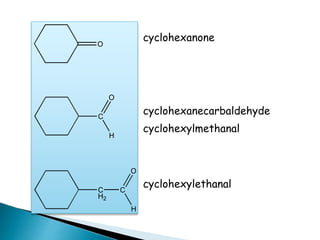
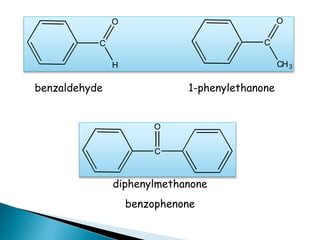
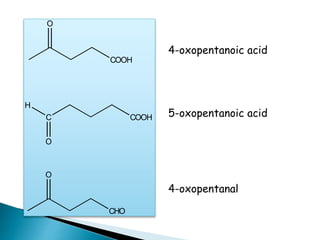
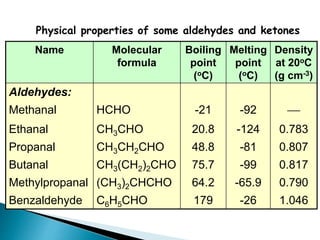
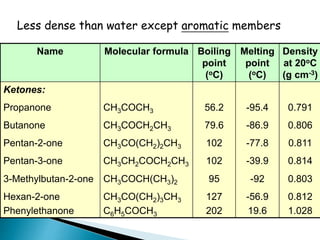
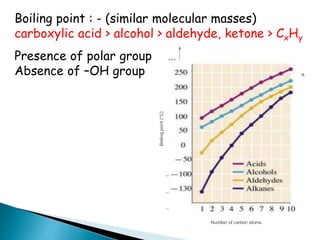
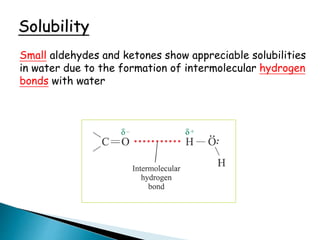
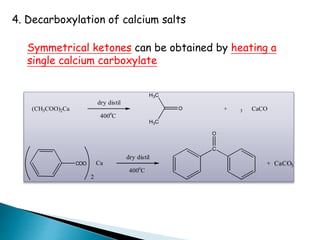
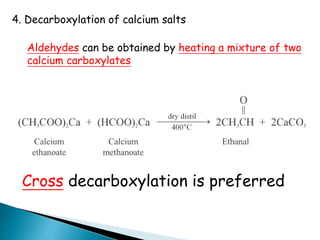
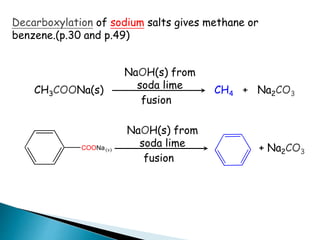
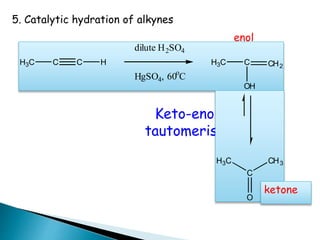
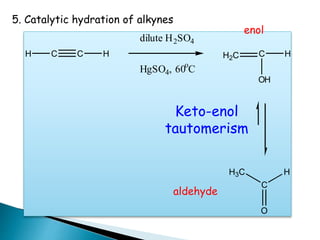
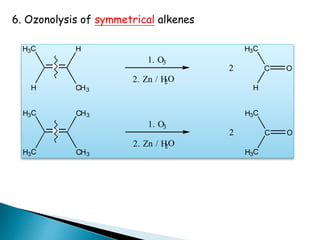
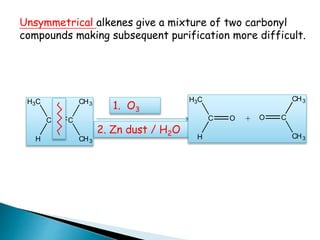
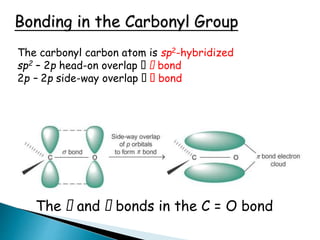
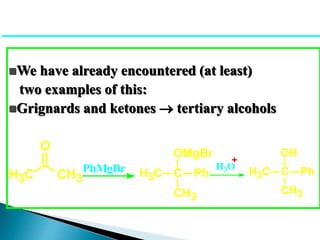
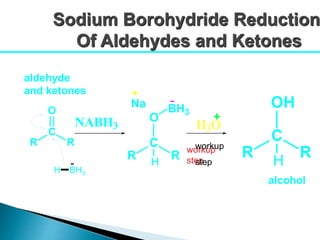
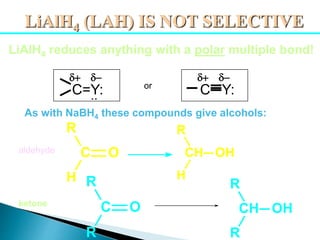
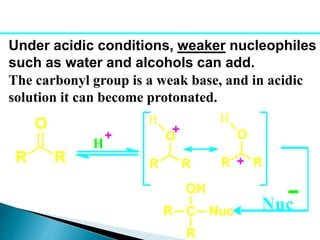
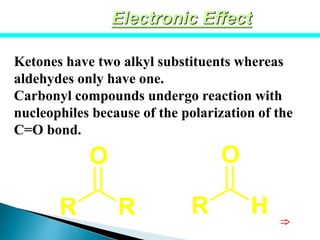
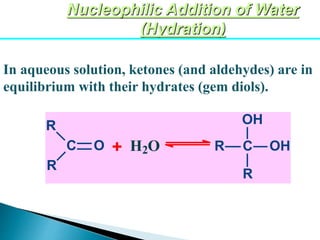
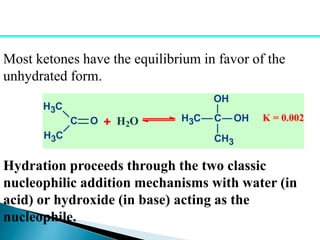
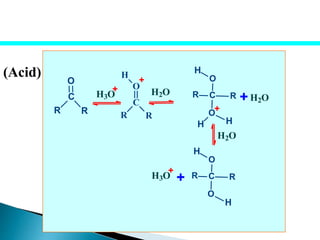
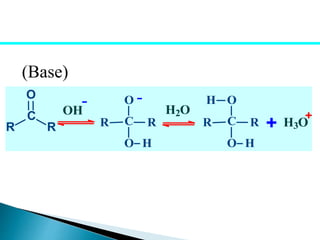
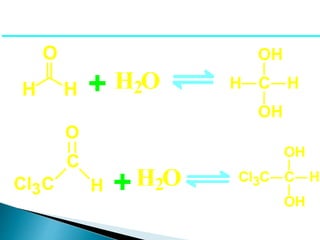
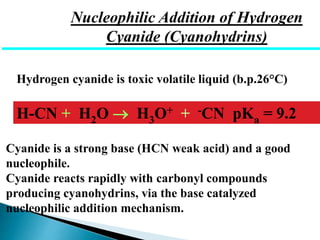
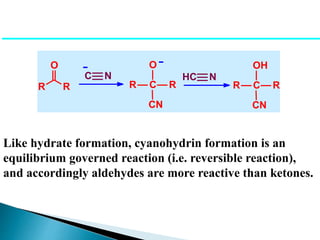
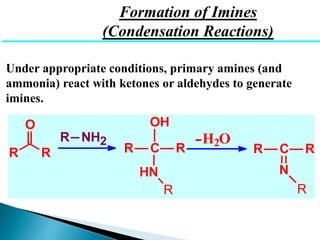
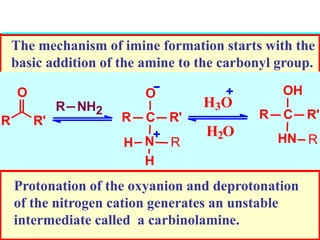
The document discusses carbonyl compounds, specifically aldehydes and ketones, including their structure, nomenclature, physical properties, and chemical reactivity. It highlights nucleophilic addition reactions, where nucleophiles attack the carbonyl carbon, leading to the formation of various derivatives like alcohols and imines. The reactivity differences between aldehydes and ketones are explained, particularly how aldehydes are generally more reactive due to lower steric hindrance and increased electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon.







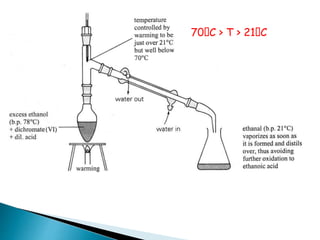
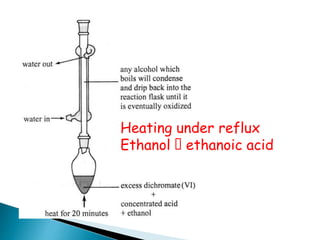
![2 alcohol ketone
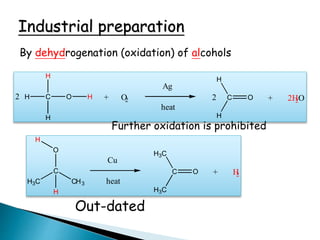
Further oxidation of ketone to carboxylic acid has not
synthetic application since
carboxylic acid
C O
H3C
H3C
[o] H3C
C O
HO
+ other products
High T
1. it requires more drastic reaction conditions
2. it results in a mixture of organic products](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l7carbonylcompoundsshort-191207164325/85/carbonyl-compounds-short-25-320.jpg)
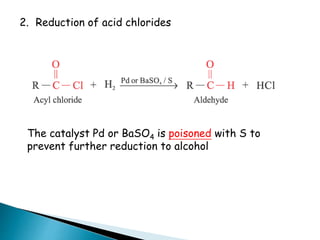














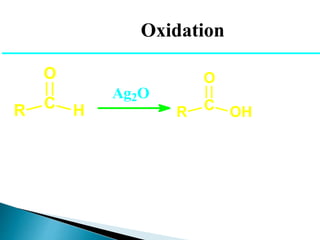
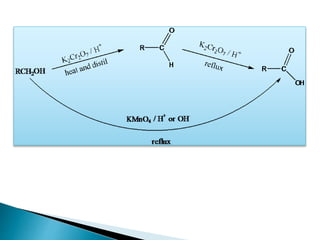
![Oxidation
•Unlike ketones, aldehydes can be oxidized easily to
carboxylic acids (Chromic acid, permanganate etc).
R C H
O
[O]
R C OH
O
Even weak oxidants like silver (I) oxide can perform this
reaction, and this is a good, mild selective way to prepare
carboxylic acids in the presence of other (oxidizable)
functionalities. E.g.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l7carbonylcompoundsshort-191207164325/85/carbonyl-compounds-short-64-320.jpg)