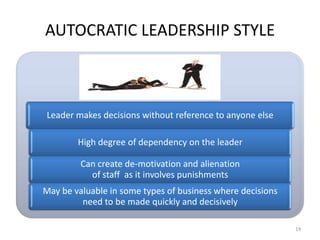
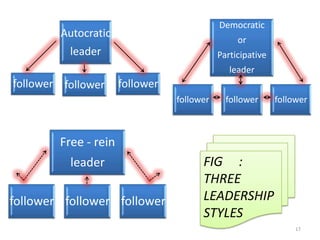
This document discusses various aspects of leadership including definitions, ingredients, approaches, theories, styles, qualities, importance, skills, and differences between managers and leaders. It defines leadership as the process of influencing others to work willingly towards common goals. Some key leadership theories discussed include Fiedler's contingency theory, path-goal theory, and transformational vs transactional leadership. The document also compares leadership styles such as autocratic, democratic, and free-rein and lists important leadership qualities and skills.