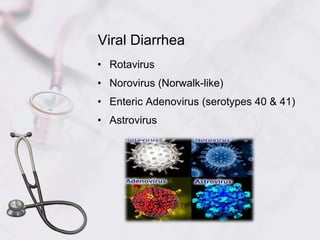
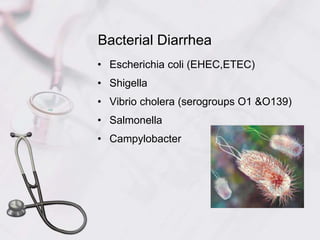
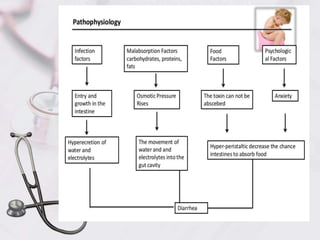
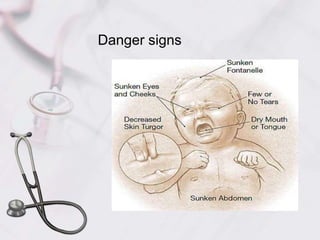
Acute diarrhea in children is defined as watery stools occurring more than 3 times per day lasting less than 2 weeks. It is a major cause of death in children under 5 worldwide. Risk factors include poor sanitation and hygiene. Etiologies include viral (e.g. rotavirus), bacterial (e.g. E. coli), and parasitic (e.g. Giardia) infections. Management involves oral rehydration, continued feeding, zinc supplementation, and treating complications like dehydration. Prevention strategies incorporate vaccination, breastfeeding, clean water/food, and handwashing.