1) Diarrheal diseases are a major cause of mortality and morbidity in children worldwide, especially in developing countries, with nearly 1.5 million children dying from acute diarrhea in India alone each year.
2) The causes of diarrhea in children include viral, bacterial, and protozoal infections transmitted through contaminated food and water, as well as non-infectious causes like malnutrition and inflammatory bowel diseases.
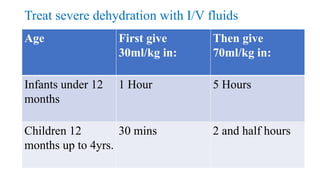
3) Treatment of diarrhea involves oral rehydration with solutions like ORS to correct fluid and electrolyte imbalances, continued feeding, and potentially antibiotics for bacterial causes or zinc supplementation.