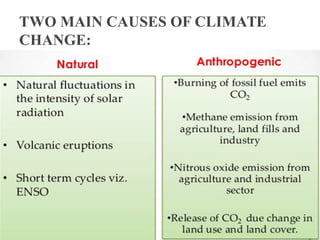
This document discusses how climate change affects agriculture in several ways. The two main causes of climate change are increased carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. Climate change can impact crops, soil, pests and diseases, livestock, and water availability. While increased carbon dioxide can boost plant growth, rising temperatures and changing weather patterns pose challenges for farmers. Adaptation strategies include modifying planting times, using different crops, developing resilient varieties, and improving water and land management. Agriculture also contributes to climate change but can help reduce emissions through practices like better crop residue management.