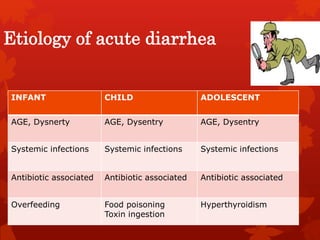
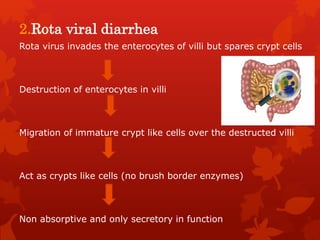
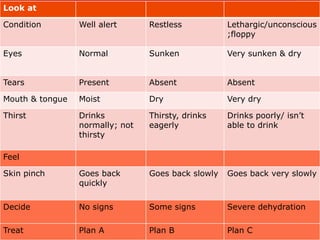
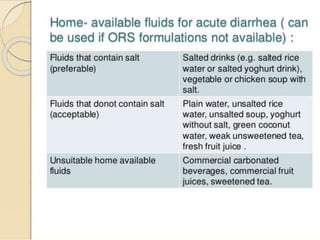
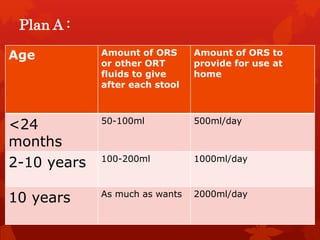
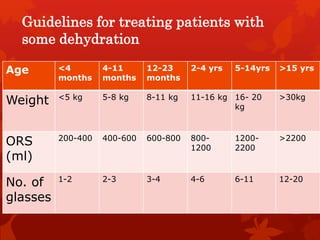
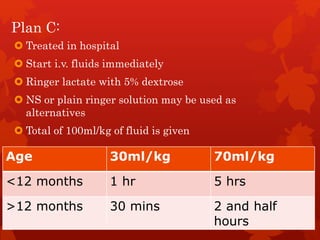
Acute diarrhea is defined as sudden onset of loose or watery stools lasting less than 14 days. It is a major cause of death in children worldwide. Rotavirus is a leading cause of acute diarrhea in infants and young children. Management involves oral rehydration therapy based on the degree of dehydration. For mild dehydration, oral rehydration solution is given at home. Moderate dehydration is treated with oral and/or intravenous fluids in a healthcare setting. Severe dehydration requires intravenous fluids in a hospital. Early feeding and zinc supplementation are also recommended. Antibiotics may be used in certain infections but are not routinely recommended.