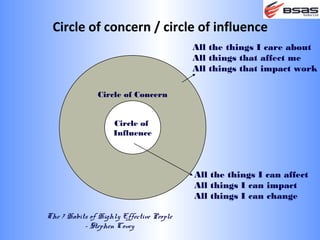
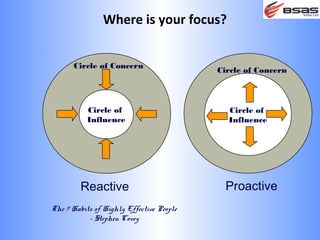
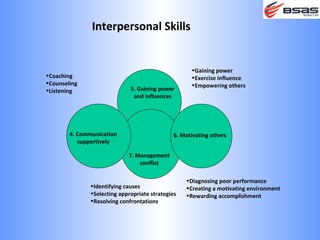
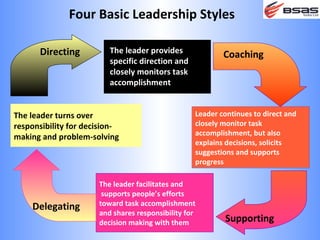
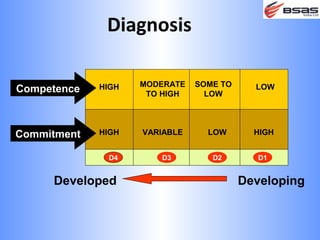
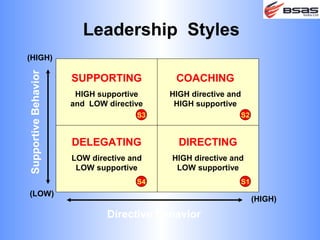
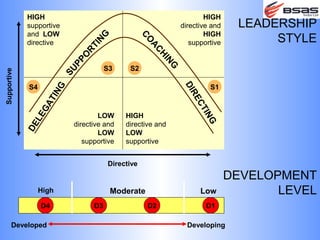
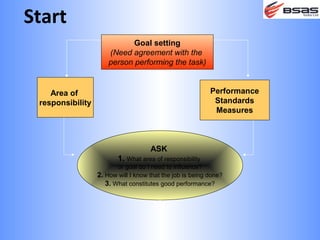
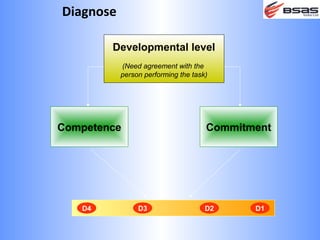
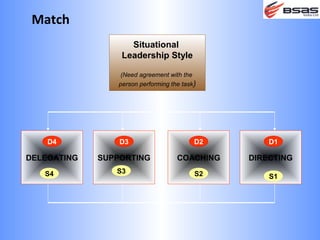
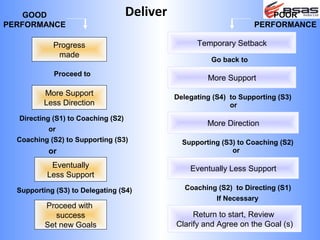
The document discusses situational leadership, emphasizing the need for leaders to adapt their style based on the developmental level and commitment of their followers. It outlines key leadership traits, skills required, and various styles such as directing, coaching, supporting, and delegating. Additionally, it highlights the importance of understanding the relationship between leaders, followers, and the environment to effectively influence and motivate teams.