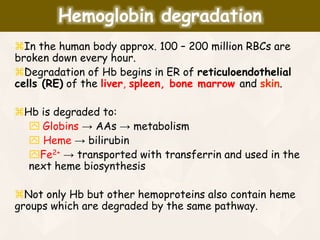
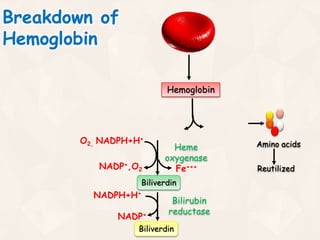
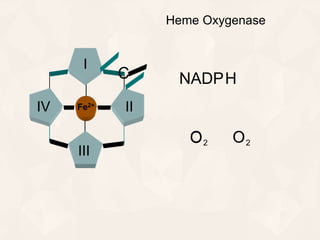
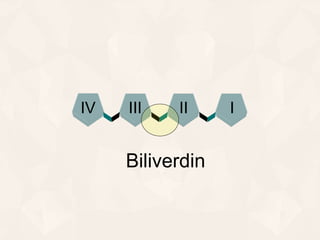
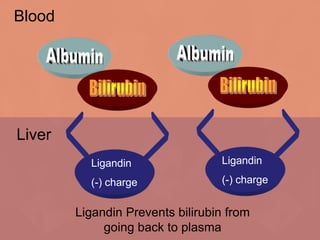
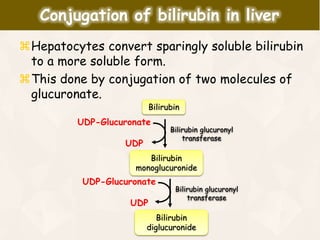
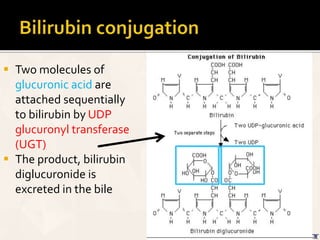
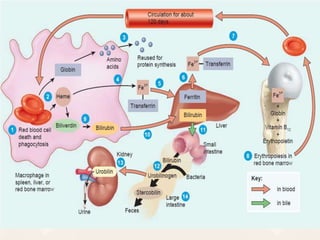
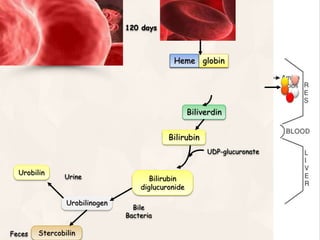
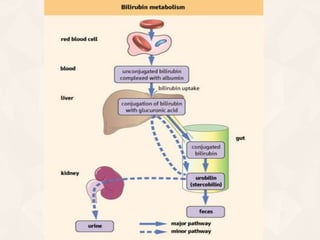
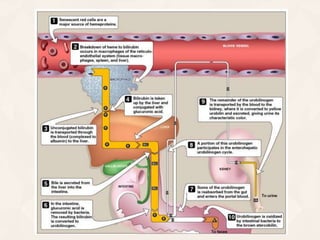
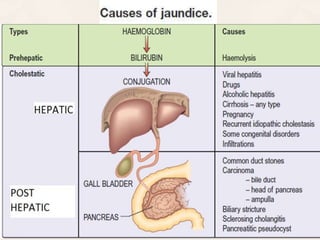
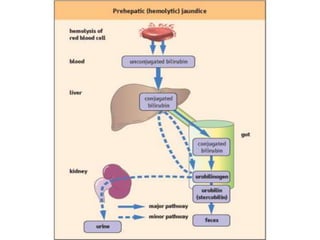
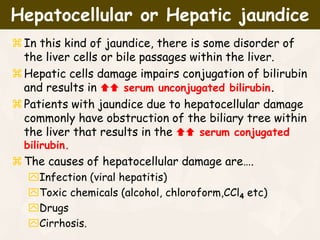
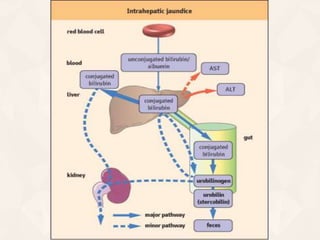
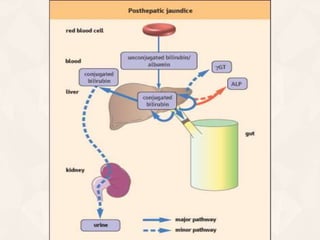
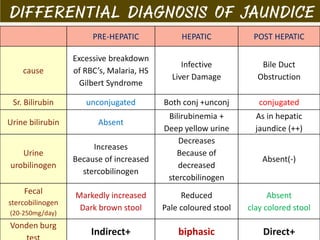
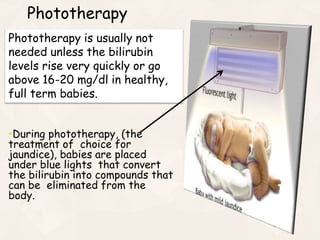
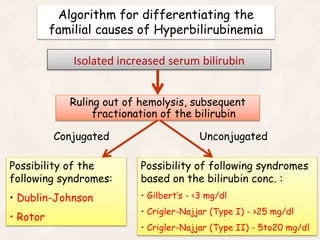
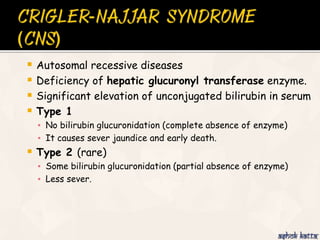
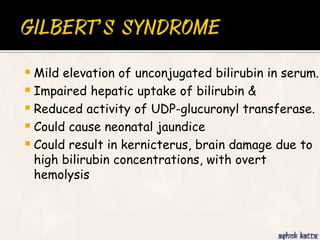
The document summarizes the process of hemoglobin degradation and bilirubin metabolism. It discusses how hemoglobin is broken down into globin, heme, and iron. Heme is further degraded into biliverdin and then bilirubin by heme oxygenase. Bilirubin is conjugated in the liver and secreted into bile. It is excreted in feces or reabsorbed and appears in urine. Conditions that interfere with bilirubin metabolism can cause jaundice. The document classifies types of jaundice and inherited disorders of bilirubin metabolism.