Embed presentation
Downloaded 780 times
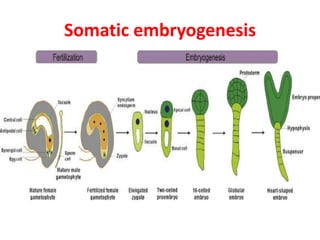
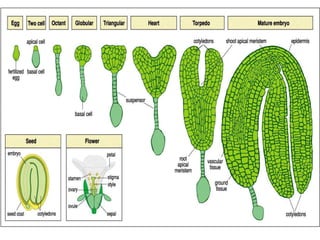
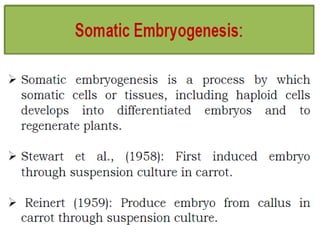

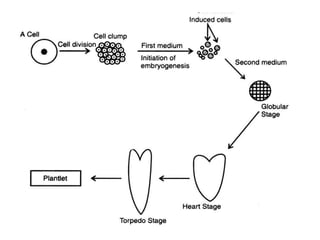

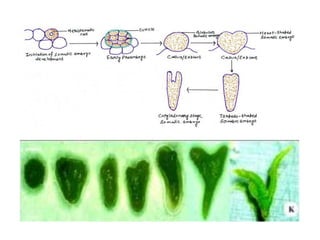

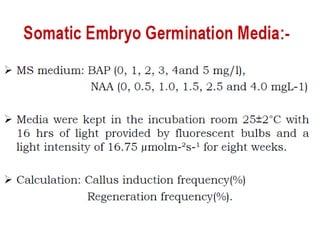
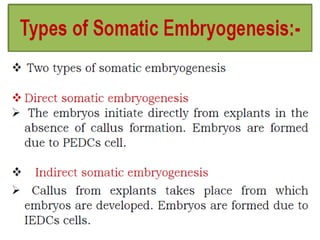
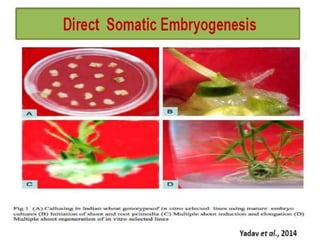
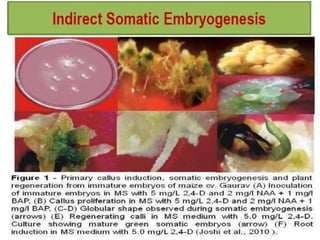



Somatic embryogenesis is the process where embryos form from sporophytic cells in vitro rather than from a zygote. There are different types of embryos including zygotic, formed from fertilized eggs, and somatic embryos which form directly from other plant tissues and organs in culture. The correct developmental stage of the explant tissue is crucial for initiation of embryogenic callus formation in somatic embryogenesis, with young or juvenile explants producing more embryos than older explants.


















