Acid-base balance is essential for normal cell function. Acidosis occurs when blood has too much acid or too little base, lowering pH, while alkalosis occurs when blood has too much base or too little acid, raising pH. Acid-base balance is regulated by buffers, respiration, and the kidneys. Disorders occur when these mechanisms are disrupted, causing metabolic or respiratory acidosis/alkalosis that can impact cells, enzymes, and potassium levels.


















![DEFINITIONS
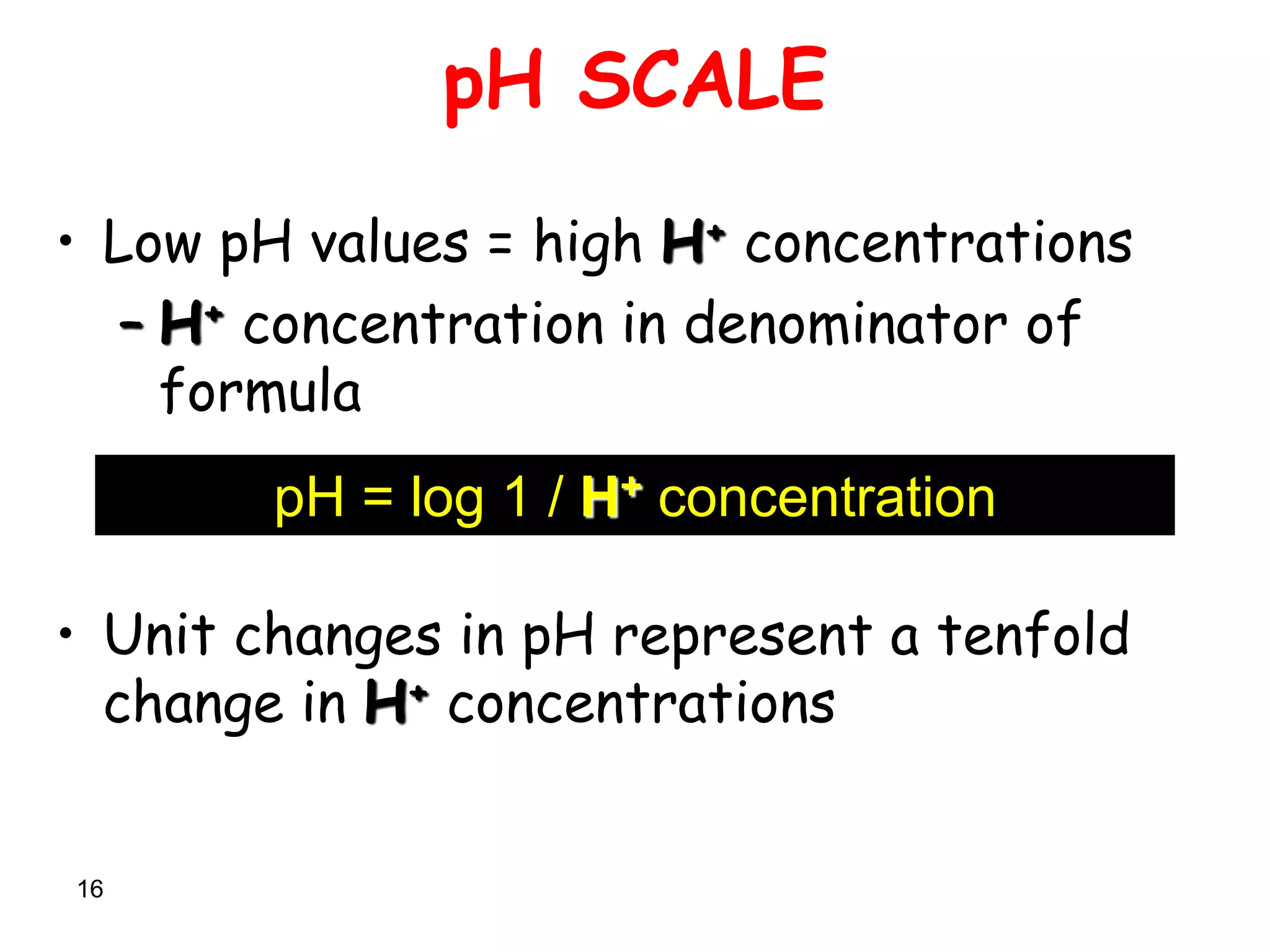
pH : Negative logarithm to the base 10 of
concentration of free H +
Acids: Any chemical substance capable of
releasing a [H+] into solution
BASE: Any substance capable of combining with
Or accepting a hydrogen Ion in a solution
is called a base](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-20-2048.jpg)










![BUFFERS
Buffer Strength:
The capacity to resist the changes in the pH
of the solution when acid or base is added to
the solution.
It depends on:
pKa value
Ratio between the salt & acid parts of the buffer
[Salt]
[Acid]
The concentration of acid & salt parts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-32-2048.jpg)
![1. pKa value:
Buffers act with maximum strength if the pH
of the solution is nearing to the its pKa value.
BUFFERS
2. Buffers will have maximum strength if the
salt & its acid parts have same concentration
i.e
[Salt]
[Acid]
= 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-33-2048.jpg)









![pH = pKa + log [ Hco3
-]
[H2co3 ]
pH = logpKa + [ Hco3-]
[ dissolved co2 ]
= pKa + log
[ Hco3-]
Dissociation constant * pCo2
= pKa + log [ Hco3-]
0.03 * 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-43-2048.jpg)
![= 6.1 + log
24
1.2
= 6.1 + log 20
= 6.1 + 1.3
= 7.4
pH =
[ Hco3-]
pCo2
=
Kidney
Lungs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-44-2048.jpg)
![6.8 6.9 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 8.0
Death
Death
20:1
Disslolved co2
[ Hco3-]
1
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-45-2048.jpg)













































![6.8 6.9 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 8.0
Death
Death
=
[ Hco3-]
pCo2
8
25
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
ACID BASE
Partially compensated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-91-2048.jpg)
![6.8 6.9 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 8.0
Death
Death
=
[ Hco3-]
pCo2
8
25
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
ACID BASE
Partially compensated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-92-2048.jpg)
![6.8 6.9 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 8.0
Death
Death
=
[ Hco3-]
pCo2
18
25
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
ACID BASE
completely compensated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-160419045758/75/Acid-base-balance-93-2048.jpg)
































