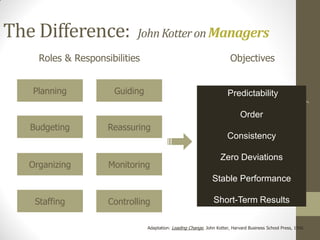
The document discusses the differences between leadership and management, with leadership focusing more on long term vision, change, and inspiring others while management prioritizes stability, procedures, and short term goals. It also examines different types of leadership including situational, transitional, and hierarchical leadership and how managers can transition to become effective leaders.