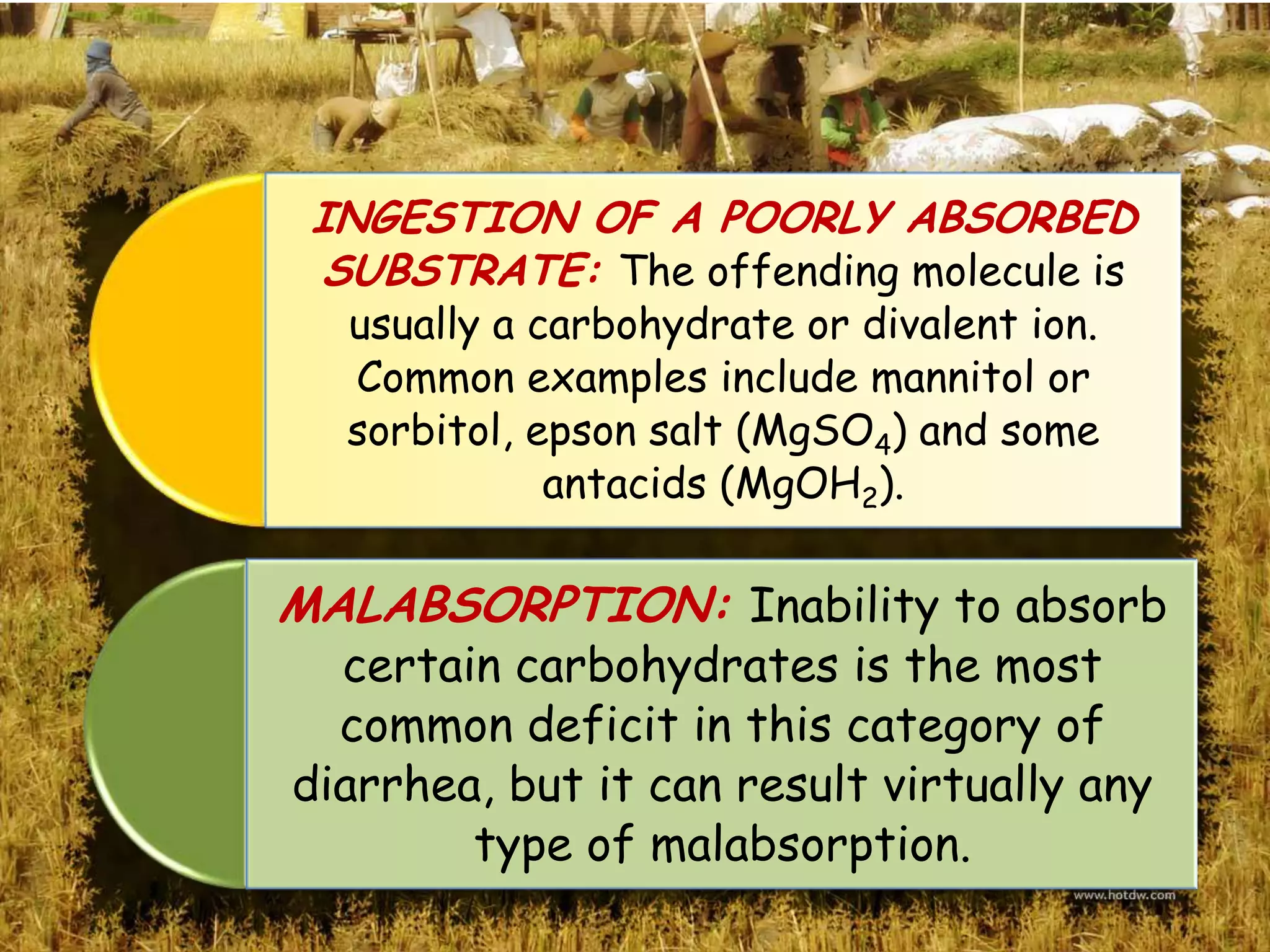
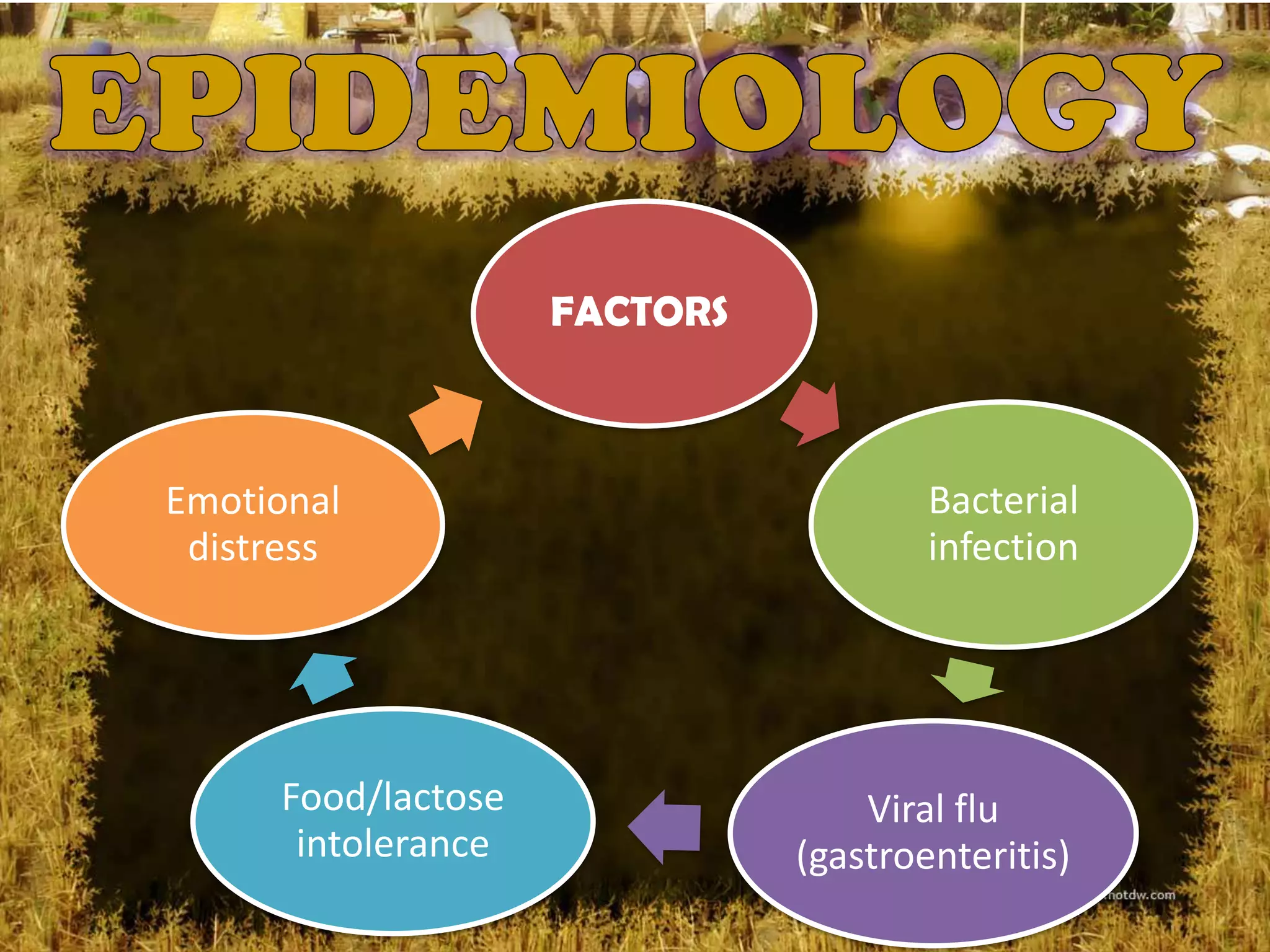
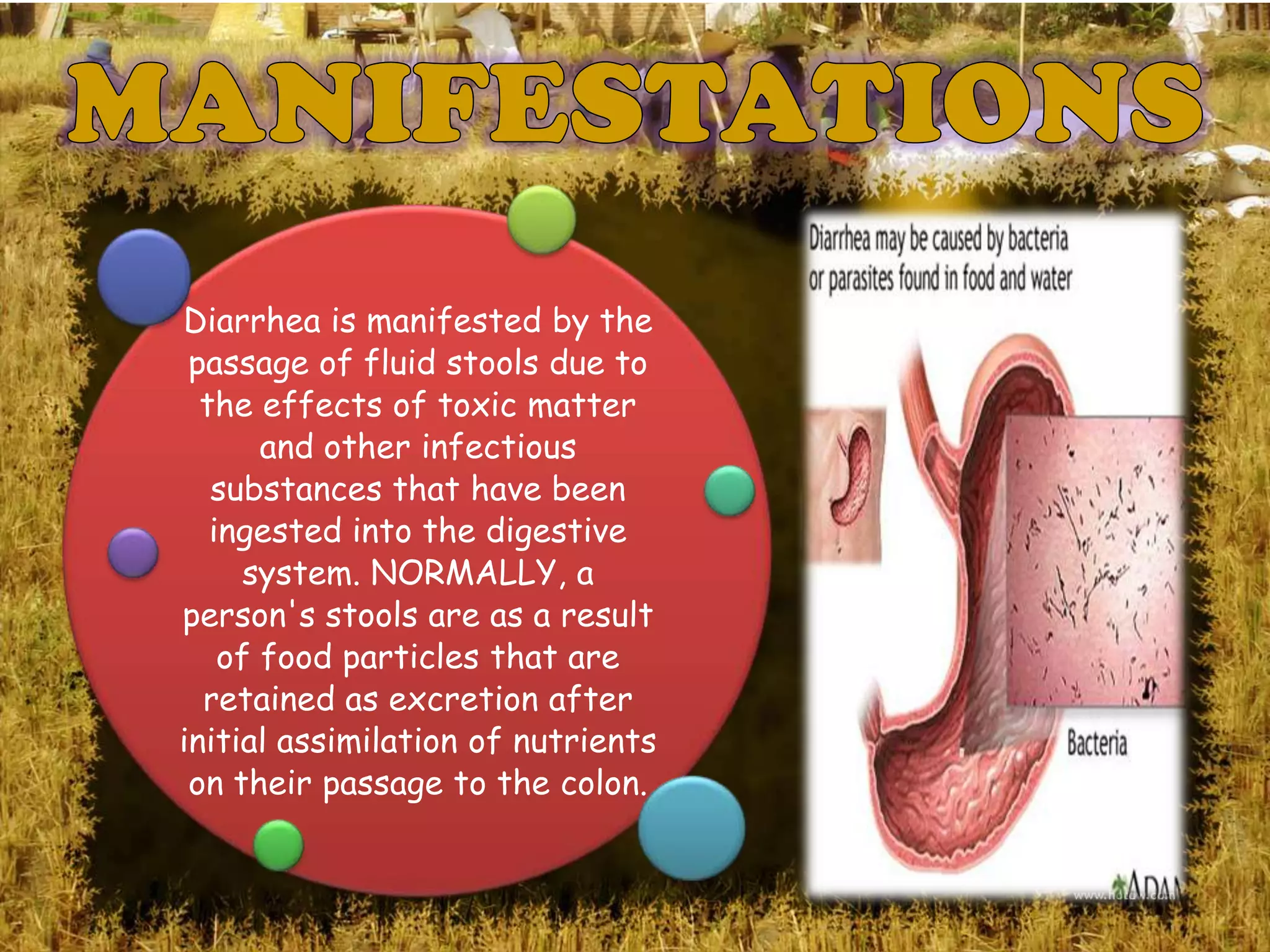
Diarrhea is defined as three or more unformed stools in 24 hours and is commonly caused by ingestion of contaminated food or water. Common pathogens that cause diarrhea include E. coli, Salmonella, Campylobacter, rotaviruses, and cryptosporidium. Diarrhea occurs when the secretion of water into the intestines exceeds absorption, resulting in loose or watery stool. Proper treatment involves preventing or treating dehydration by giving clear fluids and rest.