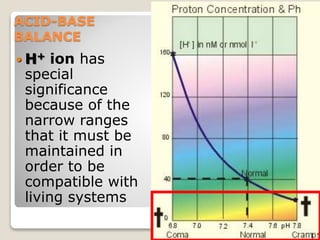
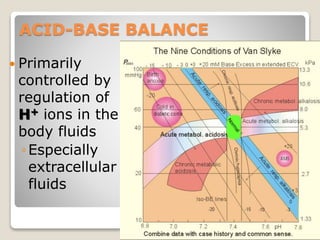
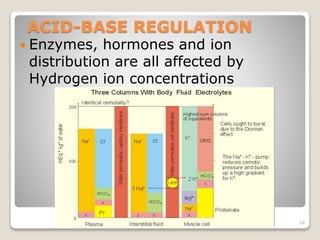
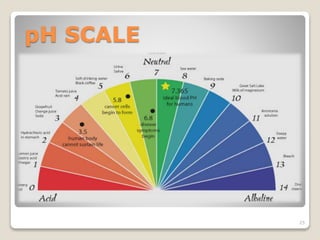
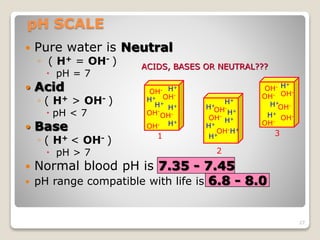
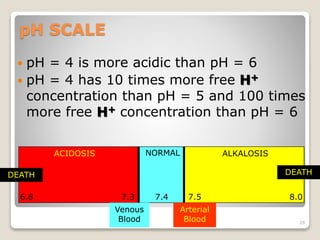
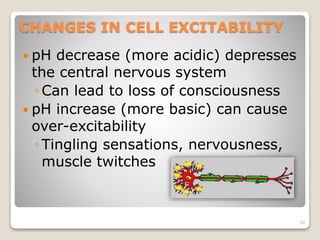
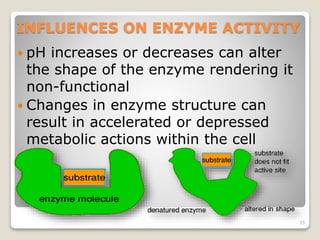
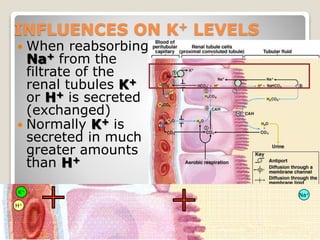
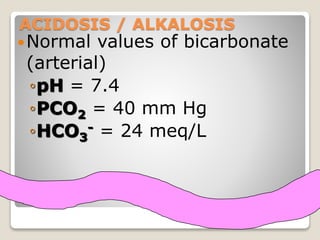
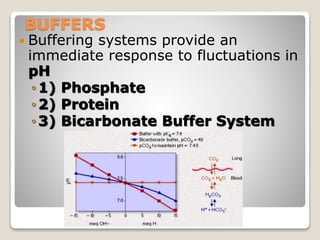
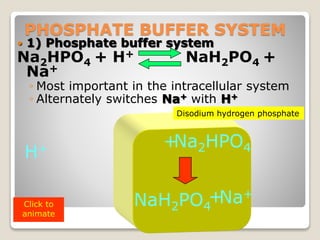
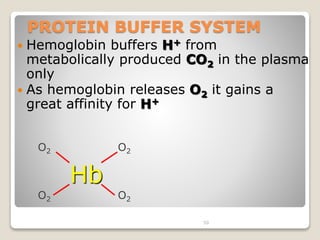
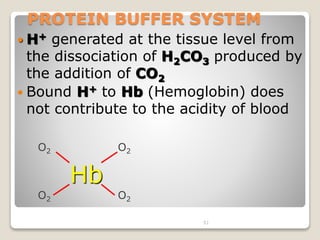
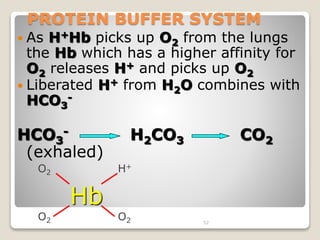
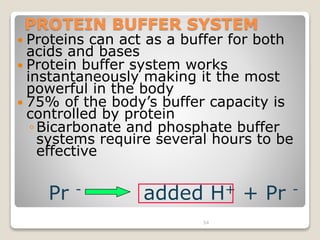
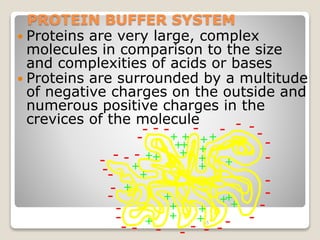
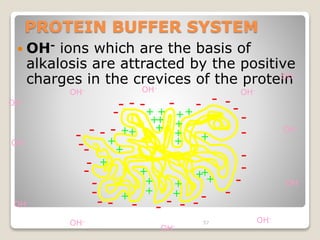
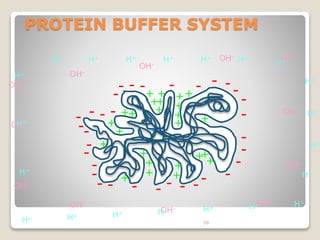
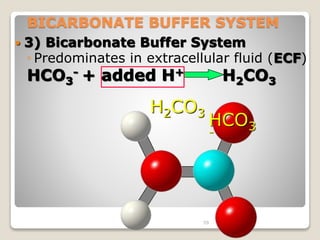
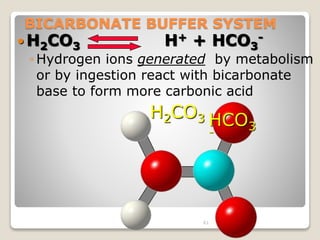
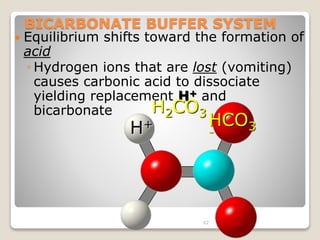
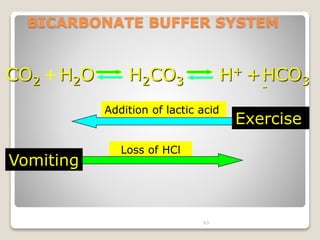
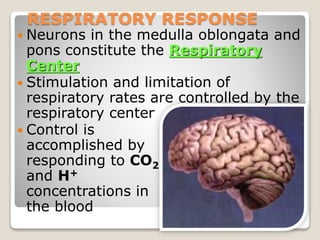
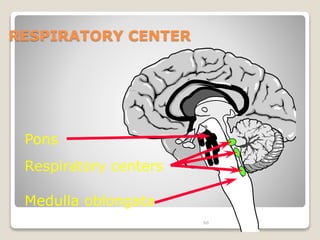
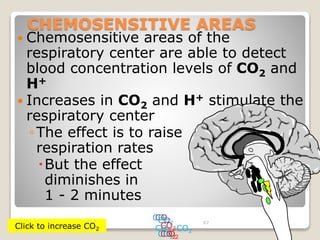
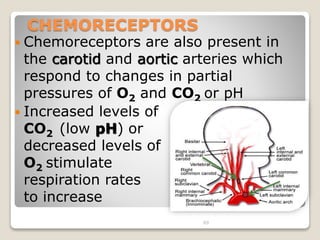
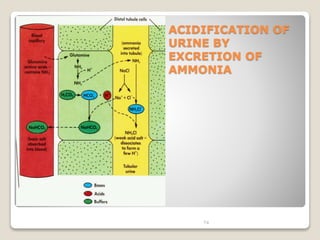
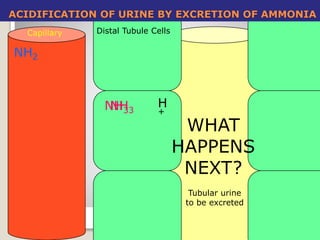
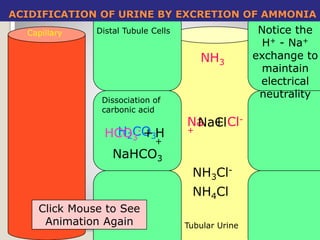
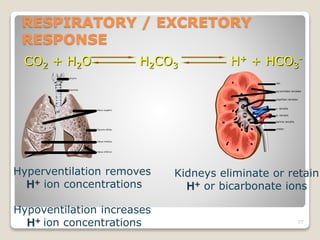
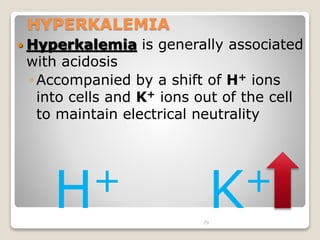
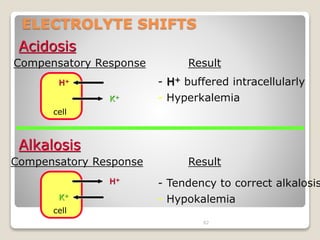
This document details the physiological processes involved in acid-base homeostasis, including the roles of chemical buffers, respiratory regulation, and renal responses in maintaining optimal hydrogen ion concentration for bodily functions. It discusses the importance of pH levels on enzyme activity and cellular excitability, as well as the implications of acidosis and alkalosis in various diseases. The mechanisms by which the body compensates for acid-base imbalances are also outlined, specifically focusing on the immediate buffering systems, respiratory adjustments, and renal regulation over time.