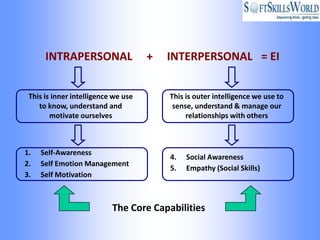
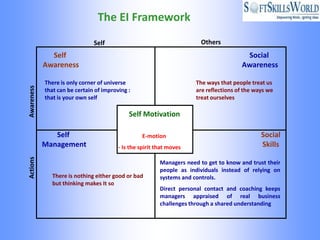
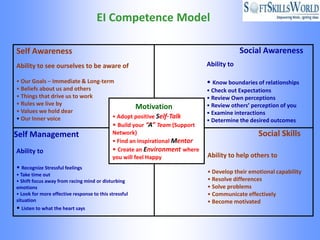
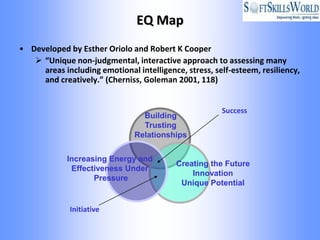
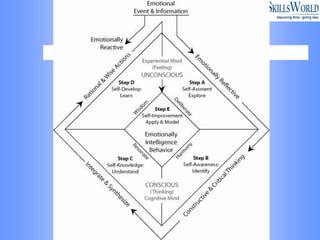
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) as a crucial skill encompassing self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, social awareness, and social skills, differentiating it from traditional IQ measures. It emphasizes the importance of EI in workplace effectiveness, decision-making, leadership, and interpersonal relationships, highlighting its role in fostering better job performance and satisfaction. Additionally, it suggests that EI can be developed through training and coaching, and addresses the implications and challenges of measuring EI in various organizational contexts.