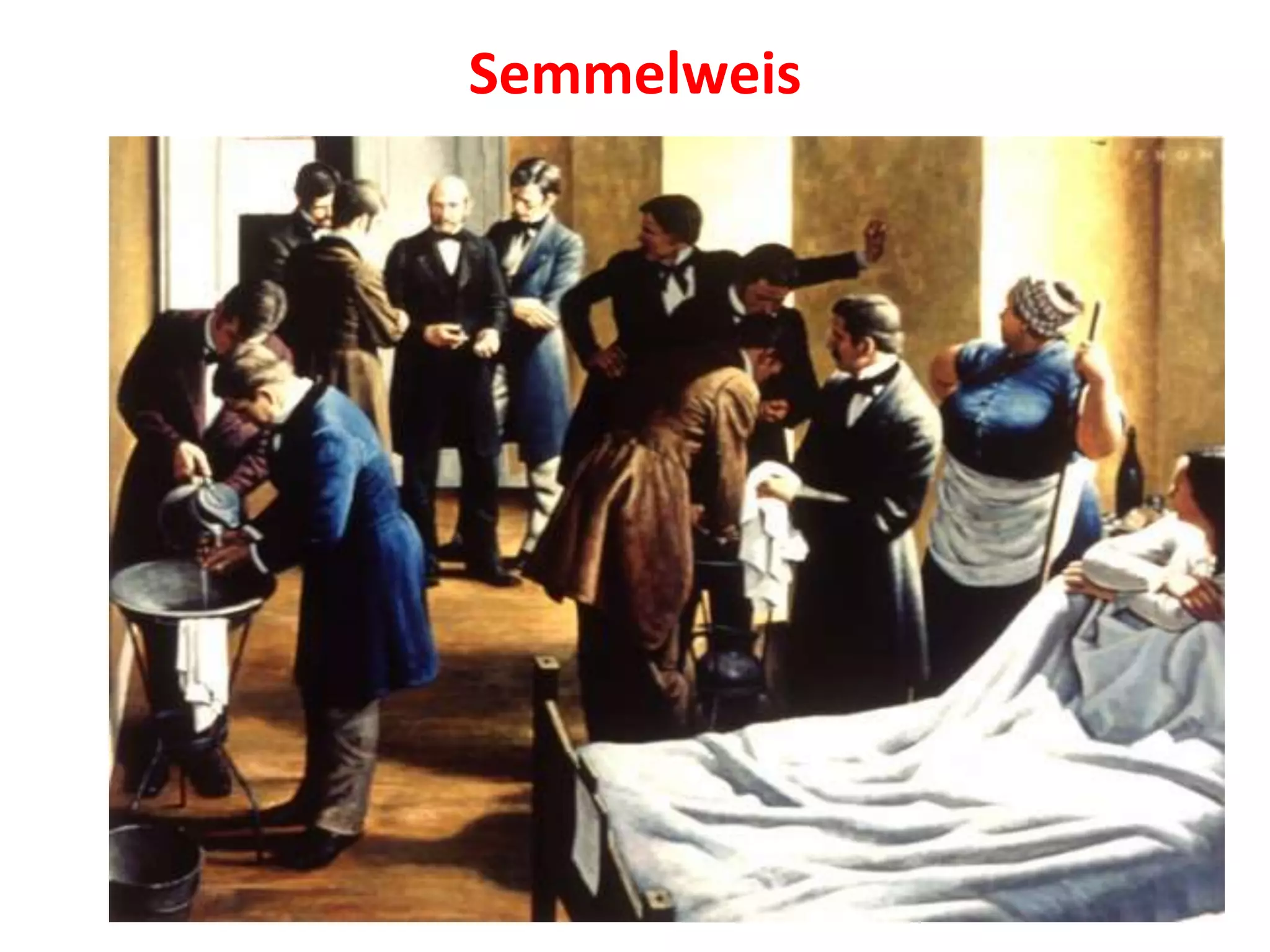
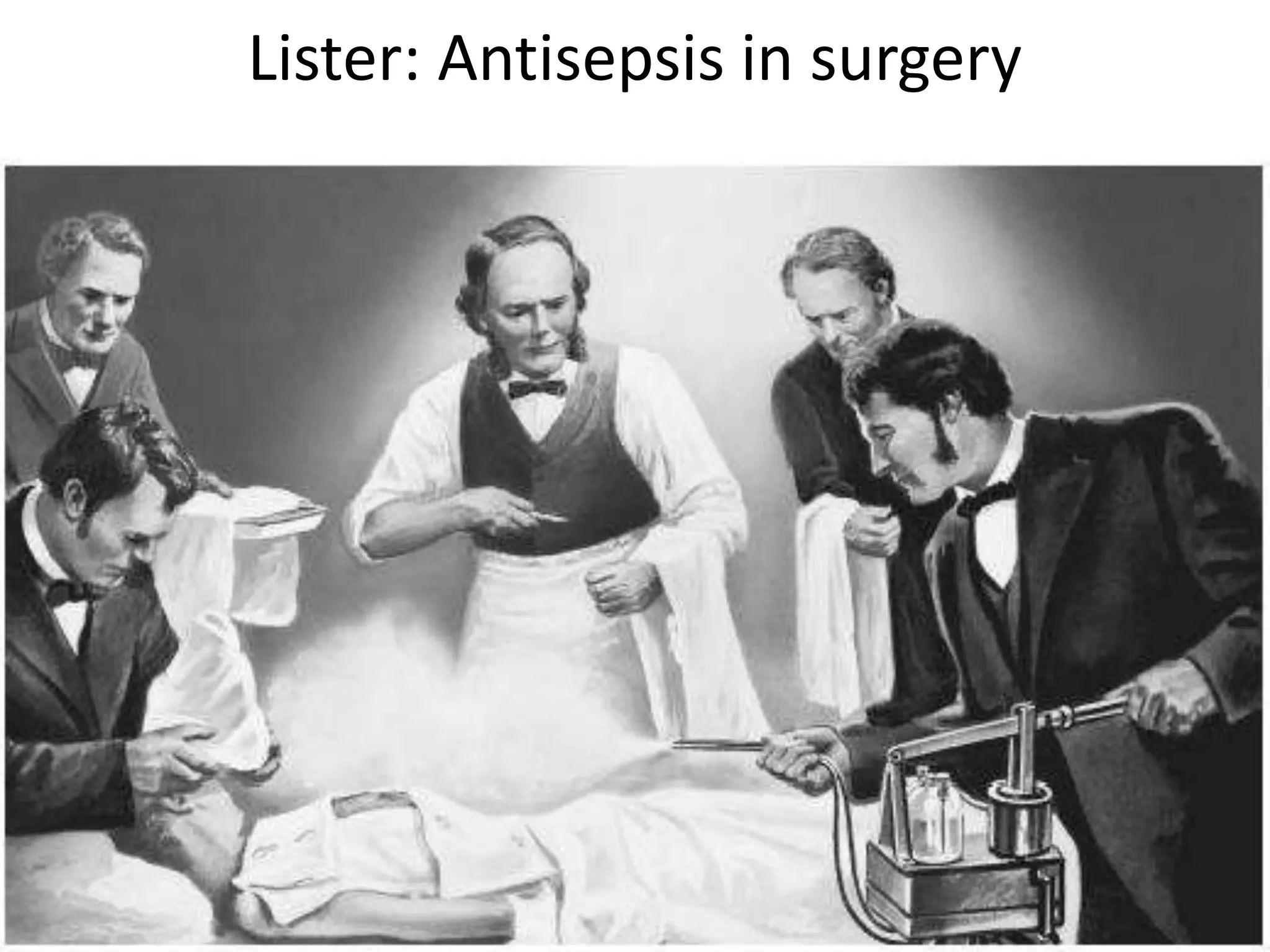
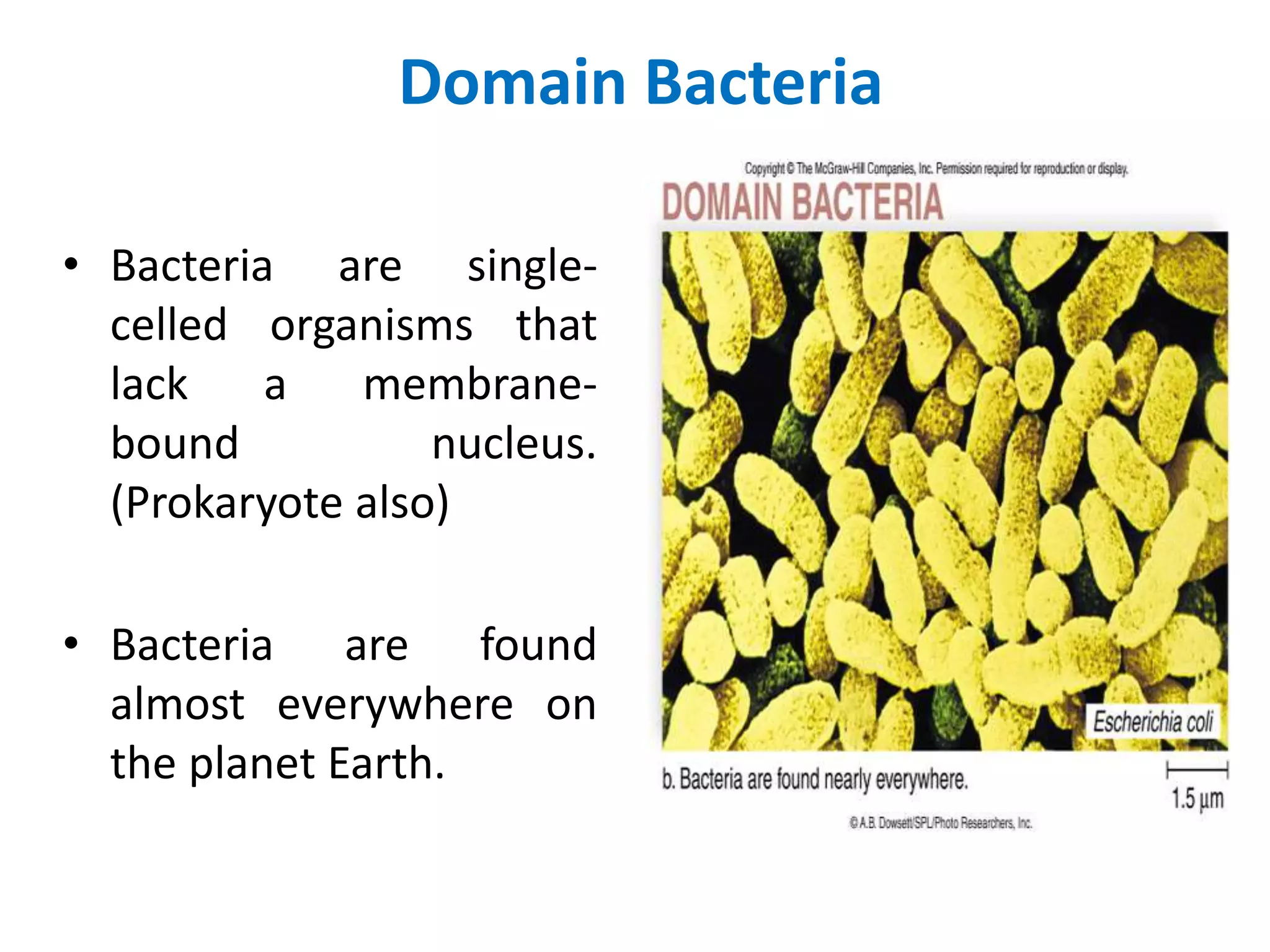
Louis Pasteur in 1859 used swan-necked flasks to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation by showing that liquids in the flasks did not grow microbes due to being protected from dust and microbes in the air. Edward Jenner developed the first vaccine for smallpox in the late 1700s by inoculating people with material from cowpox lesions. Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1928 after observing a mold that produced a chemical clearing surrounding bacteria on a culture plate.