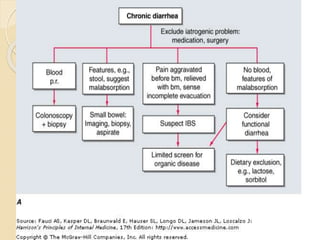
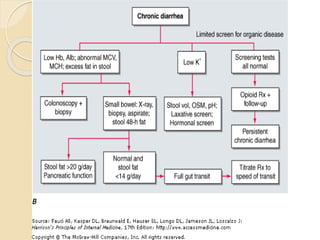
This document discusses chronic diarrhea, defining it as diarrhea lasting more than 2 weeks. It outlines different types of diarrhea based on duration, including acute (<2 weeks), prolonged (7-14 days), and persistent (>14 weeks). The causes of chronic diarrhea are discussed for different age groups, including post-gastrointestinal infections, cow's milk protein intolerance, and celiac disease in infants. Pathophysiological causes of chronic diarrhea include secretory, osmotic, steatorrheal, inflammatory, and dysmotility mechanisms. The importance of a thorough history and physical exam is emphasized to guide diagnostic testing and treatment approaches, which may be curative, suppressive, or empirical depending on the underlying cause.



![Persistent diarrhea
Persistent diarrhea (PD) is an episode of diarrhea of
presumed infectious etiology, which starts acutely but
lasts for more than 14 days, and excludes chronic or
recurrent diarrheal disorders such as tropical sprue,
gluten sensitive enteropathy or other hereditary
disorders[WHO] (INDIAN PEDIATRICS, JAN 2011)
passage of >=3 watery stools per day for >2 weeks in
a child who either fails to gain weight or loses
weight.(ESPGHAN)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicdiarrhoea-120919043435-phpapp01-181206145821/85/Chronic-diarrhoea-in-children-4-320.jpg)





![Differential Diagnosis of
Osmotic Vs Secretory Diarrhea
OSMOTIC DIARRHEA
SECRETORY
DIARRHEA
Volume of stool <200 mL/24 hr >200 mL/24 hr
Response to fasting Diarrhea stops Diarrhea continues
Stool Na+ <70 mEq/L >70 mEq/L
Reducing substances[*] Positive Negative
Stool pH <5 >6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicdiarrhoea-120919043435-phpapp01-181206145821/85/Chronic-diarrhoea-in-children-10-320.jpg)