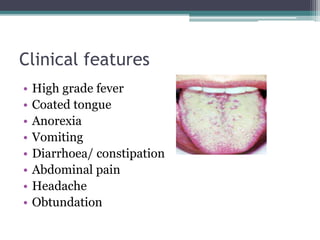
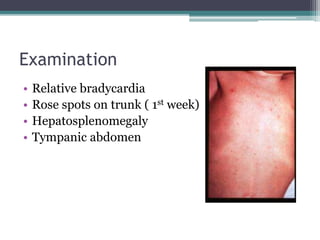
Enteric fever, also known as typhoid fever, is caused by the bacteria Salmonella enterica typhi or Salmonella paratyphi A, B, or C. It is transmitted through the fecal-oral route and has an incubation period of 7-14 days. Clinical features include sustained high fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, and rose-colored spots on the trunk. Complications can affect the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, hepatobiliary system, genitourinary system, and bones. Treatment involves antibiotics, hydration, and rest. Prevention focuses on proper sanitation, hand washing, and vaccination.